Mysql高阶语句与MySQL存储过程
文章目录
- Mysql高阶语句
-
- 一、MySQL高阶进阶SQL语句
-
- 1、select
- 2、distinct
- 3、where
- 4、and or
- 5、in
- 6、between
- 7、通配符
- 8、order by
- 9、函数
- 12、别名
- 13、子查询
- 14、EXISTS
- 二、MySQL高阶进阶SQL语句2
-
- 1、连接查询
- 2、create view 视图
- 3、union联集
- 4、交集值
- 5、无交集值
- 6、case
- 7、空值(NULL) 和 无值(‘’) 的区别
- MySQL存储过程
-
- 存储过程的概念
- 存储过程的优点
- 创建存储过程
- 创建存储过程
- 存储过程的参数
- 删除存储过程
- 存储过程的控制语句
Mysql高阶语句
准备环境
mysql -uroot -p
create database kgc;
use kgc;
create table location(region varchar(10),store_name char(20)); # 表一结构
create table store_info(storm_name char(20),sales int(10),date char(15)); #表二结构
# 表一数据内容
insert into location values ('East','Bostion');
insert into location values ('East','New York');
insert into location values ('West','Los Angeles');
insert into location values ('West','Houstion');
# 表二数据内容
insert into store_info values('Los Angeles',1500,'2023-01-30');
insert into store_info values('Los Angeles',300,'2023-01-30');
insert into store_info values('Houstion',200,'2023-01-30');
insert into store_info values('Bostion',700,'2023-01-30');
select * from region;
select * from fare;
一、MySQL高阶进阶SQL语句
1、select
显示表格中一个或数个字段的所有资料
语法:select 字段 from 表名
select region from store_info;
2、distinct
不显示重复的数据记录
语法:select distinct ‘字段’ from ‘表名’;
select distinct storm_name from store_info ;
3、where
有条件查询
语法:select “字段” from"表名" where ‘条件’;
select storm_name from store_info where sales > 1000;
4、and or
==**且 ,或
语法:select “字段” from “表名” where “条件1” {[and|or] “条件2”}+ ;
select sales from store_info where sales > 500 and sales < 1000;
select sales from store_info where sales > 500 or sales < 1000;
5、in
显示已知的值的数据记录
语法:select “字段” from “表名” where “字段” in (‘值1’, ‘值2’, …);
select * from store_info where storm_name in (‘Los Angeles’,‘Houston’);
6、between
显示两个值范围内的数据记录
语法:select “字段” from “表名” where “字段” between ‘值1’ and ‘值2’;
select * from store_info where date between ‘2020-12-05’ and ‘2020-12-10’;
7、通配符
通常通配符都是跟 LIKE 一起使用的
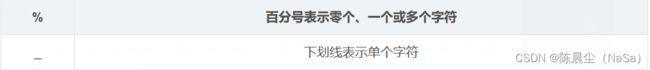

like:用于匹配模式来查找资料
语法:select “字段” from “表名” where “字段” like{模式};
select * from store_info where storm_name like ‘Los%’;
select storm_name from store_info where storm_name like ‘Los%’;
8、order by
按关键字排序
语法:select “字段” from “表名” [where “条件”] order by “字段”[ASC, DESC];
select sales,date,storm_name from store_info order by sales desc;
9、函数
select abs(-1), rand(), mod(5,3), power(2,3), round(1.89);
select round(1.8937,3), truncate(1.235,2), ceil(5.2), floor(2.1), least(1.89,3,6.1,2.1);
- by后面的栏位的查询结果进行汇总分组,通常是结合聚合函数一起使用的
- group by 有一个原则,就是 select 后面的所有列中,没有使用聚合函数的列,必须出现在group by后面。
语法:select 字段1,sum(字段2) from表名 group by 字段1;
select store_name,sum(sales) from store_info select 字段1,wum(字段2) from 表名 group by 字段1;
11、having
- 用来过滤由group by语句返回的记录集,通常与group by语句联合使用。
- having语句的存在弥补了where关键字不能与聚合函数联合使用的不足。如果被select的只有函数栏,那就不需要group by子句。
语法:select 字段1,sum(字段2) from 表名 group by 字段1 having(函数条件);
select site,count(money),sum(money),date from from group by site having sum(money) >=700;
12、别名
字段别名、表格别名
select location.store_name from location,store_info where location.store_name = store_info.store_name;
13、子查询
连接表格,在WHERE 子句或HAVING 子句中插入另一个SQL 语句
SELECT 字段1 FROM 表格1 WHERE 字段2 [比较运算符] #外查询
(SELECT 字段1 FROM 表格2 WHERE 条件) #内查询
- 可以是符号的运算符
例:=、>、<、>=、<= - 也可以是文字的运算符
例:LIKE、IN、BETWEEN
select A.site,region from REGION AS A where A.site in
(select B.site from FARE AS B where money<2000);
select B.site,money,date from FARE AS B where site in
(select A.site from REGION AS A where region = 'north');
14、EXISTS
- 用来测试内查询有没有产生任何结果,类似布尔值是否为真
- 如果有的话,系统就会执行外查询中的SQL语句,若是没有,那整个SQL语句就不会产生任何结果。
语法:
SELECT 字段1 FROM 表1 WHERE EXISTS (SELECT * FROM 表2 WHERE 条件);
例:
select region from REGION where exists (select * from FARE where money = '700');
二、MySQL高阶进阶SQL语句2
环境准备
use kgc;
create table location (Region char(20),Store_Name char(20));
insert into location values('East','Boston');
insert into location values('East','New York');
insert into location values('West','Los Angeles');
insert into location values('West','Houston');
create table store_info (Store_Name char(20),Sales int(10),Date char(10));
insert into store_info values('Los Angeles','1500','2020-12-05');
insert into store_info values('Houston','250','2020-12-07');
insert into store_info values('Los Angeles','300','2020-12-08');
insert into store_info values('Boston','700','2020-12-08');
select * from location;
select * from store_Info
1、连接查询
- 内连接 inner join: 只返回两个表中联结字段相等的行
- 左连接 left join:返回包括左表中的所有记录和右表中联结字段相等的记录
- 右连接 right join :返回包括右表中的所有记录和左表中联结字段相等的记录
内连接1 inner join
语法:select 字段 from 表名1 表别名1 inner join 表名2 表别名2 on 表别名1.联结字段 = 表别名2.联结字段;
例:
select * from location A inner join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name ;
== 内连接2 inner join(using)函数
语法:select 字段 from 表名1 inner join 表名2 using(联结字段);
例:
select * from location inner join store_info using(store_name}; #必须保证要查询的交集字符字段名一样才可以
左连接 left join
语法:select 字段 from 表1 表别名1 left join 表2 表别名2 on 表别名1.联结字段1 = B.联结字段2 ;
例:
select * from location A left join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name ;
右连接 right join
语法:select 字段 from 表1 表别名1 right join 表2 表别名2 on 表别名1.联结字段1 = 表别名2.联结字段2;
例:
select * from location A right join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name ;
多表查询
语法:
select 字段 from 表1,表2 where 表1.联结字段 = 表2.联结字段;
2、create view 视图
视图,可以被当作是虚拟表或存储查询
- 视图跟表格的不同是,表格中有实际储存数据记录,而视图是建立在表格之上的一个架构,它本身并不实际储存数据记录。
- 临时表在用户退出或同数据库的连接断开后就自动消失了,而视图不会消失。
- 视图不含有数据,只存储它的定义,它的用途一般可以简化复杂的查询。比如你要对几个表进行连接查询,而且还要进行统计排序等操作,写SQL语句会很麻烦的,用视图将几个表联结起来,然后对这个视图进行查询操作,就和对一个表查询一样,很方便。
语法:create view "视图表名" AS "select 语句";
例子
create view v_aa AS select A.region region sum (B.sales) sales from location A inner join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name group by region;
3、union联集
将两个SQL语句的结果合并起来,两个SQL语句产生的字段需要是同样的资料种类
- UNION:生成结果的资料值将没有重复,且按照字段的顺序进行排序。
语法:
select 语句1 union select 语句2;
- union all:将生成结果的资料值都列出来,无论有无重复
语法:select 语句1 union all select 语句2;
4、交集值
取两个SQL语句结果的交集
- 右连接查询交集字符
5、无交集值
显示第一个SQL语句的结果,且与第二个SQL语句没有交集的结果,还不能重复
6、case
是 SQL 用来做为 if-then-else之类逻辑的关键字
语法:
select case("字段名")
--> when "条件1" then "结果1"
--> when "条件2" then "结果2"
...
[lese "结果N"]
END
FROM "表名";
# "条件" 可以是一个数值或是公式。 ELSE 子句则并不是必须的。
例子:
select store_name, case store_name
when 'Los Angeles' then sales * 2
when 'Boston' then 2000
else sales end "New sales",date from store_Info;
#"New sales" 是用于 case那个字段的字段名。
7、空值(NULL) 和 无值(‘’) 的区别
- 无值的长度为 0,不占用空间的;而 NULL 值的长度是 NULL,是占用空间的。
- IS NULL 或者 IS NOT NULL,是用来判断字段是不是为 NULL 或者不是 NULL,不能查出是不是无值的。
- 无值的判断使用='‘或者<>’'来处理。<> 代表不等于; !=也代表不等于。
- 在通过 count()指定字段统计有多少行数时,如果遇到 NULL 值会自动忽略掉,遇到无值会加入到记录中进行计算。
(1)使用length函数查看字符的长度
- null长度就为null
- 字符1234的长度就为4
- 空值的长度为0
select length(null), length(‘1234’), length(‘’);
(2)查看表里面字符为null的行和不为null的行
语法:
select 字段 from 表名 where 字段 is null;
select 字段 from 表名 where 字段 is not null;
例:
select * from cs where name is null;
select * from cs where name is not null;
(3)查看空值的行和不为空值的行
语法:
select 字段 from 表名 where 字段 = '';
select 字段 from 表名 where 字段 != '';
select 字段 from 表名 where 字段 <> '';
例:
select * from cs where name = '';
select * from cs where name <> '';
select * from cs where name != '';
(4)统计所有的行数和忽略为null值的行
语法:
select count(*) from 表名;
select count(name) from 表名;
例子
select count(*) from cs;
select count(name) from cs;
语法:
select "字段" from "表名" where "字段" regexp {模式};
(1)匹配以es结尾的字符串的字段
select * from store_info where store_name regexp ‘es$’;
(2)匹配字符串里包含to的字段
select * from store_info where store_name regexp ‘to’;
(3)匹配字符串以A-G开头的字段
select * from store_info where store_name regexp ’ ^ [A-G] ’ ;
(4)匹配字符串以 HO | Bo 开头的字段
select * from store_info where store_name regexp ‘Ho|Bo’;
MySQL存储过程
存储过程的概念
- 存储过程是一组为了完成特定功能的SQL语句集合。
- 存储过程在使用过程中是将常用或者复杂的工作预先使用SQL语句写好并用一个指定的名称存储起来,这个过程经编译和优化后存储在数据库服务器中。当需要使用该存储过程时,只需要调用它即可。存储过程在执行上比传统SQL速度更快、执行效率更高。
存储过程的优点
- 执行一次后,会将生成的二进制代码驻留缓冲区,提高执行效率
- SQL语句加上控制语句的集合,灵活性高
- 在服务器端存储,客户端调用时,降低网络负载
- 可多次重复被调用,可随时修改,不影响客户端调用
- 可完成所有的数据库操作,也可控制数据库的信息访问权限
创建存储过程
- 执行一次后,会将生成的二进制代码驻留缓冲区,提高执行效率
- SQL语句加上控制语句的集合,灵活性高
- 在服务器端存储,客户端调用时,降低网络负载
- 可多次重复被调用,可随时修改,不影响客户端调用
- 可完成所有的数据库操作,也可控制数据库的信息访问权限
创建存储过程
语法:
delimiter $$ #将语句的结束符号从分号;临时改为两个$$(可以是自定义)
create procedure cs() #创建存储过程,过程名为Proc,不带参数
-> begin #过程体以关键字 begin开始
-> select * from store_info; #过程体语句
-> end $$ #过程体以关键字 end 结束
delimiter ; #将语句的结束符号恢复为分号
##调用存储过程##
call cs;
存储过程的参数
- IN 输入参数:表示调用者向过程传入值(传入值可以是字面量或变量)
- OUT 输出参数:表示过程向调用者传出值(可以返回多个值)(传出值只能是变量)
- INOUT 输入输出参数:既表示调用者向过程传入值,又表示过程向调用者传出值(值只能是变量)
删除存储过程
- 存储过程内容的修改方法是通过删除原有存储过程,之后再以相同的名称创建新的存储过程。如果要修改存储过程的名称,可以先删除原存储过程,再以不同的命名创建新的存储过程。
语法:
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS Proc; #仅当存在时删除,不添加 IF EXISTS 时,如果指定的过程不存在,则产生一个错误
存储过程的控制语句
- if
- while
(2)循环语句while ···· end while
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE proc3()
-> begin
-> declare var int(10);
-> set var=0;
-> while var<6 do
-> insert into t values(var);
-> set var=var+1;
-> end while;
-> end $$
DELIMITER ;
CALL Proc3;












