WebApplicationType分析
最近在研究Spring,先看一个简单的例子。
@SpringBootApplication
public class SampleWebServicesApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SampleWebServicesApplication.class, args);
}
}
SpringApplication源码
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
启动程序首先初始化了一个SpringApplication对象。来看一看在它的构造器了发生了什么。
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private Set<Class<?>> primarySources;
private WebApplicationType webApplicationType;
private Class<?> mainApplicationClass;
private List<ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers;
private List<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners;
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this(null, primarySources);
}
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
deduce英文翻译为:推断。
web环境检测:WebApplicationType分析
先来看SpringBoot支持那些Web类型:
ClassUtils.isPresent(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) 方法并不是简简单单看看classLoader之中有没有出现过传参的class。它的底层调用的是java.lang.Class#forName(java.lang.String, boolean, java.lang.ClassLoader)。这个方法会加载你指定的className到jvm,如果给回你要的class给你,常常在反射中使用。所以
public enum WebApplicationType {
/**
* 不启动内嵌的WebServer,不是运行web application
*/
NONE,
/**
* 启动内嵌的基于servlet的web server
*/
SERVLET,
/**
* 启动内嵌的reactive web server,这个application是一个reactive web application
*/
REACTIVE;
private static final String[] SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet",
"org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" };
private static final String WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet";
private static final String WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler";
private static final String JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer";
private static final String SERVLET_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext";
private static final String REACTIVE_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.ReactiveWebApplicationContext";
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
// 尝试加载org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler,如果成功并且加载org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet和org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer失败,则这个application是WebApplicationType.REACTIVE类型。
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
// 如果ClassLoader里面同时加载这两个 javax.servlet.Servlet和 org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext成功。则application是WebApplicationType.NONE 类型。
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
// application是 WebApplicationType.SERVLET 类型。
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
static WebApplicationType deduceFromApplicationContext(Class<?> applicationContextClass) {
if (isAssignable(SERVLET_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS, applicationContextClass)) {
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
if (isAssignable(REACTIVE_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS, applicationContextClass)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
//省略其他代码
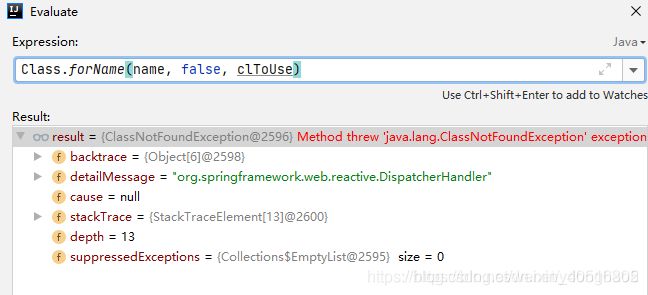
这个例子中,加载org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler抛出异常。
而org.springframework.util.ClassUtils#isPresent(String className, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) 的实现如下:
public static boolean isPresent(String className, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
try {
forName(className, classLoader);
return true;
}
catch (IllegalAccessError err) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Readability mismatch in inheritance hierarchy of class [" +
className + "]: " + err.getMessage(), err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Typically ClassNotFoundException or NoClassDefFoundError...
return false;
}
}
加载失败则return false,那么怎么加载失败呢?
这个deduceFromClasspath()方法中最重要的功能 是根据 java.lang.Class#forName(java.lang.String, boolean, java.lang.ClassLoader) 的加载class功能,而class加载是依赖jar包是否引起而判断的,所以如果引入了javax.servlet.Servlet的jar,则会启动Servlet模式,如果引入的jar是spring-boot-starter-webflux,而且没引入servlet相关的jar,则会启动Reactive模式。
这也是Spring Boot的设计思想:拔插而决定application的启动方式。
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「袁小黑」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/ydonghao2/article/details/106990239