Android系统10 RK3399 init进程启动(四十九) init第二阶段分析
配套系列教学视频链接:
安卓系列教程之ROM系统开发-百问100ask
说明
系统:Android10.0
设备: FireFly RK3399 (ROC-RK3399-PC-PLUS)
前言
本文通过代码梳理的方式,给大家介绍Android init祖先进程第二阶段的工作流程。
selinux初始化: 第一阶段的selinux初始化,完成策略二进制文件的加载,并设置默认selinux模式。之前的课程已经详细讲解过,此处就不过多讲解,可以参考之前的selinux相关系列文章开始学习:
https://blog.csdn.net/ldswfun/article/details/124637428
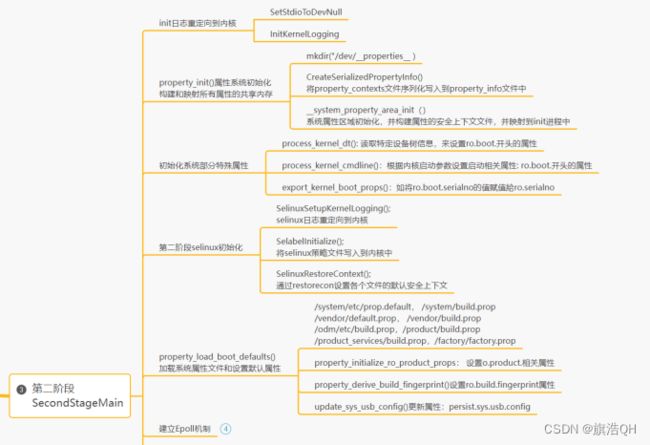
第二阶段:重点完成属性初始化,启动rc脚本的解析和执行,建立epoll机制监控各种事项。
详细框图如下所示:
第二阶段展开的完整内容为:
整体代码: system/core/init/init.cpp
int SecondStageMain(int argc, char** argv) {
if (REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC) {
InstallRebootSignalHandlers();
}
SetStdioToDevNull(argv);
InitKernelLogging(argv);
LOG(INFO) << "init second stage started!";
// Set init and its forked children's oom_adj.
if (auto result = WriteFile("/proc/1/oom_score_adj", "-1000"); !result) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to write -1000 to /proc/1/oom_score_adj: " << result.error();
}
// Enable seccomp if global boot option was passed (otherwise it is enabled in zygote).
GlobalSeccomp();
// Set up a session keyring that all processes will have access to. It
// will hold things like FBE encryption keys. No process should override
// its session keyring.
keyctl_get_keyring_ID(KEY_SPEC_SESSION_KEYRING, 1);
// Indicate that booting is in progress to background fw loaders, etc.
// //创建 /dev/.booting 文件,就是个标记,表示booting进行中
close(open("/dev/.booting", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_CLOEXEC, 0000));
//创建/dev/__properties__/property_info,并对内容进行序列化
// 构建和映射所有属性的共享内存
property_init();
// If arguments are passed both on the command line and in DT,
// properties set in DT always have priority over the command-line ones.
//uboot启动时可以给出启动参数: androidboot.android_dt_dir指定一个路径
// 没有指定就是默认路径: /proc/device-tree/firmware/android/
//一般这个路径中会设置一个fstab, 用于指定vendor和其他分区的挂载点
//并设置 ro.boot.开头的属性。RK3399上没有相关信息
process_kernel_dt();
//将内核中cmdline中所有的有=号的参数,以及特殊的androidboot.xx=xxx的形式设置成相应的属性
//如果是模拟器, bootargs中包含: androidboot.hardware=ranchu 和 init=/init
// 就会设置ro.kernel.androidboot.hardware= ranchu ro.kernel.init=/init 和ro.boot.hardware=ranchu,
//如果是真机, 只针对androidboot.xx=xx的参数设置,
//如androidboot.storagemedia=emmc, 就会有ro.boot.storagemedia=emmc
process_kernel_cmdline();
// Propagate the kernel variables to internal variables
// used by init as well as the current required properties.
// 将列表中特定属性的值设置到另外一个属性的值中去
//如将ro.boot.serialno的值设置到ro.serialno中去
//一般ro.boot开头的属性很多都是来自内核的cmdline
export_kernel_boot_props();
// Make the time that init started available for bootstat to log.
//设置init和selinux 执行时间
property_set("ro.boottime.init", getenv("INIT_STARTED_AT"));
property_set("ro.boottime.init.selinux", getenv("INIT_SELINUX_TOOK"));
// Set libavb version for Framework-only OTA match in Treble build.
//设置avb版本
const char* avb_version = getenv("INIT_AVB_VERSION");
if (avb_version) property_set("ro.boot.avb_version", avb_version);
// See if need to load debug props to allow adb root, when the device is unlocked.
const char* force_debuggable_env = getenv("INIT_FORCE_DEBUGGABLE");
if (force_debuggable_env && AvbHandle::IsDeviceUnlocked()) {
load_debug_prop = "true"s == force_debuggable_env;
}
// Clean up our environment.
unsetenv("INIT_STARTED_AT");
unsetenv("INIT_SELINUX_TOOK");
unsetenv("INIT_AVB_VERSION");
unsetenv("INIT_FORCE_DEBUGGABLE");
// Now set up SELinux for second stage.
// 第二阶段再次设置安全上下文
SelinuxSetupKernelLogging();
SelabelInitialize();
//通过restorecon设置各个文件的默认安全上下文
SelinuxRestoreContext();
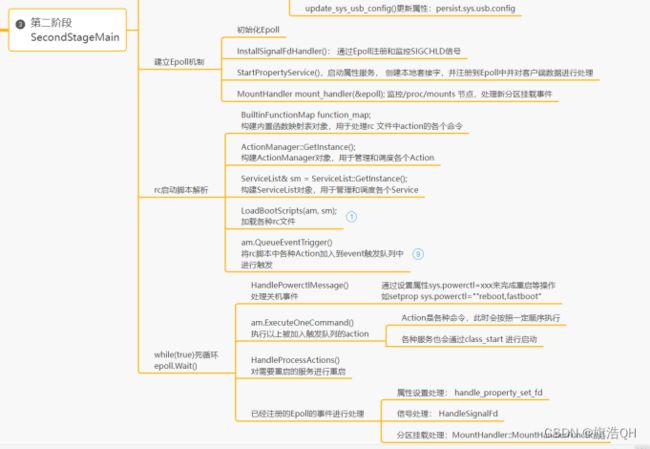
//初始化epoll
Epoll epoll;
if (auto result = epoll.Open(); !result) {
PLOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
//通过epoll监控子进程退出时发送SIGCHLD信号,并通过HandleSignalFd()进行处理
InstallSignalFdHandler(&epoll);
//加载各个分区中的属性文件,如prop.default, build.pro, default.prop,之前详细讲过属性文件
property_load_boot_defaults(load_debug_prop);
//卸载挂载点debug_ramdisk
UmountDebugRamdisk();
// 主要是根据ro.vndk.version 版本号,将/system/vendor_overlay/"和/product/vendor_overlay/挂载在vendor上
fs_mgr_vendor_overlay_mount_all();
export_oem_lock_status();
//创建本地套接字, 用于接收客户端的设置请求,并将套接字文件描述符加入到epoll监控机制
//套接字有数据之后的处理函数是: handle_property_set_fd()
StartPropertyService(&epoll);
MountHandler mount_handler(&epoll);
// 读取USB设备控制器的节点/sys/class/udc/xxx,如fe800000.dwc3,并设置属性sys.usb.controller=fe800000.dwc3
set_usb_controller();
//构建内置函数映射表对象,用于处理rc 文件中action的各个命令
const BuiltinFunctionMap function_map;
//Action关联内置函数映射表对象
Action::set_function_map(&function_map);
//这个主要设置./ apex 这些分区的挂载信息权限的。这块可以参考资料:https://cizixs.com/2017/08/29/linux-namespace/
if (!SetupMountNamespaces()) {
if (!SetupMountNamespaces()) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "SetupMountNamespaces failed";
}
// 一个容器, 记录u:r:init:s0和u:r:vendor_init:s0类型的安全上下文
//android P版本以上,给vendor oem增加u:r:vendor_init:s0权限
subcontexts = InitializeSubcontexts();
// 构建ActionManager对象,用于管理和调度各个Action
ActionManager& am = ActionManager::GetInstance();
// 构建ServiceList对象,用于管理和调度各个Service
ServiceList& sm = ServiceList::GetInstance();
//加载各种rc文件, 优先加载bootargs中androidboot.init_rc=xxx指定的rc文件
//一般很少指定这个, 所有都是按照如下顺序去加载rc文件
// /init.rc->/system/etc/init目录rc->/product/etc/init目录rc-->/product_services/etc/init
// -->/odm/etc/init --> /vendor/etc/init
LoadBootScripts(am, sm);
// Turning this on and letting the INFO logging be discarded adds 0.2s to
// Nexus 9 boot time, so it's disabled by default.
if (false) DumpState();
// Make the GSI status available before scripts start running.
//GSI 是google 原生代码的镜像,一般用于VTS测试
if (android::gsi::IsGsiRunning()) {
property_set("ro.gsid.image_running", "1");
} else {
property_set("ro.gsid.image_running", "0");
}
// 构建一个新的action, 类似on SetupCgroups, 并执行SetupCgroupsAction命令
am.QueueBuiltinAction(SetupCgroupsAction, "SetupCgroups");
// 将early-init加入到event触发队列中。
am.QueueEventTrigger("early-init");
// Queue an action that waits for coldboot done so we know ueventd has set up all of /dev...
am.QueueBuiltinAction(wait_for_coldboot_done_action, "wait_for_coldboot_done");
// ... so that we can start queuing up actions that require stuff from /dev.
am.QueueBuiltinAction(MixHwrngIntoLinuxRngAction, "MixHwrngIntoLinuxRng");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(SetMmapRndBitsAction, "SetMmapRndBits");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(SetKptrRestrictAction, "SetKptrRestrict");
Keychords keychords;
am.QueueBuiltinAction(
[&epoll, &keychords](const BuiltinArguments& args) -> Result {
for (const auto& svc : ServiceList::GetInstance()) {
keychords.Register(svc->keycodes());
}
keychords.Start(&epoll, HandleKeychord);
return Success();
},
"KeychordInit");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(console_init_action, "console_init");
// Trigger all the boot actions to get us started.
am.QueueEventTrigger("init");
// Starting the BoringSSL self test, for NIAP certification compliance.
am.QueueBuiltinAction(StartBoringSslSelfTest, "StartBoringSslSelfTest");
// Repeat mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng in case /dev/hw_random or /dev/random
// wasn't ready immediately after wait_for_coldboot_done
am.QueueBuiltinAction(MixHwrngIntoLinuxRngAction, "MixHwrngIntoLinuxRng");
// Initialize binder before bringing up other system services
am.QueueBuiltinAction(InitBinder, "InitBinder");
// Don't mount filesystems or start core system services in charger mode.
std::string bootmode = GetProperty("ro.bootmode", "");
if (bootmode == "charger") {
am.QueueEventTrigger("charger");
} else {
am.QueueEventTrigger("late-init");
}
// Run all property triggers based on current state of the properties.
am.QueueBuiltinAction(queue_property_triggers_action, "queue_property_triggers");
while (true) {
// By default, sleep until something happens.
auto epoll_timeout = std::optional{};
if (do_shutdown && !shutting_down) {
do_shutdown = false;
if (HandlePowerctlMessage(shutdown_command)) {
shutting_down = true;
}
}
if (!(waiting_for_prop || Service::is_exec_service_running())) {
/*
将按照trigger表的顺序,依次取出action链表中与trigger匹配的action。
每次均执行一个action中的一个command对应函数(一个action可能携带多个command)。
当一个action所有的command均执行完毕后,再执行下一个action。
当一个trigger对应的action均执行完毕后,再执行下一个trigger对应action。
*/
am.ExecuteOneCommand();
}
if (!(waiting_for_prop || Service::is_exec_service_running())) {
if (!shutting_down) {
//重启死掉的子进程
auto next_process_action_time = HandleProcessActions();
// If there's a process that needs restarting, wake up in time for that.
if (next_process_action_time) {
epoll_timeout = std::chrono::ceil(
*next_process_action_time - boot_clock::now());
if (*epoll_timeout < 0ms) epoll_timeout = 0ms;
}
}
// If there's more work to do, wake up again immediately.
//有command等着处理的话,不等待
if (am.HasMoreCommands()) epoll_timeout = 0ms;
}
//没有事件到来的话,最多阻塞epoll_timeout_ms时间
if (auto result = epoll.Wait(epoll_timeout); !result) {
LOG(ERROR) << result.error();
}
}
return 0;
}