【C语言14】C语言实现顺序表(这可能是CSDN有史以来讲解最详细的顺序表)
顺序表
-
- 什么是顺序表
- 顺序表的接口创建及使用
-
- 1.创建
- 2.初始化
- 3.扩容
- 4.尾插
- 5.打印
- 6.头插
- 7.尾删
- 8.头删
- 9.查找
- 10.删除任意位置
- 11.插入任意位置
- 12.修改
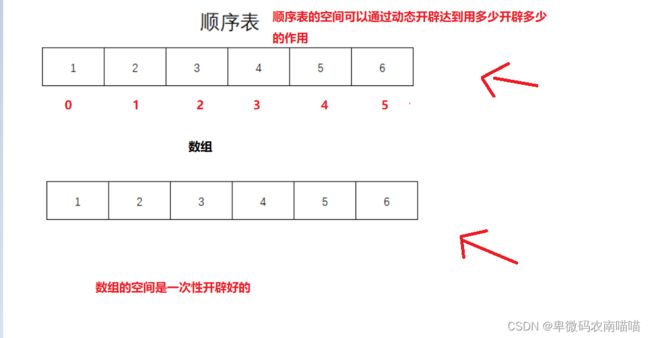
什么是顺序表
官方定义:顺序表是在计算机内存中以数组的形式保存的线性表,线性表的顺序存储是指用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表中的各个元素、使得线性表中在逻辑结构上相邻的数据元素存储在相邻的物理存储单元中,即通过数据元素物理存储的相邻关系来反映数据元素之间逻辑上的相邻关系,采用顺序存储结构的线性表通常称为顺序表。顺序表是将表中的结点依次存放在计算机内存中一组地址连续的存储单元中
**顺序表和数组同样是连续的空间
数组必须提前开辟好空间,而顺序表可以随开随用。
顺序表的接口创建及使用
1.创建
那我们就开始创建属于我们的顺序表吧! 我们首先创建3个文件,分别是Seqlist.h SeqList.c test.c
分别记录测试,函数的声明与使用
typedef int SLDataType;//这是我们自行定义的类型
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType * a;//指向动态开辟的内存
int sz;//记录使用的空间个数
int capacity;//记录空间总容量
}SL;
此时,我们就完成了顺序表的第一步
2.初始化
在tese.c 文件中,我们定义好测试函数及主函数,同时创建变量s1;
#include"SeqList.h"
void Tese()
{
SL s1;
SLInit(&s1);
}
int main()
{
Test();
return 0;
}
在SeqList.c 文件中,我们实现初始化函数功能
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;//a指向的空间为空
ps->sz = ps->capacity = 0;//容量与使用空间为空
}
3.扩容
当完成顺序表初始化函数后,我们要先创建扩容函数,因为我们的顺序表只完成了初始化,还没有进行开辟空间的操作。
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->capacity == ps->sz)//判断空间容量
{
//如果相等,判断是初次开辟还是进行扩容
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
//realloc在初次开辟时功能与mallocc相同
SLDataType* ptr = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a,sizeof(SLDataType) * newcapacity);
if (ptr == NULL)
{
perror("realloc");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = ptr;//赋值
ps->capacity = newcapacity;//更新空间容量
}
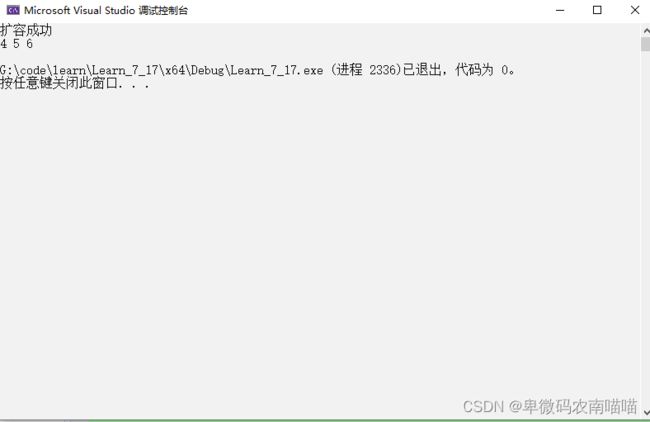
printf("扩容成功\n");
}
4.尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);//判断是否扩容
ps->a[ps->sz] = x;
ps->sz++;
}
5.打印
在我们插入数据后,我们可以通过调试来观察是否尾插成功,但是为了直观体验,我们编写一个打印函数来进行显示操作;
void SLprint(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a [i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
我们调用test.c文件进行验证,看各函数功能是否正常
#include"SeqList.h"
void Test()
{
SL s1;
SLInit(&s1);
SLPushBack(&s1, 1);
SLPushBack(&s1, 2);
SLPushBack(&s1, 3);
SLPushBack(&s1, 4);
SLprint(&s1);
}
int main()
{
Test();
return 0;
}
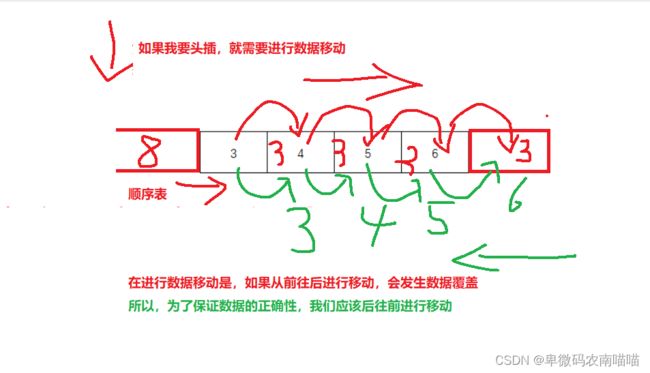
6.头插
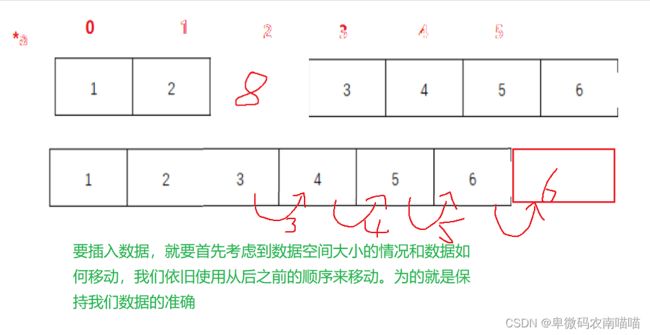
头插相较于尾插,需要考虑数据的移动,我们依旧画图进行分析
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int end = ps->sz - 1;
while (end >= 0)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
end--;
}
ps->a[0] = x;
ps->sz++;
}
tese.c调用
void Test()
{
SL s1;
SLInit(&s1);
SLPushBack(&s1, 3);
SLPushBack(&s1, 4);
SLPushBack(&s1, 5);
SLPushBack(&s1, 6);
SLPushFront(&s1, 8);
SLprint(&s1);
}
int main()
{
Test();
return 0;
}
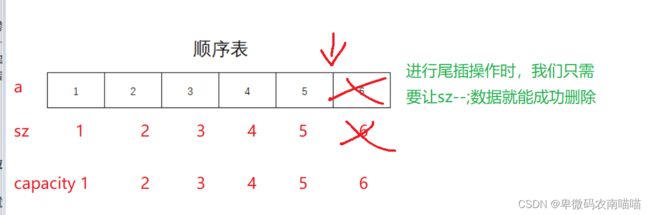
7.尾删
即删除最后一个元素,大部分人所想也许是把最后一个元素置为0或者-1,这是可行的,但如果最后一个数就是0呢?
其实我们这里只需要元素数量减去一个就好了,即size–,这样我们就无法访问最后一个元素了,它便是无效的数据。
void SLPopBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
ps->sz--;
}
8.头删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
int begin = 0;
while (begin < ps->sz)
{
ps->a[begin] = ps->a[begin + 1];
begin++;
}
ps->sz--;
}
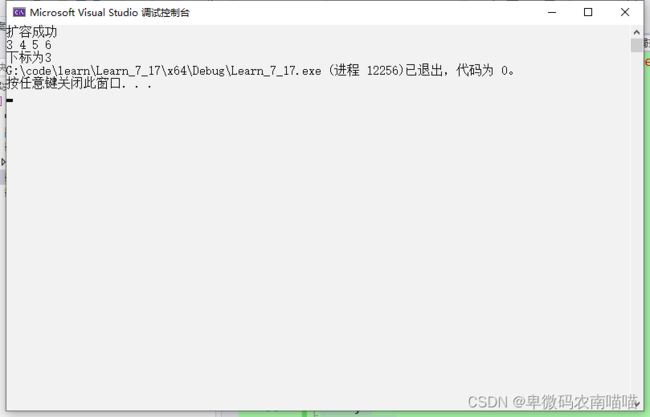
9.查找
对于查找接口,我们只需要遍历数据比较即可
太过简单,就不画图了
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i <=ps->sz; i++)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void Test()
{
SL s1;
SLInit(&s1);
SLPushBack(&s1, 3);
SLPushBack(&s1, 4);
SLPushBack(&s1, 5);
SLPushBack(&s1, 6);
int flang = SLFind(&s1,6);
SLprint(&s1);
if (flang == -1)
{
printf("找不到\n");
}
else
{
printf("下标为%d", flang );
}
}
int main()
{
Test();
return 0;
}
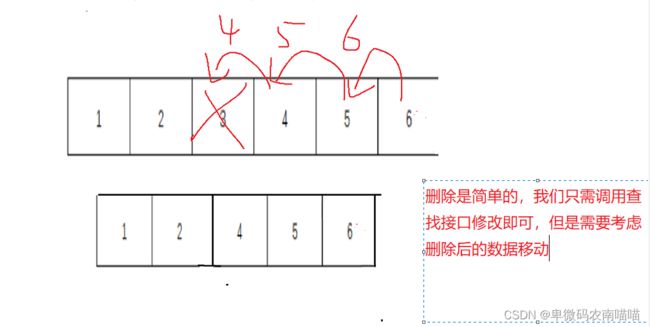
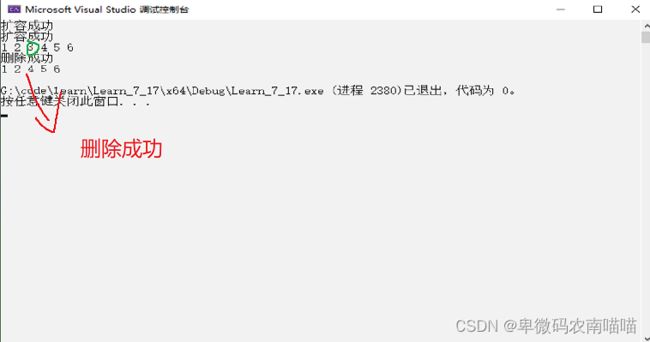
10.删除任意位置
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
int flang =SLFind(ps, pos);
if (flang == -1)
{
printf("无法删除,请确认数据\n");
}
else
{
while (flang < ps->sz)
{
ps->a[flang] = ps->a[flang+1];
flang++;
}
ps->sz--;
printf("删除成功\n");
}
}
void Test()
{
SL s1;
SLInit(&s1);
SLPushBack(&s1, 1);
SLPushBack(&s1, 2);
SLPushBack(&s1, 3);
SLPushBack(&s1, 4);
SLPushBack(&s1, 5);
SLPushBack(&s1, 6);
SLprint(&s1);
SLErase(&s1, 3);//删除3
SLprint(&s1);
}
int main()
{
Test();
return 0;
}
11.插入任意位置
void SLInster(SL* ps, SLDataType pos,SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
int flang = SLFind(ps, pos);
if (flang == -1)
{
printf("无法修改,请确认数据\n");
}
else
{
int end = ps->sz;
while (end>=flang)
{
ps->a[end+1] = ps->a[end];
end--;
}
ps->a[flang] = x;
ps->sz++;
printf("修改成功\n");
}
}
void Test()
{
SL s1;
SLInit(&s1);
SLPushBack(&s1, 1);
SLPushBack(&s1, 2);
SLPushBack(&s1, 3);
SLPushBack(&s1, 4);
SLPushBack(&s1, 5);
SLPushBack(&s1, 6);
SLprint(&s1);
SLInster(&s1, 2,8);
SLprint(&s1);
}
int main()
{
Test();
return 0;
}
12.修改
此时进入我们最后一个接口,当我们晚上上方所有接口后,修改接口对于我们异常简单。我们只限于要调用查找函数找到该数据的位置直接进行修改即可。
void SLModify(SL* ps, SLDataType pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
int flang = SLFind(ps, pos);
if (flang == -1)
{
printf("无法修改,请确认参数\n");
}
else
{
ps->a[flang] = x;
printf("修改成功\n");
}
}
此时,我们完成了所有接口实现;
完整代码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"SeqList.h"
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->sz = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->capacity == ps->sz)//判断空间容量
{
//如果相等,判断是初次开辟还是进行扩容
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
//realloc在初次开辟时功能与mallocc相同
SLDataType* ptr = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a,sizeof(SLDataType) * newcapacity);
if (ptr == NULL)
{
perror("realloc");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = ptr;//赋值
ps->capacity = newcapacity;//更新空间容量
printf("扩容成功\n");
}
}
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i <=ps->sz; i++)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void SLprint(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i <ps->sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);//判断是否扩容
ps->a[ps->sz] = x;
ps->sz++;
}
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int end = ps->sz - 1;
while (end >= 0)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
end--;
}
ps->a[0] = x;
ps->sz++;
}
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->sz--;
}
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
int begin = 0;
while (begin < ps->sz)
{
ps->a[begin] = ps->a[begin + 1];
begin++;
}
ps->sz--;
}
void SLErase(SL* ps, SLDataType pos)
{
assert(ps);
int flang =SLFind(ps, pos);
if (flang == -1)
{
printf("无法删除,请确认数据\n");
}
else
{
while (flang < ps->sz)
{
ps->a[flang] = ps->a[flang+1];
flang++;
}
ps->sz--;
printf("删除成功\n");
}
}
void SLInster(SL* ps, SLDataType pos,SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
int flang = SLFind(ps, pos);
if (flang == -1)
{
printf("无法修改,请确认数据\n");
}
else
{
int end = ps->sz;
while (end>=flang)
{
ps->a[end+1] = ps->a[end];
end--;
}
ps->a[flang] = x;
ps->sz++;
printf("修改成功\n");
}
}
void SLModify(SL* ps, SLDataType pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
int flang = SLFind(ps, pos);
if (flang == -1)
{
printf("无法修改,请确认参数\n");
}
else
{
ps->a[flang] = x;
printf("修改成功\n");l
}
}
如果这份博客对大家有帮助,希望各位给卑微南喵一个免费的点赞作为鼓励,谢谢大家!
制作不易,但如果能对大家有帮助,就是值得的 。欢迎评论区留言。