MyBatis框架的基础用法
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、MyBatis是什么?
- 二、创建MyBatis项目
-
- 1.添加依赖
- 2.配置数据库信息
- 3.配置mybatis中的xml路径
- 三、增删查改
-
- 1.查询操作
-
- 根据id查询用户。
- 查询所有用户
- 2.添加操作
-
- 添加用户
- 添加并返回用户的自增id
- 3.修改操作
- 4.删除操作
- @Transactional
- 四、注意事项和常见操作
-
- 1.#和¥的差别
- 2.SQI注入问题
- 3.resultMap用法
- 4.模糊查询
- 5.多表联查
- 6.动态SQL
-
- (1)
标签 - (2)
标签 - (3)
标签 - (4)
、 标签 - (6)
- (1)
前言
前面学习了Spring、Spring Boot、Spring MVC一些优秀的后端程序开发框架,但是对于完整的后端开发来说,数据库是必不可少的,而今天学习的MyBatis是一款优秀的持久层框架,是更简单完成程序和数据库交互的工具,也是更简单的操作和读取数据库工具。
一、MyBatis是什么?
MyBatis是一款持久层框架,它支持自定义SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。可以通过简单的XML或注解来配置和映射原始类型、接口等。
二、创建MyBatis项目
1.添加依赖
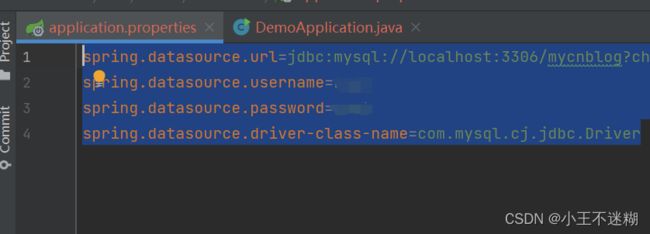
2.配置数据库信息
必须要连上数据库,程序才能运行起来,不报错。
3.配置mybatis中的xml路径
三、增删查改
1.查询操作
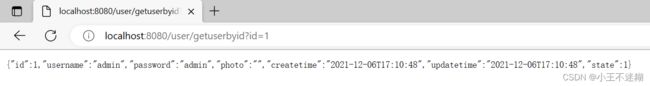
根据id查询用户。
(2)构建Mapper层的代码实现(接口+XML)
a.创建接口;

b.创建XML实现。
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
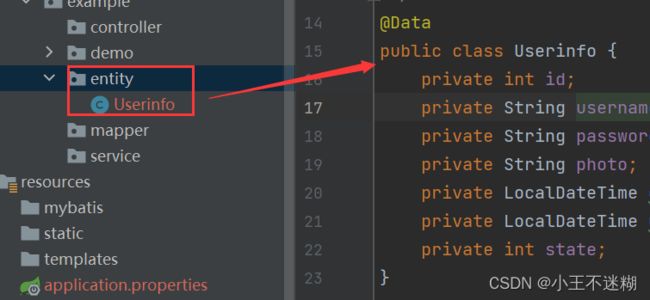
public Userinfo getUserById(Integer id) {
return userMapper.getUserById(id);
}
}
(4)实现控制器
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/get-user-id")
public Userinfo getUserById(Integer id) {
if (id == null) return null;
return userService.getUserById(id);
}
}
进行单元测试:
在mapper中直接快捷键(Alt+Insert)生成单元测试。

单元测试代码:
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
void getUserById() {
Userinfo userinfo = userMapper.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(userinfo);
}
查询所有用户
(1)xml中的配置。
<select id="getAll" resultType="com.example.demo.entity.Userinfo">
select * from userinfo
</select>
(2)测试。
//查询所有用户信息
@Test
void getAll() {
List<Userinfo> list = userMapper.getAll();
Assertions.assertEquals(3,list.size());
}
2.添加操作
添加用户
(1)在接口中声明方法。
//添加操作
int add(Userinfo userinfo);
(2)在xxx.xml中提供实现。
<insert id="add">
insert into userinfo(username,password,createtime,updatetime)
values(#{username},#{password},#{createtime},#{updatetime})
</insert>
(3)检测(单元测试)。
@Test
void add() {
//伪代码,构建一个对象
Userinfo userinfo = new Userinfo();
userinfo.setUsername("张三");
userinfo.setPassword("123");
userinfo.setCreatetime(LocalDateTime.now());
userinfo.setUpdatetime(LocalDateTime.now());
//执行添加操作
int result = userMapper.add(userinfo);
System.out.println(result);
Assertions.assertEquals(1,result);
}
添加并返回用户的自增id
useGeneratedKey,keyProperty:程序中实体类的属性,而非数据库的字段。
关键是xml中的实现。
<insert id="addGetId" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into userinfo(username,password,createtime,updatetime)
values(#{username},#{password},#{createtime},#{updatetime})
</insert>
3.修改操作
(1)修改接口。
//修改用户
int upUserName(Userinfo userinfo);
(2)xml配置。
<update id="upUserName">
update userinfo set username=#{username} where id=#{id}
</update>
(3)测试。
在 @Test
void upUserName() {
Userinfo userinfo = new Userinfo();
userinfo.setId(5);
userinfo.setUsername("陈尔尔");
int result = userMapper.upUserName(userinfo);
System.out.println(result);
}
4.删除操作
(1)接口。
//删除根据Id
int delById(@Param("id") Integer id);
(2)xml配置。
<delete id="delById">
delete from userinfo where id=#{id}
</delete>
(3)测试。
@Test
void delById() {
Integer id = 6;
int result = userMapper.delById(id);
System.out.println(result);
}
@Transactional
测试但是不对数据库中的值做出真的修改。
四、注意事项和常见操作
1.#和¥的差别
#{}:预编译处理。
¥{}:字符直接替换。
直接替换,可能会带来越权查询和操作数据库。但有一些方面是需要的,使用¥{sort}实现排序,模糊查询等一些需要直接注入的情景。
<select id="getUserByDesc" resultType="com.example.demo.entity.Userinfo">
select * from userinfo order by id ${order}
</select>
区别:
(1)¥存在SQL注入的问题,而#不存在;
(2)¥直接替换,#是预处理。
2.SQI注入问题
SQL注入可以利用修改SQL语句查询到数据库信息,例如where 后的条件(1=1)只要是true就可以查询到数据库信息。
3.resultMap用法
使用场景:实现程序中属性和表中字段映射的功能(当程序中的属性和表中的字段不一致时,可以强行映射到一起)。
<resultMap id="baseMap" type="com.example.demo.entity.Userinfo">
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<result column="username" property="username"></result>
<result column="password" property="password"></result>
<result column="photo" property="photo"></result>
<result column="createtime" property="createtime"></result>
<result column="updatetime" property="updatetime"></result>
<result column="state" property="state"></result>
</resultMap>
当程序中的属性和数据库中的字段名不一致时的解决方案:
(1)使用resultMap标签(在mapper.xml中定义);
(2)使用数据库别名as重命名。
4.模糊查询
最主要的是配置xml。
其中SQL的写法有两种方式。
<select id="findUserByName" resultType="com.example.demo.entity.Userinfo">
<!-- 模糊查询有两种写法 -->
<!-- select * from userinfo where username like '%${username}%'-->
select * from userinfo where username like concat('%',#{username},'%')
</select>
5.多表联查
(1)一对一
id为1的用户文章信息和用户名。
<select id="getArticleById" resultType="com.example.demo.entity.vo.ArticleinfoVO">
select a.*,u.username from articleinfo as a left join userinfo as u on a.id = u.id where a.id=#{id}
</select>
(2)一对多。
id为1的用户的所有文章。
<select id="getArticleById" resultType="com.example.demo.entity.vo.Articleinfo">
select * from articleinfo where id=#{id}
</select>
最终的一个实现:联表查询语句(left join/inner join)+ XXXVO
6.动态SQL
(1)标签
<!-- 使用if标签添加 -->
<insert id="add2">
insert into userinfo(username,
<if test="photo!=null">
photo,
</if>
password)
values(#{username},
<if test="photo!=null">
#{photo},
</if>
#{password})
</insert>
(2)标签
prefix:最前面的固定值;
suffix:最后的固定值;
suffixOverrides:最后要覆盖的值。
<!-- 使用if trim标签添加 -->
<insert id="add2">
insert into userinfo
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="username!=null">
username,
</if>
<if test="password!=null">
password,
</if>
<if test="photo!=null">
photo
</if>
</trim>
<trim prefix="values(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="username!=null">
#{username},
</if>
<if test="password!=null">
#{password},
</if>
<if test="photo!=null">
#{photo}
</if>
</trim>
</insert>
(3)标签
特征:
1.where标签通常要配合if标签一起使用;
2.where标签会删除最前面的and关键字(注意不会删除最后面);
3.where标签中如果没有内容,那么它也不会生成where sql 关键字。
<!-- <where>标签 -->
<select id="getListByParam" resultType="com.example.demo.entity.Userinfo">
select * from userinfo
<where>
<if test="username!=null">
username=#{username}
</if>
<if test="password!=null">
and password=#{password}
</if>
</where>
</select>
(4)、标签
<update id="setById">
update userinfo
<set>
<if test="username!=null">
username=#{username}
</if>
</set>
<where>
<if test="id!=null">
id=#{id}
</if>
</where>
(6)
collection为设置的集合。(需要删除的数据)
open为开始。
close为结束。
item为集合中的数据。
separator为集合中数据的分隔符。
<!-- <foreach>标签 -->
<delete id="dels">
delete from userinfo where id in
<foreach collection="ids" open="(" close=")" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</delete>