【复习8-9天内容】【我们一起60天准备考研算法面试(大全)-第十三天 13/60】
专注 效率 记忆
预习 笔记 复习 做题
欢迎观看我的博客,如有问题交流,欢迎评论区留言,一定尽快回复!(大家可以去看我的专栏,是所有文章的目录)
文章字体风格:
红色文字表示:重难点★✔
蓝色文字表示:思路以及想法★✔
如果大家觉得有帮助的话,感谢大家帮忙
点赞!收藏!转发!
本博客带大家一起学习,我们不图快,只求稳扎稳打。
由于我高三是在家自学的,经验教训告诉我,学习一定要长期积累,并且复习,所以我推出此系列。
只求每天坚持40分钟,一周学5天,复习2天
也就是一周学10道题
60天后我们就可以学完81道题,相信60天后,我们一定可以有扎实的代码基础!我们每天就40分钟,和我一起坚持下去吧!
qq群:878080619
第十三天【考研408-数据结构(笔试)】
- 八、拓扑排序
-
- 1. 有向图的拓扑序列
- 九、最小生成树、最短路
-
- 1. Prim算法求最小生成树(和dijk算法差不多)
- 2. Dijkstra求最短路 I
- 3. Floyd求最短路
- 4. spfa求最短路
- 十、哈希表
-
- 1. 模拟散列表
-
-
- 开散列方法(拉链法)
- 开放寻址法代码
-
-
- 本质:(最多存1e5个数)
-
-
- 2. 未出现过的最小正整数( 2018年全国硕士研究生招生考试 )
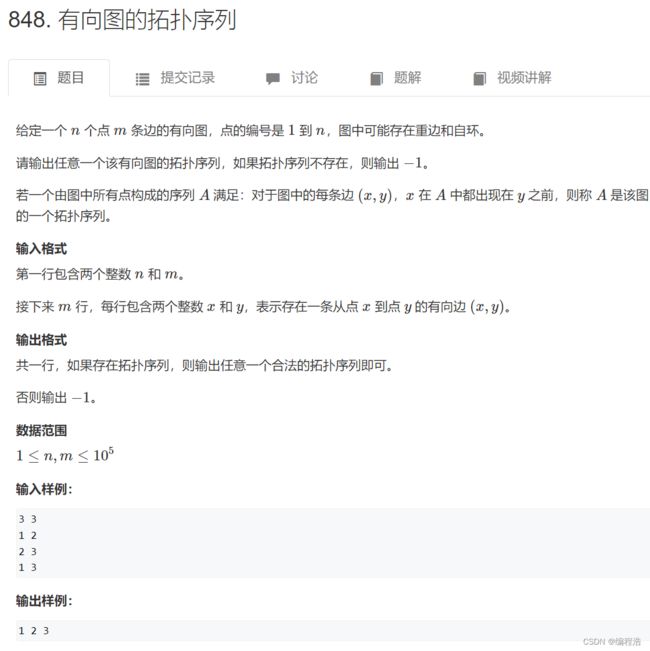
八、拓扑排序
1. 有向图的拓扑序列
这就是一个模板
算法原理可以csdn搜一下
#include 九、最小生成树、最短路
1. Prim算法求最小生成树(和dijk算法差不多)
原题链接

从1节点出发,每次走最短路径(距离集合的最短路径用d表示)选出最短路径再加到res上
(prim算法和dijkstra算法差不多,只是d的表示含义不同)
#include 2. Dijkstra求最短路 I
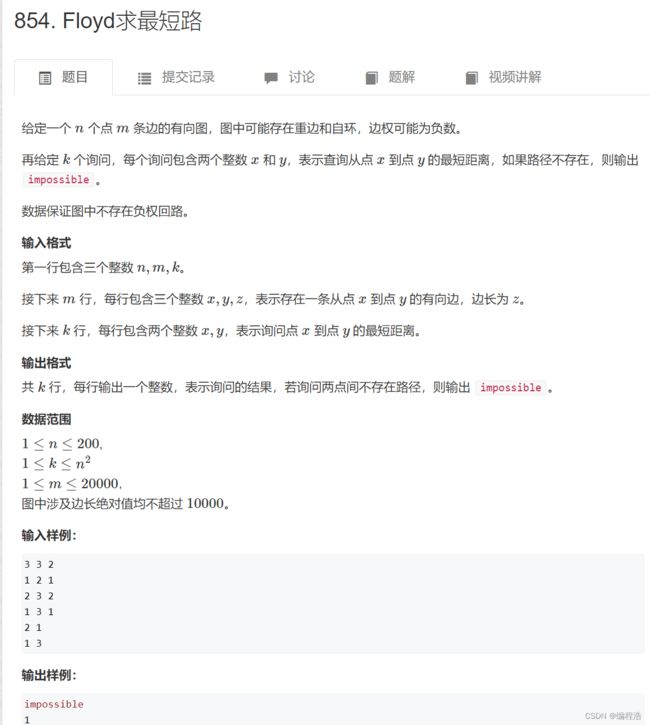
#include 3. Floyd求最短路
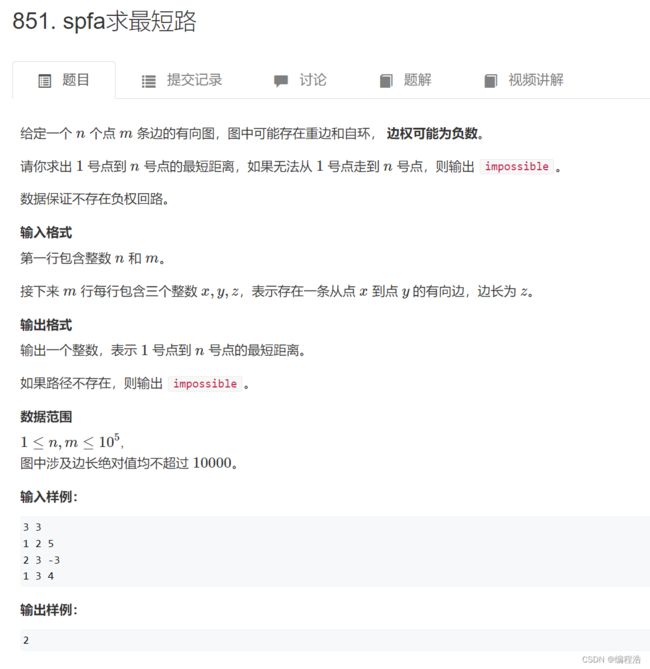
#include 4. spfa求最短路
权值可能为负
所以需要每条路径都走
而不是像dijkstra算法只走一部分
所以spfa算法用普通队列存储即可
并且每个点可能走多次,所以st需要再次false
#include 十、哈希表
1. 模拟散列表
![]()
开散列方法(拉链法)
就记住有N个链表头节点
对于原数据可以 (x % N + N) % N;找到合适位置插入到头节点
#include 开放寻址法代码
本质:(最多存1e5个数)
#include 2. 未出现过的最小正整数( 2018年全国硕士研究生招生考试 )
![]()
由于我们需要从1去找 是否出现在数组中
如果1去遍历一遍数组
2遍历一遍数组
太麻烦
如何一步到位?
其实可以用
哈希思想
把数组出现的数都映射存储到数组中
如何都没有出现
那么一定是大于数组的个数+1的那个值
class Solution {
public:
int findMissMin(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<bool> hash(n + 1);
for (int x: nums)
if (x >= 1 && x <= n)
hash[x] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
if (!hash[i])
return i;
return n + 1;
}
};