Python 操作Mysql(PyMysql)
Python 操作 Mysql 常用方式:
- PyMysql:纯 Python 语言编写的 Mysql 操作客户端,安装方便,支持 Python3。
- SQLAlchemy:是一个非常强大的 ORM 框架,不提供底层的数据库操作,主要是通过定义模型对应数据表结构,在 Python Web 编程领域应用广泛。
在实际项目中,如果仅仅是简单的爬虫或者自动化,建议使用 PyMysql;否则建议使用 SQLAlchemy,它更强大方便。
下面使用 PyMySQL 连接 Mysql数据库,并实现简单的增删改查。
一、PyMySQL操作
PyMySQL 是在 Python3.x 版本中用于连接 MySQL 服务器的一个库。
1、PyMySQL 安装
检查是否安装PyMySQL:
pip list
如果未安装,使用 pip命令安装 PyMySQL。
pip install PyMySQL #安装最新版本
还需要安装一下 cryptography包:
pip install cryptography
因为 python连接数据库是的加密方式需要 cryptography包。如果你不安装cryptography,python连接数据库会报错“:RuntimeError: ‘cryptography’ package is required for sha256_password or caching_sha2_password auth methods。该错误提示的意思是:sha256_password和caching_sha2_password两种加密方式需要cryptography。
2、数据库连接
连接 Mysql数据库之前,我们创建一个 py_db数据库。
数据库连接:使用 pymysql 中的 connect() 方法,传入数据库的 HOST 地址、端口号、用户名、密码、待操作数据库的名称,即可以获取数据库的连接对象。
import pymysql
# 获取数据库连接
dbConn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',
port=3306,
user='root',
password='***',
database='py_db',
# charset='utf8',
cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# 使用 cursor() 方法创建一个游标对象 cursor
cursor = dbConn.cursor()
print(cursor) # 2.1 游标
- 获取游标:通过连接对象使用 cursor()方法来获取游标对象
- 释放游标:通过连接对象使用 close()方法来释放游标对象。
我们可以通过游标对象来操作增删改查等。
注意:操作完毕之后,我们需要将游标对象和数据库连接对象资源释放掉。
3、创建表
创建数据库表:可以使用 execute()方法来为数据库创建表。
注意:execute()方法可以执行标准的SQL语句,比如:创建表,插入,修改,删除等操作。
import pymysql
# 获取数据库连接
dbConn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',
port=3306,
user='root',
password='123456',
database='py_db',
# charset='utf8',
cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# 使用 cursor() 方法创建一个游标对象 cursor
cursor = dbConn.cursor()
create_table_sql = "CREATE TABLE `t_user` ( \
`id` bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,\
`user_name` varchar(145) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci NOT NULL,\
`pazzword` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL,\
`sex` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL,\
`age` int DEFAULT NULL,\
`birthday` date DEFAULT NULL,\
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)\
) ENGINE=InnoDB"
# 使用 execute() 方法执行 SQL
res = cursor.execute(create_table_sql)
print(res) # 0
# 释放资源
cursor.close()
dbConn.close()
4、插入操作
Python执行SQL语句常用方法:
- execute()方法:执行 一条SQL语句。
- executemany()方法:传入插入的 SQL 语句及位置变量列表,可以实现一次插入多条数据。
- commit()方法:提交事务,将数据提交到数据库中。
- rowcount:这是一个只读属性,并返回执行execute()方法后影响的行数。
4.1 插入一条记录
# 使用 cursor() 方法创建一个游标对象 cursor
cursor = dbConn.cursor()
insert_sql = "INSERT INTO `t_user`(`user_name`, `pazzword`, `sex`, `age`, `birthday`) VALUES ('赵云', '123456', '男', 20, now())"
try:
# 执行 SQL语句
res = cursor.execute(insert_sql)
print(res) # 1
# 提交事务
dbConn.commit()
except:
# 回滚
dbConn.rollback()
raise
finally:
# 释放资源
cursor.close()
dbConn.close()
4.2 使用变量传递参数
推荐使用变量向SQL语句中传递参数,防止SQL注入。
import time
insert_sql = "INSERT INTO `t_user`(`user_name`, `pazzword`, `sex`, `age`, `birthday`) VALUES ('%s', '%s', '%s', %s, '%s')" % \
('赵云2', '123456', '男', 18, time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()))
try:
# 执行 SQL语句
res = cursor.execute(insert_sql)
print(res) # 1
# 提交事务
dbConn.commit()
except:
# 回滚
dbConn.rollback()
raise
finally:
# 释放资源
cursor.close()
dbConn.close()
4.3 插入多条记录
import time
insert_sql = "INSERT INTO `t_user`(`user_name`, `pazzword`, `sex`, `age`, `birthday`) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s)"
insert_datas = [
("赵子龙1", "123456", "男", 18, time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime())),
("赵子龙2", "123456", "男", 19, time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime())),
("赵子龙3", "123456", "男", 20, time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()))]
try:
# 执行 SQL语句
# res = cursor.execute(insert_sql)
res = cursor.executemany(insert_sql, insert_datas)
print(res) # 3
# 提交事务
dbConn.commit()
except:
# 回滚
dbConn.rollback()
raise
finally:
# 释放资源
cursor.close()
dbConn.close()
注意:PyMysql 会将 SQL 语句中的所有字段的传参值当做字符串类型进行处理。
5、更新操作
和插入操作类似,只需要变更 SQL 语句即可,推荐使用变量传递参数。
update_sql = 'UPDATE `t_user` SET `user_name` = %s, `pazzword` = %s, `sex` = %s, `age` = %s WHERE `id` = %s'
update_datas = ("安琪拉", "123456", "女", 18, 2)
try:
# 执行 SQL语句
res = cursor.execute(update_sql, update_datas)
print(res) # 1
# 提交事务
dbConn.commit()
...
6、删除操作
和插入操作类似,只需要变更 SQL 语句即可,推荐使用变量传递参数。
delete_sql = 'DELETE FROM `t_user` WHERE `id` = %s'
delete_datas = [(1),(2)]
try:
# 执行 SQL语句
res = cursor.executemany(delete_sql, delete_datas)
print(res) # 2
# 提交事务
dbConn.commit()
...
二、查询操作
Python查询数据库常用方法:
- fetchone() 方法:返回单条记录的结果集,结果集是一个对象。
- fetchall()方法:返回所有记录的结果行,结果集是一个列表。
- rowcount:这是一个只读属性,并返回执行execute()方法后影响的行数。
1、查询单条记录
select_sql = "SELECT * FROM `t_user` WHERE id = %s "
select_datas = (5)
try:
# 执行 SQL语句
cursor.execute(select_sql, select_datas)
res = cursor.fetchone()
print(res) # {'id': 5, 'user_name': '赵子龙1', 'pazzword': '123456', 'sex': '男', 'age': 18, 'birthday': datetime.date(2023, 2, 13)}
except:
raise
finally:
# 释放资源
cursor.close()
dbConn.close()
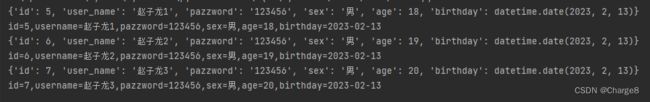
2、查询多条记录
select_sql = "SELECT * FROM `t_user` WHERE id >= %s AND sex = %s"
select_datas = (5, "男")
try:
# 执行 SQL语句
cursor.execute(select_sql, select_datas)
res = cursor.fetchmany(5)
for row in res:
id = row['id']
username = row['user_name']
pazzword = row['pazzword']
sex = row['sex']
age = row['age']
birthday = row['birthday']
# 打印结果
print(row)
print("id=%s,username=%s,pazzword=%s,sex=%s,age=%s,birthday=%s" % \
(id, username, pazzword, sex, age, birthday))
except:
raise
finally:
# 释放资源
cursor.close()
dbConn.close()
三、事务机制
1、事务机制
事务应该具有4个属性:原子性、一致性、隔离性、持久性。这四个属性通常称为ACID特性。
- 原子性(atomicity)。一个事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中包括的诸操作要么都做,要么都不做。
- 一致性(consistency)。事务必须是使数据库从一个一致性状态变到另一个一致性状态。一致性与原子性是密切相关的。
- 隔离性(isolation)。一个事务的执行不能被其他事务干扰。即一个事务内部的操作及使用的数据对并发的其他事务是隔离的,并发执行的各个事务之间不能互相干扰。
- 持久性(durability)。持续性也称永久性(permanence),指一个事务一旦提交,它对数据库中数据的改变就应该是永久性的。接下来的其他操作或故障不应该对其有任何影响。
2、事务操作
对于支持事务的数据库, 在 Python数据库编程中,当游标建立之时,就自动开始了一个隐形的数据库事务。
- commit()方法:执行当前游标的所有操作。
- rollback()方法:回滚当前游标的所有操作。
所以,上面的增删改查操作应该就好理解啦。
– 求知若饥,虚心若愚。