组件-utest
目录
1、简介
1.1、utest
1.2、testcase
1.3、test unit
1.4、utest应用框架
1.5、测试用例运行流程
1.5.1、测试命令使用示例
1.6、配置
1.6.1、宏
1.6.2、配置选项
2、API
2.1、assert 宏
2.2.1、utest_assert()函数
2.2.2、utest_assert_string()函数
2.2.3、utest_assert_buf()函数
2.2、UTEST_UNIT_RUN宏
2.3、UTEST_TC_EXPORT宏
2.4、测试用例 LOG 输出接口
2.4.1、utest_log_lv_set()函数
2.5、其他内部函数
2.5.1、utest_help()函数
2.5.2、file_basename()函数
2.5.3、utest_handle_get()函数
3、实现原理
3.1、utest_tc_export结构体
3.2、UtestTcTab 代码段
3.2.1、GCC链接脚本定义UtestTcTab代码段
3.3、测试用例命令表
3.3.1、utest_init()函数
3.4、单元测试
3.4.1、utest_unit_run()函数
4、MSH 命令
4.1、utest_list 命令
4.1.1、utest_tc_list()函数
4.2、utest_run命令
4.2.1、utest_testcase_run()函数
4.2.2、utest_run()函数
1、简介
1.1、utest
utest(unit test)是 RT-Thread 开发的单元测试框架。设计 utest 的初衷是方便使用统一的框架接口编写测试程序,实现单元测试、覆盖测试以及集成测试的目的。
1.2、testcase
测试用例(testcase,简称 tc)是为实现特定测试目标而执行的单个测试,是包括测试输入、执行条件、测试过程和预期结果的规范,是一个有明确的结束条件和明确的测试结果的有限循环。 具体来说通过utest 测试框架提供的 API 完成针对某一功能的测试代码就是一个测试用例。
注:utest测试框架定义用户编写的测试程序为测试用例,一个测试用例仅包含一个testcase 函数(类似 main 函数),可包含多个测试单元函数。
1.3、test unit
测试单元(test unit)是被测功能细分后的测试点,每个测试点可以是被测功能的最小可测单位。当然,不同的分类方式会细分出不同的测试单元。
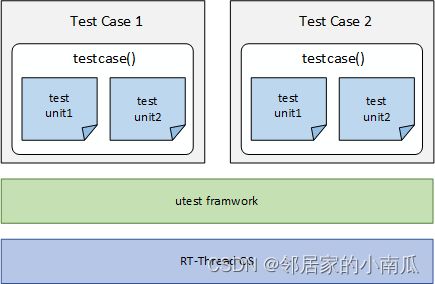
1.4、utest应用框架
测试用例基于utest 测试框架提供的服务接口进行程序设计,支持将多个测试用例编译到一起进行测试。一个测试用例对应唯一的 testcase 函数,在 testcase 中包含多个测试单元(test unit)。
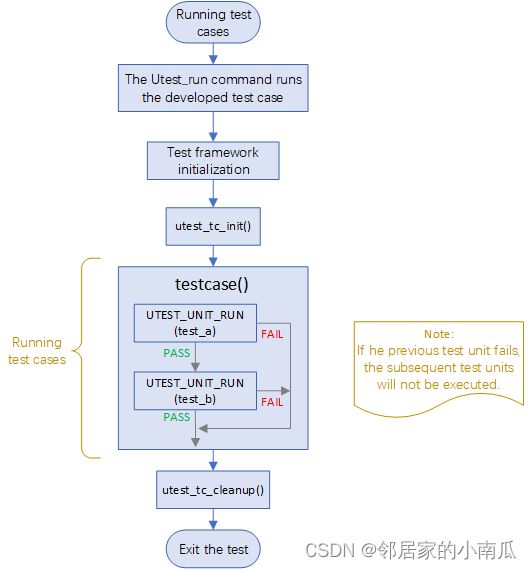
1.5、测试用例运行流程
1)utest 测试框架是顺序执行 testcase 函数中的所有测试单元
2)上一个 UTEST_UNIT_RUN 宏执出现了 assert,后面的所有 UTEST_UNIT_RUN 会跳过执行
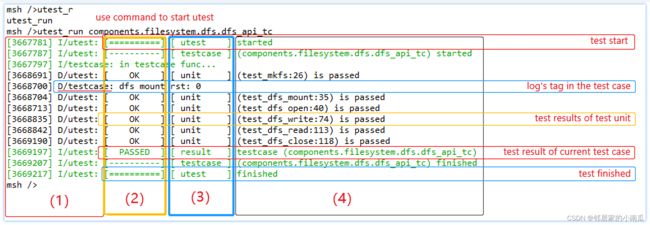
1.5.1、测试命令使用示例
msh />utest_list
[14875] I/utest: Commands list :
[14879] I/utest: [testcase name]:components.filesystem.dfs.dfs_api_tc; [run timeout]:30
[14889] I/utest: [testcase name]:components.filesystem.posix.posix_api_tc; [run timeout]:30
[14899] I/utest: [testcase name]:packages.iot.netutils.iperf.iperf_tc; [run timeout]:30
msh />
msh />utest_run components.filesystem.dfs.dfs_api_tc
[83706] I/utest: [==========] [ utest ] started
[83712] I/utest: [----------] [ testcase ] (components.filesystem.dfs.dfs_api_tc) started
[83721] I/testcase: in testcase func...
[84615] D/utest: [ OK ] [ unit ] (test_mkfs:26) is passed
[84624] D/testcase: dfs mount rst: 0
[84628] D/utest: [ OK ] [ unit ] (test_dfs_mount:35) is passed
[84639] D/utest: [ OK ] [ unit ] (test_dfs_open:40) is passed
[84762] D/utest: [ OK ] [ unit ] (test_dfs_write:74) is passed
[84770] D/utest: [ OK ] [ unit ] (test_dfs_read:113) is passed
[85116] D/utest: [ OK ] [ unit ] (test_dfs_close:118) is passed
[85123] I/utest: [ PASSED ] [ result ] testcase (components.filesystem.dfs.dfs_api_tc)
[85133] I/utest: [----------] [ testcase ] (components.filesystem.dfs.dfs_api_tc) finished
[85143] I/utest: [==========] [ utest ] finished
msh />
测试用例运行的日志从左到右被分成了四列,分别是 log 日志头信息、结果栏、属性栏、详细信息展示栏。日志中使用 result 属性标识该测试用例测试结果(PASSED or FAILED)。
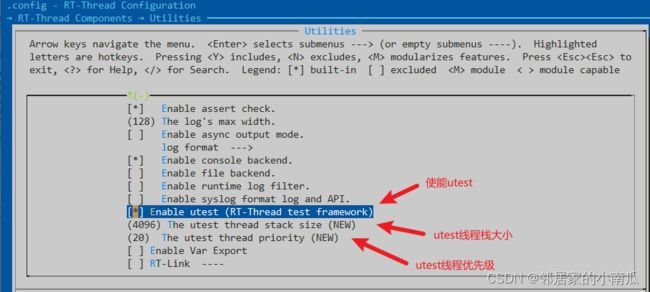
1.6、配置
1.6.1、宏
| 宏 | 说明 |
| UTEST_NAME_MAX_LEN | utest测试用例最大名称 |
| UTEST_THREAD_STACK_SIZE | utest线程栈大小(UTEST_THR_STACK_SIZE) |
| UTEST_THREAD_PRIORITY | utest线程优先级(UTEST_THR_PRIORITY) |
1.6.2、配置选项
2、API
2.1、assert 宏
| assert 宏 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| uassert_true(value) | value 为 true 则测试通过,否则测试失败 |
| uassert_false(value) | value 为 false 则测试通过,否则测试失败 |
| uassert_null(value) | value 为 null 则测试通过,否则测试失败 |
| uassert_not_null(value) | value 为非 null 值则测试通过,否则测试失败 |
| uassert_int_equal(a, b) | a 和 b 值相等则测试通过,否则测试失败 |
| uassert_int_not_equal(a, b) | a 和 b 值不相等则测试通过,否则测试失败 |
| uassert_str_equal(a, b) | 字符串 a 和字符串 b 相同则测试通过,否则测试失败 |
| uassert_str_not_equal(a, b) | 字符串 a 和字符串 b 不相同则测试通过,否则测试失败 |
| uassert_in_range(value, min, max) | value 在 min 和 max 的范围内则测试通过,否则测试失败 |
| uassert_not_in_range(value, min, max) | value 不在 min 和 max 的范围内则测试通过,否则测试失败 |
注:这里的assert 仅记录通过和失败的数量,不会产生断言并终止程序运行。其功能不等同于 RT_ASSERT。
2.2.1、utest_assert()函数
记录通过和失败的数量。
void utest_assert(int value, const char *file, int line, const char *func, const char *msg)2.2.2、utest_assert_string()函数
1)如果a == RT_NULL或 b == RT_NULL,调用utest_assert(0, file, line, func, msg);
2)如果equal等于TRUE
a.如果字符串a等于b,则调用utest_assert(1, file, line, func, msg);
b.如果字符串a不等于b,则调用utest_assert(0, file, line, func, msg);
3)如果equal不等于TRUE
a.如果字符串a等于b,则调用utest_assert(0, file, line, func, msg);
b.如果字符串a不等于b,则调用utest_assert(1, file, line, func, msg);
void utest_assert_string(const char *a, const char *b, rt_bool_t equal, const char *file, int line, const char *func, const char *msg)2.2.3、utest_assert_buf()函数
1)如果a == RT_NULL或 b == RT_NULL,调用utest_assert(0, file, line, func, msg);
2)如果equal等于TRUE
a.如果缓存a等于b,则调用utest_assert(1, file, line, func, msg);
b.如果缓存a不等于b,则调用utest_assert(0, file, line, func, msg);
3)如果equal不等于TRUE
a.如果缓存a等于b,则调用utest_assert(0, file, line, func, msg);
b.如果缓存a不等于b,则调用utest_assert(1, file, line, func, msg);
void utest_assert_buf(const char *a, const char *b, rt_size_t sz, rt_bool_t equal, const char *file, int line, const char *func, const char *msg)2.2、UTEST_UNIT_RUN宏
测试用例(test case)中,使用 UTEST_UNIT_RUN 宏执行指定的测试单元函数。测试单元(test unit)必须使用 UTEST_UNIT_RUN 宏执行。
#define UTEST_UNIT_RUN(test_unit_func) \
utest_unit_run(test_unit_func, #test_unit_func); \
if(utest_handle_get()->failed_num != 0) return;注:如果测试单元测试失败(failed_num不为0),则直接退出测试用例。
2.3、UTEST_TC_EXPORT宏
#define UTEST_TC_EXPORT(testcase, name, init, cleanup, timeout) \
RT_USED static const struct utest_tc_export _utest_testcase \
RT_SECTION("UtestTcTab") = \
{ \
name, \
timeout, \
init, \
testcase, \
cleanup \
}| 参数 | 说明 |
| testcase | 测试用例主承载函数(规定使用名为 static void testcase(void) 的函数 |
| name | 测试用例名称(唯一)。 |
| init | 测试用例启动前的初始化函数 |
| cleanup | 测试用例结束后的清理函数 注:测试用例中创建的资源(线程、信号量、定时器、内存等)需要在测试结束前释放 |
| timeout | 测试超时时间(单位为s) 注:此参数在当前代码中未使用。 |
注:一个测试用例实现仅能使用UTEST_TC_EXPORT 导出一个测试主体函数(testcase 函数)
2.4、测试用例 LOG 输出接口
utest 测试框架依赖 ulog 日志模块进行日志输出。只要在测试用例里加入 #include "utest.h" 即可使用 ulog 日志模块的所有级别接口。 另外,utest 测试框架增加了额外的日志控制接口,如下:
#define UTEST_LOG_ALL (1u)
#define UTEST_LOG_ASSERT (2u)
void utest_log_lv_set(rt_uint8_t lv);用户可以在测试用例中使用 utest_log_lv_set 接口控制日志输出级别。UTEST_LOG_ALL 配置输出所有日志;UTEST_LOG_ASSERT 配置仅输出 uassert 失败后的日志。
2.4.1、utest_log_lv_set()函数
设置utest日志级别,只能为UTEST_LOG_ALL或UTEST_LOG_ASSERT。
void utest_log_lv_set(rt_uint8_t lv)2.5、其他内部函数
2.5.1、utest_help()函数
该接口显示帮助信息(utest用法)。
static int utest_help(void)2.5.2、file_basename()函数
该接口返回文件名。例如\path\file返回file;\file返回file;\返回\;
static const char *file_basename(const char *file)2.5.3、utest_handle_get()函数
该接口返回local_utest。
utest_t utest_handle_get(void)3、实现原理
1)调用UTEST_TC_EXPORT宏将测试用例以utest_tc_export结构体的形式放在UtestTcTab代码段。
2)在测试用例中使用UTEST_UNIT_RUN宏进行单元测试函数编写
3)使用utest_run命令进行测试。调用tc()函数进行进入测试用例,调用utest_unit_run()函数进行单元测试
3.1、utest_tc_export结构体
struct utest_tc_export {
const char *name;
uint32_t run_timeout;
rt_err_t (*init)(void);
void (*tc)(void);
rt_err_t (*cleanup)(void);
};
typedef struct utest_tc_export *utest_tc_export_t;3.2、UtestTcTab 代码段
测试框架 utest 将所有的测试用例导出到了 UtestTcTab 代码段。在 IAR 和 MDK 编译器中不需要在链接脚本中定义 UtestTcTab 段,但是在 GCC 编译时,需要在链接脚本中显式地设置 UtestTcTab段。
3.2.1、GCC链接脚本定义UtestTcTab代码段
在 GCC 链接脚本的 .text 中,增加 UtestTcTab 段的定义,格式如下所示:
/* section information for utest */
. = ALIGN(4);
__rt_utest_tc_tab_start = .;
KEEP(*(UtestTcTab))
__rt_utest_tc_tab_end = .;3.3、测试用例命令表
所有测试用例都以utest_tc_export结构体的形式放在UtestTcTab代码段。
3.3.1、utest_init()函数
初始化utes命令表(tc_table、tc_num)
int utest_init(void)以GCC为例:__rt_utest_tc_tab_start为UtestTcTab代码段起始地址。__rt_utest_tc_tab_end为UtestTcTab代码段结束地址。tc_table数组存储测试用例地址。tc_num等于测试用例数量。
tc_table = (utest_tc_export_t)&__rt_utest_tc_tab_start;
tc_num = (utest_tc_export_t) &__rt_utest_tc_tab_end - tc_table;3.4、单元测试
3.4.1、utest_unit_run()函数
调用func()函数开始进行单元测试。
void utest_unit_run(test_unit_func func, const char *unit_func_name)4、MSH 命令
4.1、utest_list 命令
列出当前系统支持的测试用例,包括测试用例的名称和测试需要的时间。该命令无参数。
4.1.1、utest_tc_list()函数
该接口用于列出所有testcase信息(名称、测试时间)。
static void utest_tc_list(void)4.2、utest_run命令
测试用例执行命令,该命令格式如下:
utest_run [-thread or -help] [testcase name] [loop num]| utest_run 命令参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| -thread | 使用线程模式运行测试框架 |
| -help | 打印帮助信息 |
| testcase name | 指定测试用例名称。支持使用通配符*,支持指定测试用例名称前部分字节。如test*,表示运行所有以'test'开头的测试用例。但*test则表示运行*test这个测试用例。 |
| loop num | 指定测试用例循环测试次数 |
1)utest_run
不指定测试用例名称,运行所有测试用例
2)utest_run -thread
不指定测试用例名称,创建一个线程,在线程中运行所有测试用例
3)utest_run 测试用例
指定测试用例名称,运行指定测试用例
4)utest_run 测试用例 测试次数
指定测试用例名称和测试次数,多次运行指定测试用例
5)utest_run -thread 测试用例
指定测试用例名称,创建一个线程,在线程中运行指定测试用例
6)utest_run -thread 测试用例 测试次数
指定测试用例名称和测试次数,创建一个线程,在线程中多次运行指定测试用例
4.2.1、utest_testcase_run()函数
MSH执行utest_run命令时,会调用此函数。
static void utest_testcase_run(int argc, char** argv)4.2.2、utest_run()函数
最终执行测试用例的函数。
static void utest_run(const char *utest_name)