数据结构--栈和队列详解
栈和队列
- 1. 栈
-
- 1.1 栈的基本概念
- 1.2 栈的基本操作
- 1.3 栈的顺序存储结构(顺序栈)
-
- 1.3.1 push ()
- 1.3.2 pop ()
- 1.3.3 peek ()
- 1.3.4 isEmpty ()、isFull ()、size ()
- 完整代码
- 1.4 栈的链式结构(链栈)
-
- 完整代码
- 2.队列
-
- 2.1队列的基本概念
- 2.2 队列的基本操作
- 2.3 队列的顺序结构(顺序队列)
-
- 2.3.1 offer ()
- 2.3.2 poll ()
- 2.3.3 peek ()
- 2.3.4 isEmpty ()、isFull ()、size ()
- 完整代码
- 2.4 队列的链式结构(链式队列)
-
- 完整代码
1. 栈
1.1 栈的基本概念
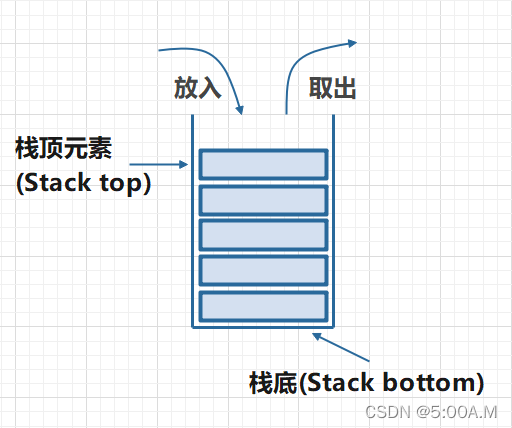
栈(Stack):是一种按照先进后出(FILO)、后进先出(LIFO)模式的容器结构。准确的讲,其实并不一定是线性结构,只是一般线性结构实现最简单,所以大多数以线性结构来实现
栈顶(Top):允许进行插入删除的那一端
栈底(Bottom):最底部,不允许进行插入和删除的另一端
空栈 :没有任何元素的栈
1.2 栈的基本操作
| 方法 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| push() | 入栈操作,若栈未满则使 val 成为新的栈顶 |
| pop() | 出栈操作,将栈顶元素取出并返回该栈顶元素 |
| peek() | 查看栈顶元素,返回栈顶元素但不删除 |
| size() | 返回该栈的长度 |
| isEmpty() | 判断栈是否为空 |
1.3 栈的顺序存储结构(顺序栈)
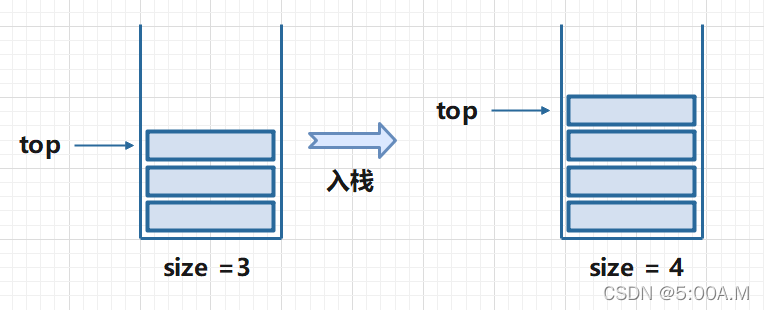
用连续的一片存储空间来存储数据元素,这样的栈称为顺序栈。类似于顺序表,用一维数组来存放顺序栈中的数据元素。
设置一个指示器 top 始终指向栈顶位置,top随着插入或删除而变化,top 的值必须小于栈的长度 size ,通常当栈为空时,to = -1

1.3.1 push ()
首先判断栈是否已满(前提默认入栈元素不能为 null),若不满进行入栈操作,若栈满证明 top == size - 1 ,则抛出异常
//入栈
public void push(T val) {
if (!isFull()) {
top++;
arr[top] = val;
return;
}
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("栈已满! top:" + top + " size:" + size);
}
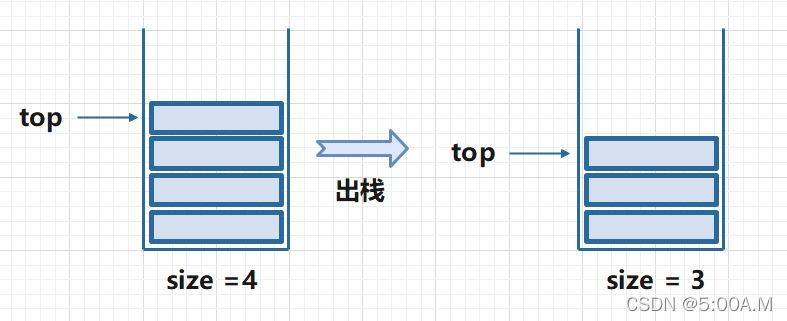
1.3.2 pop ()
首先判断栈是否为空,若栈空则返回 null,若栈不为空就返回 top 位置的元素,并置空该位置,top–
//出栈
public T pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
T result = (T) arr[top];
arr[top] = null;
top--;
return result;
}
1.3.3 peek ()
首先判断栈是否为空,若为空就返回 null,否则返回 top 位置的元素
//查看栈顶元素
public T peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
T result = (T) arr[top];
return result;
}
1.3.4 isEmpty ()、isFull ()、size ()
判断栈空条件:top == -1
判断栈满条件:top == size - 1
获取栈的长度:top + 1
//判断栈是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
//判断栈是否满溢
public boolean isFull() {
return top == size - 1;
}
//获取栈的长度
public int size() {
return top + 1;
}
完整代码
public class myStack<T> {
//栈的长度
public int size;
//栈数组
public Object[] arr;
//栈顶指示器
public int top;
//默认构造方法
public myStack() {
size = 10;
arr = new Object[size];
top = -1;
}
//出栈
public T pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
T result = (T) arr[top];
arr[top] = null;
top--;
return result;
}
//入栈
public void push(T val) {
if (!isFull()) {
top++;
arr[top] = val;
return;
}
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("栈已满! top:" + top + " size:" + size);
}
//查看栈顶元素
public T peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
T result = (T) arr[top];
return result;
}
//获取栈的长度
public int size() {
return top + 1;
}
//判断栈满
public boolean isFull() {
return top == size - 1;
}
//判断栈空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
}
1.4 栈的链式结构(链栈)
使用链式存储结构存储的栈称为链栈,链栈通常用单链表来表示,它的结点结构与单链表的结构一样,都是由 val 和 next 两部分组成。我们将栈顶设在链表的头部,即将栈顶指示器指向链表的头部,所有对栈的数据元素的增加和删除操作都在链表头部进行



完整代码
public class LinkedStack<T> {
//定义内部类,用来存放结点数据
class Node {
public T val;
public Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(T val, Node next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
//栈顶指示器
public Node top;
//栈的长度
public int size;
//默认构造方法
public LinkedStack() {
top = null;
size = 0;
}
//出栈
public T pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
T node = top.val;
top = top.next;
size--;
return node;
}
//入栈
public void push(T node) {
Node newNode = new Node(node, null);
if (!isEmpty()) {
newNode.next = top;
}
top = newNode;
size++;
}
//查看栈顶元素
public T peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return top.val;
}
//获取栈的长度
public int size() {
return size;
}
//判断栈空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == null && size == 0;
}
}
2.队列
2.1队列的基本概念
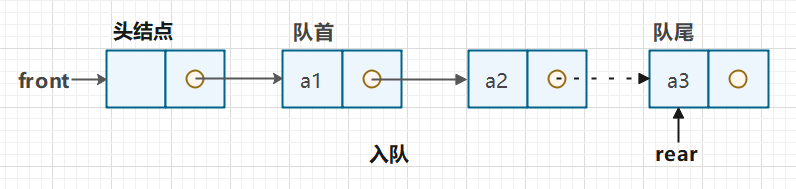
队列: 队列是一种线性表,是一种先进先出(FIFO)的线性结构。队列只允许在表的一端进行插入、删除操作。允许插入的一端称为队尾,允许删除的一端称为队头

队头(Front):允许删除的一端,又叫队首
队尾(Rear):允许插入的一端
空队列:没有任何元素的空队列
2.2 队列的基本操作
| 方法 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| poll() | 出队列操作,并返回值 |
| peek() | 查看队首元素 |
| offer() | 入队列操作 |
| size() | 返回该栈的长度 |
| isEmpty() | 判断栈是否为空 |
2.3 队列的顺序结构(顺序队列)
2.3.1 offer ()
//插入元素
public void offer(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("满队列,不能添加元素" + value);
} else {
arr[rear++] = value;
}
}
2.3.2 poll ()
//取出元素
public T poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("该队列为空,不能取出");
} else {
return (T) arr[front++];
}
}
2.3.3 peek ()
//查看队首元素
public T peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("该队列为空");
} else {
return (T) arr[front];
}
}
2.3.4 isEmpty ()、isFull ()、size ()
//判断队列是否空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
}
//判断队列是否满
public boolean isFull() {
return rear == size;
}
//返回队列长度
public int size(){
return rear - front;
}
完整代码
public class ArrayQueue<T> {
public int size; //队列长度
public int front; //队首指示器
public int rear; //队尾指示器
public Object[] arr; //队列数组
public ArrayQueue() { //默认构造方法
size = 10;
front = 0;
rear = 0;
arr = new Object[size];
}
//插入元素
public void offer(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("满队列,不能添加元素" + value);
} else {
arr[rear++] = value;
}
}
//取出元素
public T poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("该队列为空,不能取出");
} else {
return (T) arr[front++];
}
}
//查看队首元素
public T peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("该队列为空");
} else {
return (T) arr[front];
}
}
//判断队列是否空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
}
//判断队列是否满
public boolean isFull() {
return rear == size;
}
//返回队列长度
public int size(){
return rear - front;
}
}
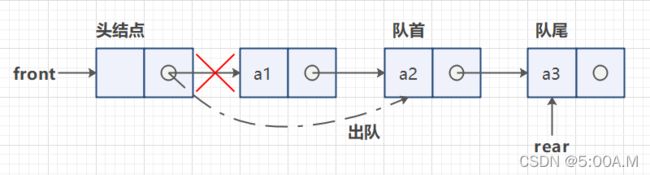
2.4 队列的链式结构(链式队列)
队列的链式存储结构其实和栈都是相似的,都在其内部定义一个内部类 Node,用于存储每个元素的结点属性,它也必循有 next ,用于指向下一个元素结点,并且它有队头和队尾指示器front 和 rear
它的入队是从队尾插入,而出队是从对头删除

空队列时,front 和 real 都指向头结点
完整代码
public class LinkedQueue<T> {
class Node { //内部类 Node,存放节点信息
public T val;
public Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(T val) {
this.val = val;
}
public Node(T val, Node next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
public Node front; //队首指示器
public Node rear; //队尾指示器
public int size; //队列长度
public LinkedQueue() { //默认构造方法
front = null;
rear = null;
}
//入队操作
public void offer(T item) {
Node newNode = new Node(item);
if (isEmpty()) {
front = newNode;
} else {
rear.next = newNode;
}
rear = newNode;
size++;
}
//出队操作
public T poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
Node node = front;
front = front.next;
if (front == null) {
rear = null;
}
size--;
return node.val;
}
//查看队首元素
public T peek() {
if (!isEmpty()) {
return front.val;
} else
return null;
}
// 判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
if ((front == rear) && (size == 0)) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
//获取队列长度
public int size() {
return size;
}
}