Linux--进程等待wait/waitpid && status详解 && (非)阻塞等待(代码)(转载)
文章目录
-
- 进程等待原因
- 进程等待方法
-
- wait
- waitpid
- 获取子进程status
- (非)阻塞等待
-
- 进程的非阻塞等待方式代码
- 进程的阻塞等待方式代码
进程等待原因
fork创建了子进程,子进程帮父进程完成某种任务后,父进程需要用 wait或者waitpid等待子进程的退出。
那为什么要进程等待?
1、通过获取子进程退出的消息,父进程可以得知子进程的执行结果。
2、进程等待可以保证子进程先退出,父进程后退出。
3、子进程退出的时候会先进入僵尸状态,进程一旦变成僵尸状态,连kill -9也没办法杀死,因为没办法杀死一个已经死去的进程。这时候会有内存泄漏的问题,就需要父进程等待,来释放子进程占用的资源。
进程等待方法
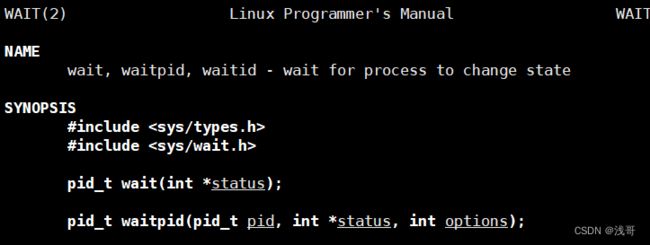
wait
wait方法:
#include
#include
pid_t wait(int *status);
返回值:
成功时返回等待进程的pid,失败返回-1。
参数:
输出型参数,获取子进程的退出状态,不关心则设置成为NULL
测试:
[zjy@VM-16-3-centos lessoncode]$ cat test.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
pid_t id = fork();
if(id == 0)
{
// child
int cnt = 5;
while(cnt)
{
printf("Child is running: cnt=%d\n", cnt);
--cnt;
sleep(1);
}
exit(0);
}
sleep(10);
printf("father wait begin\n");
// father
pid_t ret = wait(NULL);
if(ret > 0)
{
printf("father wait: %d, success\n", ret);
}
else{
printf("father wait failed\n");
}
sleep(10);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
[zjy@VM-16-3-centos lessoncode]$ while :; do ps axj | head -1 && ps axj | grep test| grep -v grep; sleep 1; echo "#######################################"; done
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
29275 29276 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
29275 29276 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
29275 29276 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
29275 29276 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
29275 29276 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
29275 29276 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 Z+ 1001 0:00 [test]
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
29275 29276 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 Z+ 1001 0:00 [test]
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
29275 29276 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 Z+ 1001 0:00 [test]
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
29275 29276 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 Z+ 1001 0:00 [test]
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
29275 29276 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 Z+ 1001 0:00 [test]
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
#######################################
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
16230 29275 29275 16230 pts/0 29275 S+ 1001 0:00 ./test
#######################################
子进程的状态从睡眠状态,变成僵尸进程,最后被父进程回收。
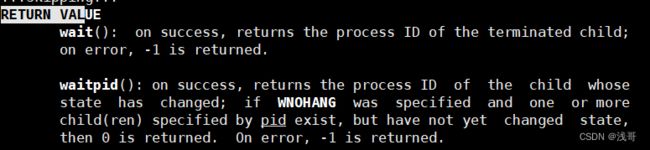
waitpid
pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *status, int options);
返回值:
1、正常返回:waitpid返回收集到的子进程的进程pid
2、如果options设置成 WNOHANG选项,表示非阻塞等待,调用时waitpid发现自己没有退出的子进程可以收集,返回0
3、如果调用出错,则返回-1,这时errno会被设置成相应的值,指示错误所在。
参数:pid:
pid=-1时,表示任一子进程,等同于wait
pid>0,等待id和pid相等的子进程。
status:
WIFEXITED(status):查看进程是否正常退出,正常退出-真
WEXITSTATUS(status):查看进程的退出码,WIFEXITED非零,提取子进程的退出码。
options
WNOHANG:如果pid的子进程没有结束,那么waitpid返回值是0,不予以等待,如果正常结束,返回该子进程的id。
0:表示非阻塞等待
获取子进程status
status是输出型参数,父进程最终拿到的status结果,和子进程如何退出是强相关的。(子进程有3中进程退出的情况,可以看上一篇博客)
那可以联系一个知识点,bash是命令行启动所有进程的父进程,bash用wait的方法得到子进程的退出结果,所以我们可以用echo $?查到子进程的退出码。
wait和waitpid,都有status参数,该参数是输出型参数,由OS填充。
如果传递NULL,表示不管子进程的退出状态信息。
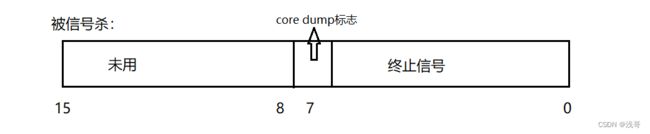
status是int类型,但是实际上,32个比特位只使用16个比特位(低16位)
exit code: (status>>8)&0xFF
signal code: status & 0x7F
不用位操作,可以使用宏来解决:
WIFEXITED(status)和WEXITSTATUS(status)
WIFEXITED(status):查看进程是否正常退出,正常退出-真
WEXITSTATUS(status):查看进程的退出码,WIFEXITED非零,提取子进程的退出码。
(非)阻塞等待
waitpid函数的第三个参数 options,0是默认行为,表示阻塞等待,WNOHANG表示非阻塞等待。
阻塞等待,表示一直干等着,等的时候什么事情都不干;非阻塞等待每隔一段时间等待,她没好,过几分钟再等待。(比如打电话这个例子)非阻塞等待可能需要多次检测,这是基于 非阻塞等待的轮循方案。
- 如果子进程已经退出,调用wait/waitpid会立即返回,并释放资源,获得子进程退出信息。
- 如果在任意是时刻都调用wait/waitpid,子进程存在且正常运行,进程可能阻塞。
- 如果不存在该子进程,则立即出错返回。
父进程在子进程退出后继续程序,如下图:
ALL IN ALL:
阻塞等待和非阻塞等待都是等待的方式,都是父进程等待子进程,等待子进程退出。
QUESTION1:
阻塞是不是意味着父进程不被调度执行了呢?
父进程等待的本质是,把父进程的PCB放进等待队列,进程状态从R变成S,在等待队列等待时,不被调度执行。
所以,
==阻塞的本质:==进程的PCB放进等待队列,并将进程的状态R改成S状态。
返回的本质:进程的PCB从等待队列放进运行队列,从而被CPU调用。
所以当我们看到某些应用或者操作系统本身,卡住了或者长时间不动,应用或者程序hang住了!
WNOHANG情况下,waitpid的返回值:
1、子进程没有退出,返回值=0
2、子进程退出,waitpid调用成功,返回>0,失败则返回-1 .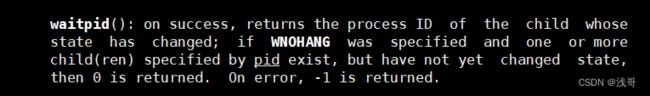
进程的非阻塞等待方式代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid < 0)
{
printf("%s fork error\n", __FUNCTION__);
return 1;
}
else if(pid == 0) { // child
printf("child is run, pid is: %d\n", getpid());
int cnt = 5;
while(cnt)
{
printf("child[%d] is running, cnt = %d\n", getpid(), cnt);
cnt--;
sleep(1);
}
exit(1);
} else {
// father
int status = 0;
pid_t ret = 0;
do {
ret = waitpid(-1, &status,WNOHANG); // 非阻塞式等待
if(ret == 0) {
// 子进程还没结束
printf("Do father things\n");
}
sleep(1);
}while(ret == 0);
if(WIFEXITED(status) &&ret == pid)
{
printf("wait child success, child return code is :%d\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));
}
else
{
printf("wait child failed, return.\n");
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
运行结果:
[zjy@VM-16-3-centos lessoncode]$ ./test
Do father things
child is run, pid is: 22362
child[22362] is running, cnt = 5
Do father things
child[22362] is running, cnt = 4
Do father things
child[22362] is running, cnt = 3
Do father things
child[22362] is running, cnt = 2
Do father things
child[22362] is running, cnt = 1
Do father things
wait child success, child return code is :1
进程的阻塞等待方式代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid < 0) {
printf("%s fork error\n", __FUNCTION__);
return 1;
}
else if(pid == 0) { // child
printf("child is run, pid is: %d\n", getpid());
int cnt = 5;
while(cnt)
{
printf("child[%d] is running, cnt = %d\n", getpid(), cnt);
cnt--;
sleep(1);
}
exit(1);
} else {
int status = 0;
pid_t ret = waitpid(-1, &status, 0); // 阻塞式等待
printf("wait test...\n");
if(WIFEXITED(status) && ret == pid)
{
printf("wait child success, child return code is :%d\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));
}
else {
printf("wait child failed, return.\n");
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
运行结果:
child is run, pid is: 25943
child[25943] is running, cnt = 5
child[25943] is running, cnt = 4
child[25943] is running, cnt = 3
child[25943] is running, cnt = 2
child[25943] is running, cnt = 1
wait test...
wait child success, child return code is :1