STM32 ws2812b多屏驱动程序
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、ws2812b的数据传输以及屏幕的组合
- 二、代码
-
- ws2812screen.c文件
- ws2812screen.h文件
- 主函数
前言
在上篇文章中使用了stm32的dma+tim的方式点亮了ws2812b的灯
但是我的需求不仅仅是点亮他,我需要他像屏幕一样显示某一些东西,ws2812显示有一个开源库AWTRIX
这个库需要使用上位机不是很符合我的需求。
所以自己写了一个屏幕的驱动,后续会不断在此基础上改进。
例如我使用的是一个5*5的小ws2812b的屏幕
但是我需要把多个屏幕组合起来。当点亮某个屏幕的时候不能总是一个个按照他的数据方向一个个数。所以我们就需要对每个灯珠进行重映射–也就是通过【x】【y】的方式来点亮屏幕。

2023/7/17 可以多块屏幕组合进行显示,可以设置数据流动方向
一、ws2812b的数据传输以及屏幕的组合
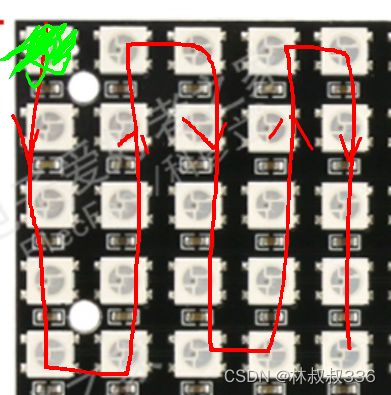
ws2812b的数据传输是有方向的以我买的屏幕为例.
绿色的是板子的第一个灯,按照这个数据流向。

再有多行板子的时候

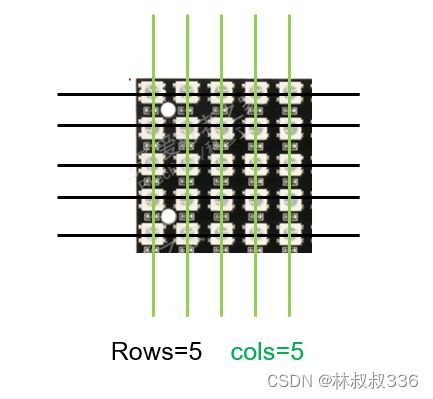
当弄清楚了数据的流向以后就需要明确板子的行列关系.
二、代码
ws2812screen.c文件
本代码段分别有initializeLedMapping(int boardRows, int boardCols, int rows, int cols)
其中的几个参数需要根据上面的自己填写。
void setLedColor(int x, int y, uint32_t colorValue) 是给点设置颜色的。设置完以后还要调用上篇文章的中
的void WS2812_Send (void)进行发送。
你还可以调用void drawDigit(int digit, int startX, int startY, uint32_t colorValueOn, uint32_t colorValueOff) 这个函数来显示阿拉伯数字
void drawColon(int x, int y, uint8_t on,uint32_t colorValueOn) 函数是显示冒号的,为后续做时钟做准备。
显示3x5的阿拉伯数字的二维布尔数组的定义
显示一个阿拉伯数字最少需要3*5的灯珠
#include "ws2812screen.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
int** ledMapping;
int totalBoards;
int ledsPerBoard; // LEDs per board
int rowsPerBoard; // Rows per board
int colsPerBoard; // Columns per board
///*
//int boardCount 几行小板子
//int boardCols 几列小板子
//int rows 小板子中灯的行数
//int cols 小板子中灯的列数
//*/
void initializeLedMapping(int boardRows, int boardCols, int rows, int cols)
{
totalBoards = boardRows*boardCols;
rowsPerBoard = rows;
colsPerBoard = cols;
ledsPerBoard = rows * cols; // Calculate total LEDs per board
// Allocate memory for the mapping table 为映射表分配内存
ledMapping = malloc(sizeof(int*) * totalBoards * colsPerBoard);
for(int i = 0; i < totalBoards; ++i)
{
for(int j = 0; j < colsPerBoard; ++j)
{
ledMapping[i*colsPerBoard+j] = malloc(sizeof(int) * rowsPerBoard * boardRows);
for(int m = 0; m < rowsPerBoard * boardRows; ++m)
{
int panelIdx = i / boardCols;
int panelLoc = i % boardCols;
int localRow = m / rows;
int localCol = m % rows;
//检查它是偶数列还是奇数列
if((panelLoc*colsPerBoard + j) % 2 == 0)
{
// 奇数 go from bottom to top
ledMapping[i*colsPerBoard+j][m] = (panelIdx * rowsPerBoard + localRow) * totalBoards * ledsPerBoard
+ panelLoc * ledsPerBoard + j * rows + localCol;
}
else
{
// 偶数 go from top to bottom
ledMapping[i*colsPerBoard+j][m] = (panelIdx * rowsPerBoard + localRow) * totalBoards * ledsPerBoard
+ panelLoc * ledsPerBoard + j * rows + rows - 1 - localCol;
}
}
}
}
}
//void initializeLedMapping(int boardCount, int rows, int cols)
//{
// totalBoards = boardCount;
// rowsPerBoard = rows;
// colsPerBoard = cols;
// ledsPerBoard = rows * cols; // Calculate total LEDs per board
//
// int panelIdx = i / 5; // 获取面板的索引
// int localX = i % 5; // 获取在面板内的x坐标
// // Allocate memory for the mapping table
// ledMapping = malloc(sizeof(int*) * totalBoards * colsPerBoard); // 5 columns per board
// for(int i = 0; i < totalBoards * colsPerBoard; ++i)
// {
// ledMapping[i] = malloc(sizeof(int) * rowsPerBoard); // 5 leds per column
// for(int j = 0; j < rowsPerBoard; ++j)
// {
// if((i % colsPerBoard) % 2 == 0)// 用于判断在当前面板内,LED的列号是奇数还是偶数
// {
// // 奇数列从下到上
// ledMapping[i][j] = (i / colsPerBoard * ledsPerBoard) + (i % colsPerBoard * rowsPerBoard) + j;
// }
// else
// {
// // 偶数列从上到下
// ledMapping[i][j] = (i / colsPerBoard * ledsPerBoard) + (i % colsPerBoard * rowsPerBoard) + (rowsPerBoard-1 - j);
// }
// }
// }
//}
//int** ledMapping;
//int totalBoards;
//int ledsPerBoard = 25; // 5*5
//void initializeLedMapping(int boardCount)
//{
int panelIdx = i / 5; // 获取面板的索引
int localX = i % 5; // 获取在面板内的x坐标
// totalBoards = boardCount;
// // Allocate memory for the mapping table
// ledMapping = malloc(sizeof(int*) * totalBoards * 5); // 5 columns per board
// for(int i = 0; i < totalBoards * 5; ++i)
// {
// ledMapping[i] = malloc(sizeof(int) * 5); // 5 leds per column
// for(int j = 0; j < 5; ++j)
// {
// if((i % 5) % 2 == 0)// 用于判断在当前面板内,LED的列号是奇数还是偶数
// {
// // 奇数列从下到上
// ledMapping[i][j] = (i / 5 * ledsPerBoard) + (i % 5 * 5) + j;
// }
// else
// {
// // 偶数列从上到下
// ledMapping[i][j] = (i / 5 * ledsPerBoard) + (i % 5 * 5) + (4 - j);
// }
// }
// }
//}
void setLedColor(int x, int y, uint32_t colorValue)
{
Set_LED_HEX(ledMapping[x][y], colorValue);
}
void cleanupLedMapping(void)
{
for(int i = 0; i < totalBoards * 5; ++i)
{
free(ledMapping[i]);
}
free(ledMapping);
}
/*
你可以用 initializeLedMapping() 来初始化你的映射表,
用 setLedColor() 来设置LED颜色,最后用 cleanupLedMapping() 来释放内存。
注意,这个版本的代码使用了动态内存分配,
所以你需要确保在不再需要映射表的时候调用 cleanupLedMapping() 来避免内存泄漏。
*/
uint8_t digits[10][5][3] = {
{{1, 1, 1}, {1, 0, 1}, {1, 0, 1}, {1, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 1}}, // 0
{{0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 0}}, // 1
{{1, 1, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 1}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 1, 1}}, // 2
{{1, 1, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 1}}, // 3
{{1, 0, 1}, {1, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}}, // 4
{{1, 1, 1}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 1, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 1}}, // 5
{{1, 1, 1}, {1, 0, 0}, {1, 1, 1}, {1, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 1}}, // 6
{{1, 1, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 1}}, // 7
{{1, 1, 1}, {1, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 1}, {1, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 1}}, // 8
{{1, 1, 1}, {1, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 1}, {0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 1}}, // 9
};
// 显示3x5的阿拉伯数字的二维布尔数组的定义
void drawDigit(int digit, int startX, int startY, uint32_t colorValueOn, uint32_t colorValueOff)
{
for(int y = 0; y < 5; y++)
{
for(int x = 0; x < 3; x++)
{
if(digits[digit][y][x])
{
setLedColor(startX + x, startY + y, colorValueOn);
}
else
{
setLedColor(startX + x, startY + y, colorValueOff);
}
}
}
}
void drawColon(int x, int y, uint8_t on,uint32_t colorValueOn)
{
// 冒号由两个点表示
setLedColor(x, y, on ? colorValueOn : 0x000000); // top dot
setLedColor(x, y + 2, on ? colorValueOn : 0x000000); // bottom dot
}
ws2812screen.h文件
#ifndef __WS2812_SCREEN_H
#define __WS2812_SCREEN_H
#include "main.h"
#include "ws2812b.h"
//void initializeLedMapping(int boardCount);
//void initializeLedMapping(int boardCount, int rows, int cols);
void initializeLedMapping(int boardRows, int boardCols, int rows, int cols);
void setLedColor(int x, int y, uint32_t colorValue);
void cleanupLedMapping(void);
void drawDigit(int digit, int startX, int startY, uint32_t colorValueOn, uint32_t colorValueOff);
void drawColon(int x, int y, uint8_t on,uint32_t colorValueOn) ;
#endif
主函数
initializeLedMapping(1,4,5,5);
drawDigit(1,0,0,0x0F000F,0x000000);
drawDigit(3,4,0,0x0F000F,0x000000);
drawColon(7, 1, 1,0x0F000F);
drawDigit(1,8,0,0x0F000F,0x000000);
drawDigit(4,12,0,0x0F000F,0x000000);
WS2812_Send();
/* USER CODE END 2 */
/* Infinite loop */
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
while (1)
{
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
drawColon(7, 1, 1,0x0F000F);
WS2812_Send();
HAL_Delay(1000);
drawColon(7, 1, 0,0x0F000F);
WS2812_Send();
HAL_Delay(1000);
}