x264源代码简单分析:宏块编码(Encode)部分
=====================================================
H.264源代码分析文章列表:
【编码 - x264】
x264源代码简单分析:概述
x264源代码简单分析:x264命令行工具(x264.exe)
x264源代码简单分析:编码器主干部分-1
x264源代码简单分析:编码器主干部分-2
x264源代码简单分析:x264_slice_write()
x264源代码简单分析:滤波(Filter)部分
x264源代码简单分析:宏块分析(Analysis)部分-帧内宏块(Intra)
x264源代码简单分析:宏块分析(Analysis)部分-帧间宏块(Inter)
x264源代码简单分析:宏块编码(Encode)部分
x264源代码简单分析:熵编码(Entropy Encoding)部分
FFmpeg与libx264接口源代码简单分析
【解码 - libavcodec H.264 解码器】
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:概述
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:解析器(Parser)部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:解码器主干部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:熵解码(EntropyDecoding)部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:宏块解码(Decode)部分-帧内宏块(Intra)
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:宏块解码(Decode)部分-帧间宏块(Inter)
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:环路滤波(Loop Filter)部分
=====================================================
本文记录x264的 x264_slice_write()函数中调用的x264_macroblock_encode()的源代码。x264_macroblock_encode()对应着x264中的宏块编码模块。宏块编码模块主要完成了DCT变换和量化两个步骤。
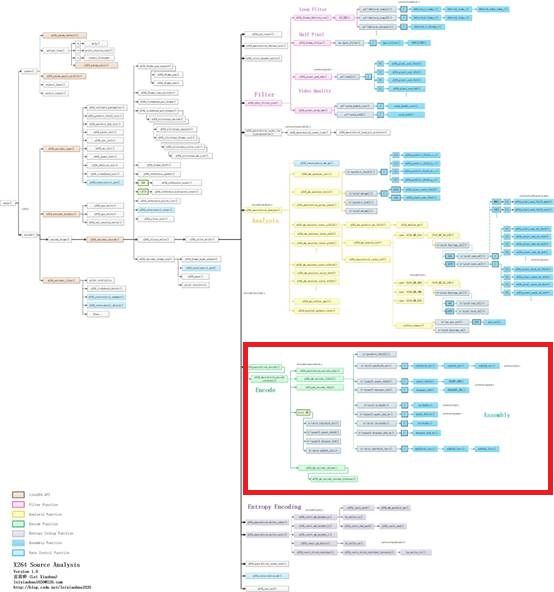
函数调用关系图
宏块编码(Encode)部分的源代码在整个x264中的位置如下图所示。
宏块编码(Encode)部分的函数调用关系如下图所示。
从图中可以看出,宏块编码模块的x264_macroblock_encode()调用了x264_macroblock_encode_internal(),而x264_macroblock_encode_internal()完成了如下功能:
x264_macroblock_encode_skip():编码Skip类型宏块。本文将会分析上述函数中除了色度编码外的几个函数。
x264_mb_encode_i16x16():编码Intra16x16类型的宏块。该函数除了进行DCT变换之外,还对16个小块的DC系数进行了Hadamard变换。
x264_mb_encode_i4x4():编码Intra4x4类型的宏块。
帧间宏块编码:这一部分代码直接写在了函数体里面。
x264_mb_encode_chroma():编码色度块。
x264_slice_write()
x264_slice_write()是x264项目的核心,它完成了编码了一个Slice的工作。有关该函数的分析可以参考文章《x264源代码简单分析:x264_slice_write()》。本文分析其调用的x264_macroblock_encode()函数。x264_macroblock_encode()
x264_macroblock_encode()用于编码宏块。该函数的定义位于encoder\macroblock.c,如下所示。//编码-残差DCT变换、量化
void x264_macroblock_encode( x264_t *h )
{
//编码-内部函数
//YUV444相当于把YUV3个分量都当做Y编码
if( CHROMA444 )
x264_macroblock_encode_internal( h, 3, 0 );
else
x264_macroblock_encode_internal( h, 1, 1 );
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_macroblock_encode()封装了x264_macroblock_encode_internal()。如果色度模式是YUV444的话,传递的参数plane_count=3而chroma=0;如果不是YUV444的话,传递的参数plane_count=1而chroma=1。
x264_macroblock_encode_internal()
x264_macroblock_encode_internal()是x264_macroblock_encode()的内部函数。该函数的定义位于encoder\macroblock.c,如下所示。/*****************************************************************************
* x264_macroblock_encode:
* 编码-残差DCT变换、量化-内部函数
*
* 注释和处理:雷霄骅
* http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020
* [email protected]
*****************************************************************************/
static ALWAYS_INLINE void x264_macroblock_encode_internal( x264_t *h, int plane_count, int chroma )
{
int i_qp = h->mb.i_qp;
int b_decimate = h->mb.b_dct_decimate;
int b_force_no_skip = 0;
int nz;
h->mb.i_cbp_luma = 0;
for( int p = 0; p < plane_count; p++ )
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[LUMA_DC+p]] = 0;
//PCM,不常见
if( h->mb.i_type == I_PCM )
{
/* if PCM is chosen, we need to store reconstructed frame data */
for( int p = 0; p < plane_count; p++ )
h->mc.copy[PIXEL_16x16]( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[p], FDEC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fenc[p], FENC_STRIDE, 16 );
if( chroma )
{
int height = 16 >> CHROMA_V_SHIFT;
h->mc.copy[PIXEL_8x8] ( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1], FDEC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fenc[1], FENC_STRIDE, height );
h->mc.copy[PIXEL_8x8] ( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2], FDEC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fenc[2], FENC_STRIDE, height );
}
return;
}
if( !h->mb.b_allow_skip )
{
b_force_no_skip = 1;
if( IS_SKIP(h->mb.i_type) )
{
if( h->mb.i_type == P_SKIP )
h->mb.i_type = P_L0;
else if( h->mb.i_type == B_SKIP )
h->mb.i_type = B_DIRECT;
}
}
//根据不同的宏块类型,进行编码
if( h->mb.i_type == P_SKIP )
{
/* don't do pskip motion compensation if it was already done in macroblock_analyse */
if( !h->mb.b_skip_mc )
{
int mvx = x264_clip3( h->mb.cache.mv[0][x264_scan8[0]][0],
h->mb.mv_min[0], h->mb.mv_max[0] );
int mvy = x264_clip3( h->mb.cache.mv[0][x264_scan8[0]][1],
h->mb.mv_min[1], h->mb.mv_max[1] );
for( int p = 0; p < plane_count; p++ )
h->mc.mc_luma( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[p], FDEC_STRIDE,
&h->mb.pic.p_fref[0][0][p*4], h->mb.pic.i_stride[p],
mvx, mvy, 16, 16, &h->sh.weight[0][p] );
if( chroma )
{
int v_shift = CHROMA_V_SHIFT;
int height = 16 >> v_shift;
/* Special case for mv0, which is (of course) very common in P-skip mode. */
if( mvx | mvy )
h->mc.mc_chroma( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1], h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2], FDEC_STRIDE,
h->mb.pic.p_fref[0][0][4], h->mb.pic.i_stride[1],
mvx, 2*mvy>>v_shift, 8, height );
else
h->mc.load_deinterleave_chroma_fdec( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1], h->mb.pic.p_fref[0][0][4],
h->mb.pic.i_stride[1], height );
if( h->sh.weight[0][1].weightfn )
h->sh.weight[0][1].weightfn[8>>2]( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1], FDEC_STRIDE,
h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1], FDEC_STRIDE,
&h->sh.weight[0][1], height );
if( h->sh.weight[0][2].weightfn )
h->sh.weight[0][2].weightfn[8>>2]( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2], FDEC_STRIDE,
h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2], FDEC_STRIDE,
&h->sh.weight[0][2], height );
}
}
//编码skip类型宏块
x264_macroblock_encode_skip( h );
return;
}
if( h->mb.i_type == B_SKIP )
{
/* don't do bskip motion compensation if it was already done in macroblock_analyse */
if( !h->mb.b_skip_mc )
x264_mb_mc( h );
x264_macroblock_encode_skip( h );
return;
}
if( h->mb.i_type == I_16x16 )
{
h->mb.b_transform_8x8 = 0;
//Intra16x16宏块编码-需要Hadamard变换
//分别编码Y,U,V
/*
* 16x16 宏块
*
* +--------+--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* + + +
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+--------+
*
*/
for( int p = 0; p < plane_count; p++, i_qp = h->mb.i_chroma_qp )
x264_mb_encode_i16x16( h, p, i_qp );
}
else if( h->mb.i_type == I_8x8 )
{
h->mb.b_transform_8x8 = 1;
/* If we already encoded 3 of the 4 i8x8 blocks, we don't have to do them again. */
if( h->mb.i_skip_intra )
{
h->mc.copy[PIXEL_16x16]( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[0], FDEC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.i8x8_fdec_buf, 16, 16 );
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 0]] ) = h->mb.pic.i8x8_nnz_buf[0];
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 2]] ) = h->mb.pic.i8x8_nnz_buf[1];
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 8]] ) = h->mb.pic.i8x8_nnz_buf[2];
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[10]] ) = h->mb.pic.i8x8_nnz_buf[3];
h->mb.i_cbp_luma = h->mb.pic.i8x8_cbp;
/* In RD mode, restore the now-overwritten DCT data. */
if( h->mb.i_skip_intra == 2 )
h->mc.memcpy_aligned( h->dct.luma8x8, h->mb.pic.i8x8_dct_buf, sizeof(h->mb.pic.i8x8_dct_buf) );
}
for( int p = 0; p < plane_count; p++, i_qp = h->mb.i_chroma_qp )
{
for( int i = (p == 0 && h->mb.i_skip_intra) ? 3 : 0 ; i < 4; i++ )
{
int i_mode = h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[4*i]];
x264_mb_encode_i8x8( h, p, i, i_qp, i_mode, NULL, 1 );
}
}
}
//Intra4x4类型
else if( h->mb.i_type == I_4x4 )
{
/*
* 帧内预测:16x16 宏块被划分为16个4x4子块
*
* +----+----+----+----+
* | | | | |
* +----+----+----+----+
* | | | | |
* +----+----+----+----+
* | | | | |
* +----+----+----+----+
* | | | | |
* +----+----+----+----+
*
*/
h->mb.b_transform_8x8 = 0;
/* If we already encoded 15 of the 16 i4x4 blocks, we don't have to do them again. */
if( h->mb.i_skip_intra )
{
h->mc.copy[PIXEL_16x16]( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[0], FDEC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.i4x4_fdec_buf, 16, 16 );
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 0]] ) = h->mb.pic.i4x4_nnz_buf[0];
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 2]] ) = h->mb.pic.i4x4_nnz_buf[1];
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 8]] ) = h->mb.pic.i4x4_nnz_buf[2];
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[10]] ) = h->mb.pic.i4x4_nnz_buf[3];
h->mb.i_cbp_luma = h->mb.pic.i4x4_cbp;
/* In RD mode, restore the now-overwritten DCT data. */
if( h->mb.i_skip_intra == 2 )
h->mc.memcpy_aligned( h->dct.luma4x4, h->mb.pic.i4x4_dct_buf, sizeof(h->mb.pic.i4x4_dct_buf) );
}
//分别编码Y,U,V
for( int p = 0; p < plane_count; p++, i_qp = h->mb.i_chroma_qp )
{
//循环16次,编码16个Intra4x4宏块
for( int i = (p == 0 && h->mb.i_skip_intra) ? 15 : 0 ; i < 16; i++ )
{
pixel *p_dst = &h->mb.pic.p_fdec[p][block_idx_xy_fdec[i]];
int i_mode = h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[i]];
if( (h->mb.i_neighbour4[i] & (MB_TOPRIGHT|MB_TOP)) == MB_TOP )
/* emulate missing topright samples */
MPIXEL_X4( &p_dst[4-FDEC_STRIDE] ) = PIXEL_SPLAT_X4( p_dst[3-FDEC_STRIDE] );
//Intra4x4宏块编码
/*
* +----+
* | |
* +----+
*/
x264_mb_encode_i4x4( h, p, i, i_qp, i_mode, 1 );
}
}
}
//包含帧间预测
else /* Inter MB */
{
int i_decimate_mb = 0;
/* Don't repeat motion compensation if it was already done in non-RD transform analysis */
if( !h->mb.b_skip_mc )
x264_mb_mc( h );
if( h->mb.b_lossless )//lossless情况没研究过
{
if( h->mb.b_transform_8x8 )
for( int p = 0; p < plane_count; p++ )
for( int i8x8 = 0; i8x8 < 4; i8x8++ )
{
int x = i8x8&1;
int y = i8x8>>1;
nz = h->zigzagf.sub_8x8( h->dct.luma8x8[p*4+i8x8], h->mb.pic.p_fenc[p] + 8*x + 8*y*FENC_STRIDE,
h->mb.pic.p_fdec[p] + 8*x + 8*y*FDEC_STRIDE );
STORE_8x8_NNZ( p, i8x8, nz );
h->mb.i_cbp_luma |= nz << i8x8;
}
else
for( int p = 0; p < plane_count; p++ )
for( int i4x4 = 0; i4x4 < 16; i4x4++ )
{
nz = h->zigzagf.sub_4x4( h->dct.luma4x4[p*16+i4x4],
h->mb.pic.p_fenc[p]+block_idx_xy_fenc[i4x4],
h->mb.pic.p_fdec[p]+block_idx_xy_fdec[i4x4] );
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[p*16+i4x4]] = nz;
h->mb.i_cbp_luma |= nz << (i4x4>>2);
}
}
else if( h->mb.b_transform_8x8 )//DCT8x8情况暂时没研究过
{
ALIGNED_ARRAY_N( dctcoef, dct8x8,[4],[64] );
b_decimate &= !h->mb.b_trellis || !h->param.b_cabac; // 8x8 trellis is inherently optimal decimation for CABAC
for( int p = 0; p < plane_count; p++, i_qp = h->mb.i_chroma_qp )
{
CLEAR_16x16_NNZ( p );
h->dctf.sub16x16_dct8( dct8x8, h->mb.pic.p_fenc[p], h->mb.pic.p_fdec[p] );
h->nr_count[1+!!p*2] += h->mb.b_noise_reduction * 4;
int plane_cbp = 0;
for( int idx = 0; idx < 4; idx++ )
{
nz = x264_quant_8x8( h, dct8x8[idx], i_qp, ctx_cat_plane[DCT_LUMA_8x8][p], 0, p, idx );
if( nz )
{
h->zigzagf.scan_8x8( h->dct.luma8x8[p*4+idx], dct8x8[idx] );
if( b_decimate )
{
int i_decimate_8x8 = h->quantf.decimate_score64( h->dct.luma8x8[p*4+idx] );
i_decimate_mb += i_decimate_8x8;
if( i_decimate_8x8 >= 4 )
plane_cbp |= 1<= 6 || !b_decimate )
{
h->mb.i_cbp_luma |= plane_cbp;
FOREACH_BIT( idx, 0, plane_cbp )
{
h->quantf.dequant_8x8( dct8x8[idx], h->dequant8_mf[p?CQM_8PC:CQM_8PY], i_qp );
h->dctf.add8x8_idct8( &h->mb.pic.p_fdec[p][8*(idx&1) + 8*(idx>>1)*FDEC_STRIDE], dct8x8[idx] );
STORE_8x8_NNZ( p, idx, 1 );
}
}
}
}
else//最普通的情况
{
/*
* 帧间预测:16x16 宏块被划分为8x8
* 每个8x8再次被划分为4x4
*
* ++====+====++====+====++
* || | || | ||
* ++====+====++====+====++
* || | || | ||
* ++====+====++====+====++
* || | || | ||
* ++====+====++====+====++
* || | || | ||
* ++====+====+=====+====++
*
*/
ALIGNED_ARRAY_N( dctcoef, dct4x4,[16],[16] );
for( int p = 0; p < plane_count; p++, i_qp = h->mb.i_chroma_qp )
{
CLEAR_16x16_NNZ( p );
//16x16DCT(实际上分解为16个4x4DCT)
//求编码帧p_fenc和重建帧p_fdec之间的残差,然后进行DCT变换
h->dctf.sub16x16_dct( dct4x4, h->mb.pic.p_fenc[p], h->mb.pic.p_fdec[p] );
if( h->mb.b_noise_reduction )
{
h->nr_count[0+!!p*2] += 16;
for( int idx = 0; idx < 16; idx++ )
h->quantf.denoise_dct( dct4x4[idx], h->nr_residual_sum[0+!!p*2], h->nr_offset[0+!!p*2], 16 );
}
int plane_cbp = 0;
//16x16的块分成4个8x8的块
for( int i8x8 = 0; i8x8 < 4; i8x8++ )
{
int i_decimate_8x8 = b_decimate ? 0 : 6;
int nnz8x8 = 0;
if( h->mb.b_trellis )
{
for( int i4x4 = 0; i4x4 < 4; i4x4++ )
{
int idx = i8x8*4+i4x4;
if( x264_quant_4x4_trellis( h, dct4x4[idx], CQM_4PY, i_qp, ctx_cat_plane[DCT_LUMA_4x4][p], 0, !!p, p*16+idx ) )
{
h->zigzagf.scan_4x4( h->dct.luma4x4[p*16+idx], dct4x4[idx] );
h->quantf.dequant_4x4( dct4x4[idx], h->dequant4_mf[p?CQM_4PC:CQM_4PY], i_qp );
if( i_decimate_8x8 < 6 )
i_decimate_8x8 += h->quantf.decimate_score16( h->dct.luma4x4[p*16+idx] );
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[p*16+idx]] = 1;
nnz8x8 = 1;
}
}
}
else
{
//8x8的块分成4个4x4的块,每个4x4的块再分别进行量化
nnz8x8 = nz = h->quantf.quant_4x4x4( &dct4x4[i8x8*4], h->quant4_mf[CQM_4PY][i_qp], h->quant4_bias[CQM_4PY][i_qp] );
if( nz )
{
FOREACH_BIT( idx, i8x8*4, nz )
{
//这几步用于建立重建帧
h->zigzagf.scan_4x4( h->dct.luma4x4[p*16+idx], dct4x4[idx] );
//反量化
h->quantf.dequant_4x4( dct4x4[idx], h->dequant4_mf[p?CQM_4PC:CQM_4PY], i_qp );
if( i_decimate_8x8 < 6 )
i_decimate_8x8 += h->quantf.decimate_score16( h->dct.luma4x4[p*16+idx] );
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[p*16+idx]] = 1;
}
}
}
if( nnz8x8 )
{
i_decimate_mb += i_decimate_8x8;
if( i_decimate_8x8 < 4 )
STORE_8x8_NNZ( p, i8x8, 0 );
else
plane_cbp |= 1<mb.i_cbp_luma |= plane_cbp;
FOREACH_BIT( i8x8, 0, plane_cbp )
{
//用于建立重建帧
//残差进行DCT反变换之后,叠加到预测数据上
h->dctf.add8x8_idct( &h->mb.pic.p_fdec[p][(i8x8&1)*8 + (i8x8>>1)*8*FDEC_STRIDE], &dct4x4[i8x8*4] );
}
}
}
}
}
/* encode chroma */
if( chroma )
{
if( IS_INTRA( h->mb.i_type ) )
{
int i_mode = h->mb.i_chroma_pred_mode;
if( h->mb.b_lossless )
x264_predict_lossless_chroma( h, i_mode );
else
{
h->predict_chroma[i_mode]( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1] );
h->predict_chroma[i_mode]( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2] );
}
}
/* encode the 8x8 blocks */
x264_mb_encode_chroma( h, !IS_INTRA( h->mb.i_type ), h->mb.i_chroma_qp );
}
else
h->mb.i_cbp_chroma = 0;
/* store cbp */
int cbp = h->mb.i_cbp_chroma << 4 | h->mb.i_cbp_luma;
if( h->param.b_cabac )
cbp |= h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[LUMA_DC ]] << 8
| h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[CHROMA_DC+0]] << 9
| h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[CHROMA_DC+1]] << 10;
h->mb.cbp[h->mb.i_mb_xy] = cbp;
/* Check for P_SKIP
* XXX: in the me perhaps we should take x264_mb_predict_mv_pskip into account
* (if multiple mv give same result)*/
if( !b_force_no_skip )
{
if( h->mb.i_type == P_L0 && h->mb.i_partition == D_16x16 &&
!(h->mb.i_cbp_luma | h->mb.i_cbp_chroma) &&
M32( h->mb.cache.mv[0][x264_scan8[0]] ) == M32( h->mb.cache.pskip_mv )
&& h->mb.cache.ref[0][x264_scan8[0]] == 0 )
{
h->mb.i_type = P_SKIP;
}
/* Check for B_SKIP */
if( h->mb.i_type == B_DIRECT && !(h->mb.i_cbp_luma | h->mb.i_cbp_chroma) )
{
h->mb.i_type = B_SKIP;
}
}
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_macroblock_encode_internal()的流程大致如下:
(1)如果是Skip类型,调用x264_macroblock_encode_skip()编码宏块。
(2)如果是Intra16x16类型,调用x264_mb_encode_i16x16()编码宏块。
(3)如果是Intra4x4类型,循环16次调用x264_mb_encode_i4x4()编码宏块。
(4)如果是Inter类型,则不再调用子函数,而是直接进行编码:a)对16x16块调用x264_dct_function_t的sub16x16_dct()汇编函数,求得编码宏块数据p_fenc与重建宏块数据p_fdec之间的残差(“sub”),并对残差进行DCT变换。b)分成4个8x8的块,对每个8x8块分别调用x264_quant_function_t的quant_4x4x4()汇编函数进行量化。c)分成16个4x4的块,对每个4x4块分别调用x264_quant_function_t的dequant_4x4()汇编函数进行反量化(用于重建帧)。d)分成4个8x8的块,对每个8x8块分别调用x264_dct_function_t的add8x8_idct()汇编函数,对残差进行DCT反变换,并将反变换后的数据叠加(“add”)至预测数据上(用于重建帧)。(5) 如果对色度编码,调用x264_mb_encode_chroma()。
从Inter宏块编码的步骤可以看出,编码就是“DCT变换+量化”两步的组合。下文将会按照顺序记录x264_macroblock_encode_skip(),x264_mb_encode_i16x16(),x264_mb_encode_i4x4()三个函数。
x264_macroblock_encode_skip()
x264_macroblock_encode_skip()用于编码Skip宏块。该函数的定义位于encoder\macroblock.c,如下所示。//编码skip类型宏块
static void x264_macroblock_encode_skip( x264_t *h )
{
/*
* YUV420P的时候在这里相当于在non_zero_count[]填充了v(v=0):
* YUV422P,YUV444P的时候填充了w(w=0)
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 w w w w
* | 0 0 0 0 w w w w
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 w w w w
* | 0 0 0 0 w w w w
*/
//填充non_zero_count[]
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 0]] ) = 0;
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 2]] ) = 0;
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 8]] ) = 0;
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[10]] ) = 0;
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+ 0]] ) = 0;
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+ 2]] ) = 0;
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+ 0]] ) = 0;
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+ 2]] ) = 0;
if( CHROMA_FORMAT >= CHROMA_422 )
{
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+ 8]] ) = 0;
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+10]] ) = 0;
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+ 8]] ) = 0;
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+10]] ) = 0;
}
//CBP也赋值为0,即不对亮度和色度编码
h->mb.i_cbp_luma = 0;
h->mb.i_cbp_chroma = 0;
h->mb.cbp[h->mb.i_mb_xy] = 0;
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_macroblock_encode_skip()的逻辑比较简单,就是将宏块的DCT非零系数缓存non_zero_count[]设置成了0,并且将宏块的CBP也设置为0(代表没有残差信息)。
x264_mb_encode_i16x16()
x264_mb_encode_i16x16()用于编码Intra16x16的宏块。该函数的定义位于encoder\macroblock.c,如下所示。//编码I16x16宏块-需要Hadamard变换
/*
* 16x16 宏块
*
* +--------+--------+
* | | D D D D
* | |
* | | D D D D
* + + + +
* | | D D D D
* | |
* | | D D D D
* +--------+--------+
*
*/
//p代表分量
static void x264_mb_encode_i16x16( x264_t *h, int p, int i_qp )
{
//编码帧
pixel *p_src = h->mb.pic.p_fenc[p];
//重建帧
pixel *p_dst = h->mb.pic.p_fdec[p];
ALIGNED_ARRAY_N( dctcoef, dct4x4,[16],[16] );
ALIGNED_ARRAY_N( dctcoef, dct_dc4x4,[16] );
int nz, block_cbp = 0;
int decimate_score = h->mb.b_dct_decimate ? 0 : 9;
int i_quant_cat = p ? CQM_4IC : CQM_4IY;
int i_mode = h->mb.i_intra16x16_pred_mode;
if( h->mb.b_lossless )
x264_predict_lossless_16x16( h, p, i_mode );
else
h->predict_16x16[i_mode]( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[p] ); //帧内预测.p_fdec是重建帧。p_fenc是编码帧。
if( h->mb.b_lossless )
{
for( int i = 0; i < 16; i++ )
{
int oe = block_idx_xy_fenc[i];
int od = block_idx_xy_fdec[i];
nz = h->zigzagf.sub_4x4ac( h->dct.luma4x4[16*p+i], p_src+oe, p_dst+od, &dct_dc4x4[block_idx_yx_1d[i]] );
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16*p+i]] = nz;
block_cbp |= nz;
}
h->mb.i_cbp_luma |= block_cbp * 0xf;
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[LUMA_DC+p]] = array_non_zero( dct_dc4x4, 16 );
h->zigzagf.scan_4x4( h->dct.luma16x16_dc[p], dct_dc4x4 );
return;
}
CLEAR_16x16_NNZ( p );
h->dctf.sub16x16_dct( dct4x4, p_src, p_dst ); //求残差,然后进行DCT变换
if( h->mb.b_noise_reduction )
for( int idx = 0; idx < 16; idx++ )
h->quantf.denoise_dct( dct4x4[idx], h->nr_residual_sum[0], h->nr_offset[0], 16 );
//获取DC系数
for( int idx = 0; idx < 16; idx++ )
{
//每个4x4DCT块的[0]元素
dct_dc4x4[block_idx_xy_1d[idx]] = dct4x4[idx][0];
//抽取出来之后,赋值0
dct4x4[idx][0] = 0;
}
if( h->mb.b_trellis )
{
for( int idx = 0; idx < 16; idx++ )
if( x264_quant_4x4_trellis( h, dct4x4[idx], i_quant_cat, i_qp, ctx_cat_plane[DCT_LUMA_AC][p], 1, !!p, idx ) )
{
block_cbp = 0xf;
h->zigzagf.scan_4x4( h->dct.luma4x4[16*p+idx], dct4x4[idx] );
h->quantf.dequant_4x4( dct4x4[idx], h->dequant4_mf[i_quant_cat], i_qp );
if( decimate_score < 6 ) decimate_score += h->quantf.decimate_score15( h->dct.luma4x4[16*p+idx] );
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16*p+idx]] = 1;
}
}
else
{
//先分成4个8x8?
for( int i8x8 = 0; i8x8 < 4; i8x8++ )
{
//每个8x8做4个4x4量化
nz = h->quantf.quant_4x4x4( &dct4x4[i8x8*4], h->quant4_mf[i_quant_cat][i_qp], h->quant4_bias[i_quant_cat][i_qp] );
if( nz )
{
block_cbp = 0xf;
FOREACH_BIT( idx, i8x8*4, nz )
{
//建立重建的帧
//之子扫描
h->zigzagf.scan_4x4( h->dct.luma4x4[16*p+idx], dct4x4[idx] );
//反量化,用于重建图像
h->quantf.dequant_4x4( dct4x4[idx], h->dequant4_mf[i_quant_cat], i_qp );
if( decimate_score < 6 ) decimate_score += h->quantf.decimate_score15( h->dct.luma4x4[16*p+idx] );
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16*p+idx]] = 1;
}
}
}
}
/* Writing the 16 CBFs in an i16x16 block is quite costly, so decimation can save many bits. */
/* More useful with CAVLC, but still useful with CABAC. */
if( decimate_score < 6 )
{
CLEAR_16x16_NNZ( p );
block_cbp = 0;
}
else
h->mb.i_cbp_luma |= block_cbp;
//16个DC系数-Hadamard变换
h->dctf.dct4x4dc( dct_dc4x4 );
if( h->mb.b_trellis )
nz = x264_quant_luma_dc_trellis( h, dct_dc4x4, i_quant_cat, i_qp, ctx_cat_plane[DCT_LUMA_DC][p], 1, LUMA_DC+p );
else
//DC-Hadamard变换之后-量化
nz = h->quantf.quant_4x4_dc( dct_dc4x4, h->quant4_mf[i_quant_cat][i_qp][0]>>1, h->quant4_bias[i_quant_cat][i_qp][0]<<1 );
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[LUMA_DC+p]] = nz;
if( nz )
{
//之子扫描
h->zigzagf.scan_4x4( h->dct.luma16x16_dc[p], dct_dc4x4 );
/* output samples to fdec */
//DC-反变换
h->dctf.idct4x4dc( dct_dc4x4 );
//DC-反量化
h->quantf.dequant_4x4_dc( dct_dc4x4, h->dequant4_mf[i_quant_cat], i_qp ); /* XXX not inversed */
if( block_cbp )
for( int i = 0; i < 16; i++ )//循环16个4x4DCT块
dct4x4[i][0] = dct_dc4x4[block_idx_xy_1d[i]];//把DC系数重新赋值到每个DCT数组的[0]元素上
}
/* put pixels to fdec */
// fdec代表重建帧
if( block_cbp )
h->dctf.add16x16_idct( p_dst, dct4x4 );//DCT反变换后,叠加到预测数据上(通用)
else if( nz )
h->dctf.add16x16_idct_dc( p_dst, dct_dc4x4 );//DCT反变换后,叠加到预测数据上(只有DC系数的时候)
}
简单整理一下x264_mb_encode_i16x16()的逻辑,如下所示:
(1)调用predict_16x16[]()汇编函数对重建宏块数据p_fdec进行帧内预测。
(2)调用x264_dct_function_t的sub16x16_dct()汇编函数,计算重建宏块数据p_fdec与编码宏块数据p_fenc之间的残差,然后对残差做DCT变换。
(3)抽取出来16个4x4DCT小块的DC系数,存储于dct_dc4x4[]。
(4)分成4个8x8的块,对每个8x8块分别调用x264_quant_function_t的quant_4x4x4()汇编函数进行量化。
(5)分成16个4x4的块,对每个4x4块分别调用x264_quant_function_t的dequant_4x4()汇编函数进行反量化(用于重建帧)。
(6)对于dct_dc4x4[]中16个小块的DC系数作如下处理:a)调用x264_dct_function_t的dct4x4dc()汇编函数进行Hadamard变换。b)调用x264_quant_function_t的quant_4x4_dc()汇编函数进行DC系数的量化。c)调用x264_dct_function_t的idct4x4dc()汇编函数进行Hadamard反变换。d)调用x264_quant_function_t的dequant_4x4_dc()汇编函数进行DC系数的反量化。e)将反量化后的DC系数重新放到16x16块对应的位置上。(7)调用x264_dct_function_t的add16x16_idct()汇编函数,对残差进行DCT反变换,并将反变换后的数据叠加(“add”)至预测数据上(用于重建帧)。
可以看出Intra16x16编码的过程就是一个“DCT变换 + 量化 + Hadamard变换”的流程。其中“DCT变换 + 量化”是一个通用的编码步骤,而“Hadamard变换”是专属于Intra16x16宏块的步骤。
x264_mb_encode_i4x4()
x264_mb_encode_i4x4()用于编码Intra4x4的宏块。该函数的定义位于encoder\macroblock.c,如下所示。//编码Intra4x4
/*
* +----+
* | |
* +----+
*/
static ALWAYS_INLINE void x264_mb_encode_i4x4( x264_t *h, int p, int idx, int i_qp, int i_mode, int b_predict )
{
int nz;
//编码帧
pixel *p_src = &h->mb.pic.p_fenc[p][block_idx_xy_fenc[idx]];
//重建帧
pixel *p_dst = &h->mb.pic.p_fdec[p][block_idx_xy_fdec[idx]];
ALIGNED_ARRAY_N( dctcoef, dct4x4,[16] );
if( b_predict )
{
if( h->mb.b_lossless )
x264_predict_lossless_4x4( h, p_dst, p, idx, i_mode );
else
h->predict_4x4[i_mode]( p_dst );//帧内预测,存于p_dst
}
if( h->mb.b_lossless )
{
nz = h->zigzagf.sub_4x4( h->dct.luma4x4[p*16+idx], p_src, p_dst );
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[p*16+idx]] = nz;
h->mb.i_cbp_luma |= nz<<(idx>>2);
return;
}
h->dctf.sub4x4_dct( dct4x4, p_src, p_dst );//求p_src与p_dst之间的残差,并且进行DCT变换
//量化
nz = x264_quant_4x4( h, dct4x4, i_qp, ctx_cat_plane[DCT_LUMA_4x4][p], 1, p, idx );
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[p*16+idx]] = nz;
if( nz )
{
//解码并且建立重建帧(p_dst)
h->mb.i_cbp_luma |= 1<<(idx>>2);
//DCT系数重新排个序-从之子扫描变换为普通扫描
h->zigzagf.scan_4x4( h->dct.luma4x4[p*16+idx], dct4x4 );
//反量化
h->quantf.dequant_4x4( dct4x4, h->dequant4_mf[p?CQM_4IC:CQM_4IY], i_qp );
//DCT残差反变换,并且叠加到预测数据上,形成重建帧
h->dctf.add4x4_idct( p_dst, dct4x4 );
}
}
简单整理一下x264_mb_encode_i4x4()的逻辑,如下所示:
(1)调用predict_4x4[]()汇编函数对重建宏块数据p_fdec进行帧内预测。
(2)调用x264_dct_function_t的sub4x4_dct ()汇编函数,计算重建宏块数据p_fdec与编码宏块数据p_fenc之间的残差,然后对残差做DCT变换。
(3)调用x264_quant_function_t的quant_4x4()汇编函数进行量化。
(4)调用x264_quant_function_t的dequant_4x4()汇编函数进行反量化(用于重建帧)。
(5)调用x264_dct_function_t的add4x4_idct()汇编函数,对残差进行DCT反变换,并将反变换后的数据叠加(“add”)至预测数据上(用于重建帧)。
可以看出Intra4x4编码的过程就是一个“DCT变换 + 量化”的流程。
DCT和量化的知识
宏块的编码过程就是一个“DCT变换+量化”的过程。简单记录一下相关的知识。DCT变换
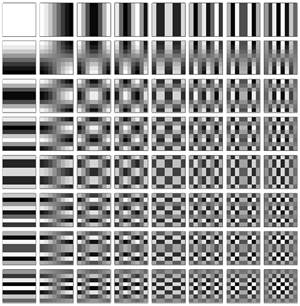
DCT变换的核心理念就是把图像的低频信息(对应大面积平坦区域)变换到系数矩阵的左上角,而把高频信息变换到系数矩阵的右下角,这样就可以在压缩的时候(量化)去除掉人眼不敏感的高频信息(位于矩阵右下角的系数)从而达到压缩数据的目的。二维8x8DCT变换常见的示意图如下所示。
早期的DCT变换都使用了8x8的矩阵(变换系数为小数)。在H.264标准中新提出了一种4x4的矩阵。这种4x4 DCT变换的系数都是整数,一方面提高了运算的准确性,一方面也利于代码的优化。4x4整数DCT变换的示意图如下所示(作为对比,右侧为4x4块的Hadamard变换的示意图)。4x4整数DCT变换的公式如下所示。
对该公式中的矩阵乘法可以转换为2次一维DCT变换:首先对4x4块中的每行像素进行一维DCT变换,然后再对4x4块中的每列像素进行一维DCT变换。而一维的DCT变换是可以改造成为蝶形快速算法的,如下所示。
同理,DCT反变换就是DCT变换的逆变换。DCT反变换的公式如下所示。同理,DCT反变换的矩阵乘法也可以改造成为2次一维IDCT变换:首先对4x4块中的每行像素进行一维IDCT变换,然后再对4x4块中的每列像素进行一维IDCT变换。而一维的IDCT变换也可以改造成为蝶形快速算法,如下所示。
除了4x4DCT变换之外,新版本的H.264标准中还引入了一种8x8DCT。目前针对这种8x8DCT我还没有做研究,暂时不做记录。
量化
量化是H.264视频压缩编码中对视频质量影响最大的地方,也是会导致“信息丢失”的地方。量化的原理可以表示为下面公式:在H.264 中,量化步长Qstep 共有52 个值,如下表所示。其中QP 是量化参数,是量化步长的序号。当QP 取最小值0 时代表最精细的量化,当QP 取最大值51 时代表最粗糙的量化。QP 每增加6,Qstep 增加一倍。
《H.264标准》中规定,量化过程除了完成本职工作外,还需要完成它前一步DCT变换中“系数相乘”的工作。这一步骤的推导过程不再记录,直接给出最终的公式(这个公式完全为整数运算,同时避免了除法的使用):
sign()为符号函数。为了更形象的显示MF的取值,做了下面一张示意图。图中深蓝色代表MF取值较大的点,而浅蓝色代表MF取值较小的点。
Wij为DCT变换后的系数。
MF的值如下表所示。表中只列出对应QP 值为0 到5 的MF 值。QP大于6之后,将QP实行对6取余数操作,再找到MF的值。
qbits计算公式为“qbits = 15 + floor(QP/6)”。即它的值随QP 值每增加6 而增加1。
f 是偏移量(用于改善恢复图像的视觉效果)。对帧内预测图像块取2^qbits/3,对帧间预测图像块取2^qbits/6。
DCT相关的源代码
DCT模块的初始化函数是x264_dct_init()。该函数对x264_dct_function_t结构体中的函数指针进行了赋值。X264运行的过程中只要调用x264_dct_function_t的函数指针就可以完成相应的功能。
x264_dct_init()
x264_dct_init()用于初始化DCT变换和DCT反变换相关的汇编函数。该函数的定义位于common\dct.c,如下所示。/****************************************************************************
* x264_dct_init:
****************************************************************************/
void x264_dct_init( int cpu, x264_dct_function_t *dctf )
{
//C语言版本
//4x4DCT变换
dctf->sub4x4_dct = sub4x4_dct;
dctf->add4x4_idct = add4x4_idct;
//8x8块:分解成4个4x4DCT变换,调用4次sub4x4_dct()
dctf->sub8x8_dct = sub8x8_dct;
dctf->sub8x8_dct_dc = sub8x8_dct_dc;
dctf->add8x8_idct = add8x8_idct;
dctf->add8x8_idct_dc = add8x8_idct_dc;
dctf->sub8x16_dct_dc = sub8x16_dct_dc;
//16x16块:分解成4个8x8块,调用4次sub8x8_dct()
//实际上每个sub8x8_dct()又分解成4个4x4DCT变换,调用4次sub4x4_dct()
dctf->sub16x16_dct = sub16x16_dct;
dctf->add16x16_idct = add16x16_idct;
dctf->add16x16_idct_dc = add16x16_idct_dc;
//8x8DCT,注意:后缀是_dct8
dctf->sub8x8_dct8 = sub8x8_dct8;
dctf->add8x8_idct8 = add8x8_idct8;
dctf->sub16x16_dct8 = sub16x16_dct8;
dctf->add16x16_idct8 = add16x16_idct8;
//Hadamard变换
dctf->dct4x4dc = dct4x4dc;
dctf->idct4x4dc = idct4x4dc;
dctf->dct2x4dc = dct2x4dc;
#if HIGH_BIT_DEPTH
#if HAVE_MMX
if( cpu&X264_CPU_MMX )
{
dctf->sub4x4_dct = x264_sub4x4_dct_mmx;
dctf->sub8x8_dct = x264_sub8x8_dct_mmx;
dctf->sub16x16_dct = x264_sub16x16_dct_mmx;
}
if( cpu&X264_CPU_SSE2 )
{
dctf->add4x4_idct = x264_add4x4_idct_sse2;
dctf->dct4x4dc = x264_dct4x4dc_sse2;
dctf->idct4x4dc = x264_idct4x4dc_sse2;
dctf->sub8x8_dct8 = x264_sub8x8_dct8_sse2;
dctf->sub16x16_dct8 = x264_sub16x16_dct8_sse2;
dctf->add8x8_idct = x264_add8x8_idct_sse2;
dctf->add16x16_idct = x264_add16x16_idct_sse2;
dctf->add8x8_idct8 = x264_add8x8_idct8_sse2;
dctf->add16x16_idct8 = x264_add16x16_idct8_sse2;
dctf->sub8x8_dct_dc = x264_sub8x8_dct_dc_sse2;
dctf->add8x8_idct_dc = x264_add8x8_idct_dc_sse2;
dctf->sub8x16_dct_dc = x264_sub8x16_dct_dc_sse2;
dctf->add16x16_idct_dc= x264_add16x16_idct_dc_sse2;
}
if( cpu&X264_CPU_SSE4 )
{
dctf->sub8x8_dct8 = x264_sub8x8_dct8_sse4;
dctf->sub16x16_dct8 = x264_sub16x16_dct8_sse4;
}
if( cpu&X264_CPU_AVX )
{
dctf->add4x4_idct = x264_add4x4_idct_avx;
dctf->dct4x4dc = x264_dct4x4dc_avx;
dctf->idct4x4dc = x264_idct4x4dc_avx;
dctf->sub8x8_dct8 = x264_sub8x8_dct8_avx;
dctf->sub16x16_dct8 = x264_sub16x16_dct8_avx;
dctf->add8x8_idct = x264_add8x8_idct_avx;
dctf->add16x16_idct = x264_add16x16_idct_avx;
dctf->add8x8_idct8 = x264_add8x8_idct8_avx;
dctf->add16x16_idct8 = x264_add16x16_idct8_avx;
dctf->add8x8_idct_dc = x264_add8x8_idct_dc_avx;
dctf->sub8x16_dct_dc = x264_sub8x16_dct_dc_avx;
dctf->add16x16_idct_dc= x264_add16x16_idct_dc_avx;
}
#endif // HAVE_MMX
#else // !HIGH_BIT_DEPTH
//MMX版本
#if HAVE_MMX
if( cpu&X264_CPU_MMX )
{
dctf->sub4x4_dct = x264_sub4x4_dct_mmx;
dctf->add4x4_idct = x264_add4x4_idct_mmx;
dctf->idct4x4dc = x264_idct4x4dc_mmx;
dctf->sub8x8_dct_dc = x264_sub8x8_dct_dc_mmx2;
//此处省略大量的X86、ARM等平台的汇编函数初始化代码
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_dct_init()初始化了一系列的DCT变换的函数,这些DCT函数名称有如下规律:
(1)DCT函数名称前面有“sub”,代表对两块像素相减得到残差之后,再进行DCT变换。x264_dct_init()的输入参数x264_dct_function_t是一个结构体,其中包含了各种DCT函数的接口。x264_dct_function_t的定义如下所示。
(2)DCT反变换函数名称前面有“add”,代表将DCT反变换之后的残差数据叠加到预测数据上。
(3)以“dct8”为结尾的函数使用了8x8DCT(未研究过),其余函数是用的都是4x4DCT。
typedef struct
{
// pix1 stride = FENC_STRIDE
// pix2 stride = FDEC_STRIDE
// p_dst stride = FDEC_STRIDE
void (*sub4x4_dct) ( dctcoef dct[16], pixel *pix1, pixel *pix2 );
void (*add4x4_idct) ( pixel *p_dst, dctcoef dct[16] );
void (*sub8x8_dct) ( dctcoef dct[4][16], pixel *pix1, pixel *pix2 );
void (*sub8x8_dct_dc)( dctcoef dct[4], pixel *pix1, pixel *pix2 );
void (*add8x8_idct) ( pixel *p_dst, dctcoef dct[4][16] );
void (*add8x8_idct_dc) ( pixel *p_dst, dctcoef dct[4] );
void (*sub8x16_dct_dc)( dctcoef dct[8], pixel *pix1, pixel *pix2 );
void (*sub16x16_dct) ( dctcoef dct[16][16], pixel *pix1, pixel *pix2 );
void (*add16x16_idct)( pixel *p_dst, dctcoef dct[16][16] );
void (*add16x16_idct_dc) ( pixel *p_dst, dctcoef dct[16] );
void (*sub8x8_dct8) ( dctcoef dct[64], pixel *pix1, pixel *pix2 );
void (*add8x8_idct8) ( pixel *p_dst, dctcoef dct[64] );
void (*sub16x16_dct8) ( dctcoef dct[4][64], pixel *pix1, pixel *pix2 );
void (*add16x16_idct8)( pixel *p_dst, dctcoef dct[4][64] );
void (*dct4x4dc) ( dctcoef d[16] );
void (*idct4x4dc)( dctcoef d[16] );
void (*dct2x4dc)( dctcoef dct[8], dctcoef dct4x4[8][16] );
} x264_dct_function_t;x264_dct_init()的工作就是对x264_dct_function_t中的函数指针进行赋值。由于DCT函数很多,不便于一一研究,下文仅举例分析几个典型的4x4DCT函数:4x4DCT变换函数sub4x4_dct(),4x4IDCT变换函数add4x4_idct(),8x8块的4x4DCT变换函数sub8x8_dct(),16x16块的4x4DCT变换函数sub16x16_dct(),4x4Hadamard变换函数dct4x4dc()。
sub4x4_dct()
sub4x4_dct()可以将两块4x4的图像相减求残差后,进行DCT变换。该函数的定义位于common\dct.c,如下所示。/*
* 求残差用
* 注意求的是一个“方块”形像素
*
* 参数的含义如下:
* diff:输出的残差数据
* i_size:方块的大小
* pix1:输入数据1
* i_pix1:输入数据1一行像素大小(stride)
* pix2:输入数据2
* i_pix2:输入数据2一行像素大小(stride)
*
*/
static inline void pixel_sub_wxh( dctcoef *diff, int i_size,
pixel *pix1, int i_pix1, pixel *pix2, int i_pix2 )
{
for( int y = 0; y < i_size; y++ )
{
for( int x = 0; x < i_size; x++ )
diff[x + y*i_size] = pix1[x] - pix2[x];//求残差
pix1 += i_pix1;//前进到下一行
pix2 += i_pix2;
}
}
//4x4DCT变换
//注意首先获取pix1和pix2两块数据的残差,然后再进行变换
//返回dct[16]
static void sub4x4_dct( dctcoef dct[16], pixel *pix1, pixel *pix2 )
{
dctcoef d[16];
dctcoef tmp[16];
//获取残差数据,存入d[16]
//pix1一般为编码帧(enc)
//pix2一般为重建帧(dec)
pixel_sub_wxh( d, 4, pix1, FENC_STRIDE, pix2, FDEC_STRIDE );
//处理残差d[16]
//蝶形算法:横向4个像素
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
int s03 = d[i*4+0] + d[i*4+3];
int s12 = d[i*4+1] + d[i*4+2];
int d03 = d[i*4+0] - d[i*4+3];
int d12 = d[i*4+1] - d[i*4+2];
tmp[0*4+i] = s03 + s12;
tmp[1*4+i] = 2*d03 + d12;
tmp[2*4+i] = s03 - s12;
tmp[3*4+i] = d03 - 2*d12;
}
//蝶形算法:纵向
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
int s03 = tmp[i*4+0] + tmp[i*4+3];
int s12 = tmp[i*4+1] + tmp[i*4+2];
int d03 = tmp[i*4+0] - tmp[i*4+3];
int d12 = tmp[i*4+1] - tmp[i*4+2];
dct[i*4+0] = s03 + s12;
dct[i*4+1] = 2*d03 + d12;
dct[i*4+2] = s03 - s12;
dct[i*4+3] = d03 - 2*d12;
}
}
从源代码可以看出,sub4x4_dct()首先调用pixel_sub_wxh()求出两个输入图像块的残差,然后使用蝶形快速算法计算残差图像的DCT系数。
add4x4_idct()
add4x4_idct()可以将残差数据进行DCT反变换,并将变换后得到的残差像素数据叠加到预测数据上。该函数的定义位于common\dct.c,如下所示。//4x4DCT反变换(“add”代表叠加到已有的像素上)
static void add4x4_idct( pixel *p_dst, dctcoef dct[16] )
{
dctcoef d[16];
dctcoef tmp[16];
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
int s02 = dct[0*4+i] + dct[2*4+i];
int d02 = dct[0*4+i] - dct[2*4+i];
int s13 = dct[1*4+i] + (dct[3*4+i]>>1);
int d13 = (dct[1*4+i]>>1) - dct[3*4+i];
tmp[i*4+0] = s02 + s13;
tmp[i*4+1] = d02 + d13;
tmp[i*4+2] = d02 - d13;
tmp[i*4+3] = s02 - s13;
}
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
int s02 = tmp[0*4+i] + tmp[2*4+i];
int d02 = tmp[0*4+i] - tmp[2*4+i];
int s13 = tmp[1*4+i] + (tmp[3*4+i]>>1);
int d13 = (tmp[1*4+i]>>1) - tmp[3*4+i];
d[0*4+i] = ( s02 + s13 + 32 ) >> 6;
d[1*4+i] = ( d02 + d13 + 32 ) >> 6;
d[2*4+i] = ( d02 - d13 + 32 ) >> 6;
d[3*4+i] = ( s02 - s13 + 32 ) >> 6;
}
for( int y = 0; y < 4; y++ )
{
for( int x = 0; x < 4; x++ )
p_dst[x] = x264_clip_pixel( p_dst[x] + d[y*4+x] );
p_dst += FDEC_STRIDE;
}
}
从源代码可以看出,add4x4_idct()首先采用快速蝶形算法对DCT系数进行DCT反变换后得到残差像素数据,然后再将残差数据叠加到p_dst指向的像素上。需要注意这里是“叠加”而不是“赋值”。
sub8x8_dct()
sub8x8_dct()可以将两块8x8的图像相减求残差后,进行4x4DCT变换。该函数的定义位于common\dct.c,如下所示。//8x8块:分解成4个4x4DCT变换,调用4次sub4x4_dct()
//返回dct[4][16]
static void sub8x8_dct( dctcoef dct[4][16], pixel *pix1, pixel *pix2 )
{
/*
* 8x8 宏块被划分为4个4x4子块
*
* +---+---+
* | 0 | 1 |
* +---+---+
* | 2 | 3 |
* +---+---+
*
*/
sub4x4_dct( dct[0], &pix1[0], &pix2[0] );
sub4x4_dct( dct[1], &pix1[4], &pix2[4] );
sub4x4_dct( dct[2], &pix1[4*FENC_STRIDE+0], &pix2[4*FDEC_STRIDE+0] );
sub4x4_dct( dct[3], &pix1[4*FENC_STRIDE+4], &pix2[4*FDEC_STRIDE+4] );
}
从源代码可以看出, sub8x8_dct()将8x8的图像块分成4个4x4的图像块,分别调用了sub4x4_dct()。
sub16x16_dct()
sub16x16_dct()可以将两块16x16的图像相减求残差后,进行4x4DCT变换。该函数的定义位于common\dct.c,如下所示。//16x16块:分解成4个8x8的块做DCT变换,调用4次sub8x8_dct()
//返回dct[16][16]
static void sub16x16_dct( dctcoef dct[16][16], pixel *pix1, pixel *pix2 )
{
/*
* 16x16 宏块被划分为4个8x8子块
*
* +--------+--------+
* | | |
* | 0 | 1 |
* | | |
* +--------+--------+
* | | |
* | 2 | 3 |
* | | |
* +--------+--------+
*
*/
sub8x8_dct( &dct[ 0], &pix1[0], &pix2[0] ); //0
sub8x8_dct( &dct[ 4], &pix1[8], &pix2[8] ); //1
sub8x8_dct( &dct[ 8], &pix1[8*FENC_STRIDE+0], &pix2[8*FDEC_STRIDE+0] ); //2
sub8x8_dct( &dct[12], &pix1[8*FENC_STRIDE+8], &pix2[8*FDEC_STRIDE+8] ); //3
}
从源代码可以看出, sub8x8_dct()将16x16的图像块分成4个8x8的图像块,分别调用了sub8x8_dct()。而sub8x8_dct()实际上又调用了4次sub4x4_dct()。所以可以得知,不论sub16x16_dct(),sub8x8_dct()还是sub4x4_dct(),本质都是进行4x4DCT。
dct4x4dc()
dct4x4dc()可以将输入的4x4图像块进行Hadamard变换。该函数的定义位于common\dct.c,如下所示。//Hadamard变换
static void dct4x4dc( dctcoef d[16] )
{
dctcoef tmp[16];
//蝶形算法:横向的4个像素
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
int s01 = d[i*4+0] + d[i*4+1];
int d01 = d[i*4+0] - d[i*4+1];
int s23 = d[i*4+2] + d[i*4+3];
int d23 = d[i*4+2] - d[i*4+3];
tmp[0*4+i] = s01 + s23;
tmp[1*4+i] = s01 - s23;
tmp[2*4+i] = d01 - d23;
tmp[3*4+i] = d01 + d23;
}
//蝶形算法:纵向
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
int s01 = tmp[i*4+0] + tmp[i*4+1];
int d01 = tmp[i*4+0] - tmp[i*4+1];
int s23 = tmp[i*4+2] + tmp[i*4+3];
int d23 = tmp[i*4+2] - tmp[i*4+3];
d[i*4+0] = ( s01 + s23 + 1 ) >> 1;
d[i*4+1] = ( s01 - s23 + 1 ) >> 1;
d[i*4+2] = ( d01 - d23 + 1 ) >> 1;
d[i*4+3] = ( d01 + d23 + 1 ) >> 1;
}
}
从源代码可以看出,dct4x4dc()实现了Hadamard快速蝶形算法。
量化相关的源代码
量化模块的初始化函数是x264_quant_init()。该函数对x264_quant_function_t结构体中的函数指针进行了赋值。X264运行的过程中只要调用x264_quant_function_t的函数指针就可以完成相应的功能。
x264_quant_init()
x264_quant_init()初始化量化和反量化相关的汇编函数。该函数的定义位于common\quant.c,如下所示。//量化
void x264_quant_init( x264_t *h, int cpu, x264_quant_function_t *pf )
{
//这个好像是针对8x8DCT的
pf->quant_8x8 = quant_8x8;
//量化4x4=16个
pf->quant_4x4 = quant_4x4;
//注意:处理4个4x4的块
pf->quant_4x4x4 = quant_4x4x4;
//Intra16x16中,16个DC系数Hadamard变换后对的它们量化
pf->quant_4x4_dc = quant_4x4_dc;
pf->quant_2x2_dc = quant_2x2_dc;
//反量化4x4=16个
pf->dequant_4x4 = dequant_4x4;
pf->dequant_4x4_dc = dequant_4x4_dc;
pf->dequant_8x8 = dequant_8x8;
pf->idct_dequant_2x4_dc = idct_dequant_2x4_dc;
pf->idct_dequant_2x4_dconly = idct_dequant_2x4_dconly;
pf->optimize_chroma_2x2_dc = optimize_chroma_2x2_dc;
pf->optimize_chroma_2x4_dc = optimize_chroma_2x4_dc;
pf->denoise_dct = x264_denoise_dct;
pf->decimate_score15 = x264_decimate_score15;
pf->decimate_score16 = x264_decimate_score16;
pf->decimate_score64 = x264_decimate_score64;
pf->coeff_last4 = x264_coeff_last4;
pf->coeff_last8 = x264_coeff_last8;
pf->coeff_last[ DCT_LUMA_AC] = x264_coeff_last15;
pf->coeff_last[ DCT_LUMA_4x4] = x264_coeff_last16;
pf->coeff_last[ DCT_LUMA_8x8] = x264_coeff_last64;
pf->coeff_level_run4 = x264_coeff_level_run4;
pf->coeff_level_run8 = x264_coeff_level_run8;
pf->coeff_level_run[ DCT_LUMA_AC] = x264_coeff_level_run15;
pf->coeff_level_run[ DCT_LUMA_4x4] = x264_coeff_level_run16;
#if HIGH_BIT_DEPTH
#if HAVE_MMX
INIT_TRELLIS( sse2 );
if( cpu&X264_CPU_MMX2 )
{
#if ARCH_X86
pf->denoise_dct = x264_denoise_dct_mmx;
pf->decimate_score15 = x264_decimate_score15_mmx2;
pf->decimate_score16 = x264_decimate_score16_mmx2;
pf->decimate_score64 = x264_decimate_score64_mmx2;
pf->coeff_last8 = x264_coeff_last8_mmx2;
pf->coeff_last[ DCT_LUMA_AC] = x264_coeff_last15_mmx2;
pf->coeff_last[ DCT_LUMA_4x4] = x264_coeff_last16_mmx2;
pf->coeff_last[ DCT_LUMA_8x8] = x264_coeff_last64_mmx2;
pf->coeff_level_run8 = x264_coeff_level_run8_mmx2;
pf->coeff_level_run[ DCT_LUMA_AC] = x264_coeff_level_run15_mmx2;
pf->coeff_level_run[ DCT_LUMA_4x4] = x264_coeff_level_run16_mmx2;
#endif
pf->coeff_last4 = x264_coeff_last4_mmx2;
pf->coeff_level_run4 = x264_coeff_level_run4_mmx2;
if( cpu&X264_CPU_LZCNT )
pf->coeff_level_run4 = x264_coeff_level_run4_mmx2_lzcnt;
}
//此处省略大量的X86、ARM等平台的汇编函数初始化代码
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_quant_init()初始化了一系列的量化相关的函数。它的输入参数x264_quant_function_t是一个结构体,其中包含了和量化相关各种函数指针。x264_quant_function_t的定义如下所示。
typedef struct
{
int (*quant_8x8) ( dctcoef dct[64], udctcoef mf[64], udctcoef bias[64] );
int (*quant_4x4) ( dctcoef dct[16], udctcoef mf[16], udctcoef bias[16] );
int (*quant_4x4x4)( dctcoef dct[4][16], udctcoef mf[16], udctcoef bias[16] );
int (*quant_4x4_dc)( dctcoef dct[16], int mf, int bias );
int (*quant_2x2_dc)( dctcoef dct[4], int mf, int bias );
void (*dequant_8x8)( dctcoef dct[64], int dequant_mf[6][64], int i_qp );
void (*dequant_4x4)( dctcoef dct[16], int dequant_mf[6][16], int i_qp );
void (*dequant_4x4_dc)( dctcoef dct[16], int dequant_mf[6][16], int i_qp );
void (*idct_dequant_2x4_dc)( dctcoef dct[8], dctcoef dct4x4[8][16], int dequant_mf[6][16], int i_qp );
void (*idct_dequant_2x4_dconly)( dctcoef dct[8], int dequant_mf[6][16], int i_qp );
int (*optimize_chroma_2x2_dc)( dctcoef dct[4], int dequant_mf );
int (*optimize_chroma_2x4_dc)( dctcoef dct[8], int dequant_mf );
void (*denoise_dct)( dctcoef *dct, uint32_t *sum, udctcoef *offset, int size );
int (*decimate_score15)( dctcoef *dct );
int (*decimate_score16)( dctcoef *dct );
int (*decimate_score64)( dctcoef *dct );
int (*coeff_last[14])( dctcoef *dct );
int (*coeff_last4)( dctcoef *dct );
int (*coeff_last8)( dctcoef *dct );
int (*coeff_level_run[13])( dctcoef *dct, x264_run_level_t *runlevel );
int (*coeff_level_run4)( dctcoef *dct, x264_run_level_t *runlevel );
int (*coeff_level_run8)( dctcoef *dct, x264_run_level_t *runlevel );
#define TRELLIS_PARAMS const int *unquant_mf, const uint8_t *zigzag, int lambda2,\
int last_nnz, dctcoef *coefs, dctcoef *quant_coefs, dctcoef *dct,\
uint8_t *cabac_state_sig, uint8_t *cabac_state_last,\
uint64_t level_state0, uint16_t level_state1
int (*trellis_cabac_4x4)( TRELLIS_PARAMS, int b_ac );
int (*trellis_cabac_8x8)( TRELLIS_PARAMS, int b_interlaced );
int (*trellis_cabac_4x4_psy)( TRELLIS_PARAMS, int b_ac, dctcoef *fenc_dct, int psy_trellis );
int (*trellis_cabac_8x8_psy)( TRELLIS_PARAMS, int b_interlaced, dctcoef *fenc_dct, int psy_trellis );
int (*trellis_cabac_dc)( TRELLIS_PARAMS, int num_coefs );
int (*trellis_cabac_chroma_422_dc)( TRELLIS_PARAMS );
} x264_quant_function_t;
x264_quant_init ()的工作就是对x264_quant_function_t中的函数指针进行赋值。下文分析其中2个函数:4x4矩阵量化函数quant_4x4(),4个4x4矩阵量化函数quant_4x4x4()。
quant_4x4()
quant_4x4()用于对4x4的DCT残差矩阵进行量化。该函数的定义位于common\quant.c,如下所示。//4x4量化
//输入输出都是dct[16]
static int quant_4x4( dctcoef dct[16], udctcoef mf[16], udctcoef bias[16] )
{
int nz = 0;
//循环16个元素
for( int i = 0; i < 16; i++ )
QUANT_ONE( dct[i], mf[i], bias[i] );
return !!nz;
}
可以看出quant_4x4()循环16次调用了QUANT_ONE()完成了量化工作。并且将DCT系数值,MF值,bias偏移值直接传递给了该宏。
QUANT_ONE()
QUANT_ONE()完成了一个DCT系数的量化工作,它的定义如下。//量化1个元素
#define QUANT_ONE( coef, mf, f ) \
{ \
if( (coef) > 0 ) \
(coef) = (f + (coef)) * (mf) >> 16; \
else \
(coef) = - ((f - (coef)) * (mf) >> 16); \
nz |= (coef); \
}quant_4x4x4()
quant_4x4x4()用于对4个4x4的DCT残差矩阵进行量化。该函数的定义位于common\quant.c,如下所示。//处理4个4x4量化
//输入输出都是dct[4][16]
static int quant_4x4x4( dctcoef dct[4][16], udctcoef mf[16], udctcoef bias[16] )
{
int nza = 0;
//处理4个
for( int j = 0; j < 4; j++ )
{
int nz = 0;
//量化
for( int i = 0; i < 16; i++ )
QUANT_ONE( dct[j][i], mf[i], bias[i] );
nza |= (!!nz)<至此有关x264中的宏块编码模块的源代码就分析完毕了。
雷霄骅
[email protected]
http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020