重点:字符串的常见操作
6.字符串的常见操作 知道方向,不要去背 1)find,index #查找 2)count 和replace #替换 3)split # 分割(数据清洗) 4)capitalize 和 title #首字母大写 5)startswitch endswitch #开头结尾(上传文件名称盘判断) 6)lower,upper #转换为大小写(用户输入同一格式) 7)center ,ljust,rjust # 居中显示(网易云歌词) 8)strip 去除空格,\n,\t #(数据清洗) 9) partition,rpartition #分割 (广播体操带队) 10)splitlines # 按行\n分割 11) isdigit isalpha isalnum # 注册时,必须是字母和数字的组合 12)join #构建字符串 13)format: #格式化输出
浮点数的判断
type(eval("123")) == int type(eval("123.23")) == float
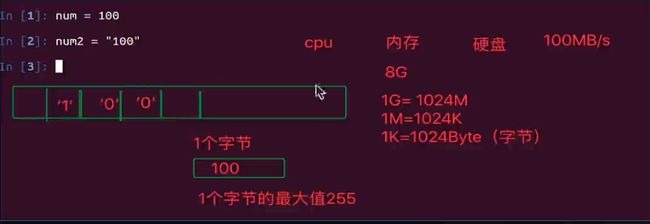
1 num = 10 和 num = "10" 的区别
num = 10 内存中占用1个字节
num = "10" 内存中占用3个字节
注意:c语言中 字符串末尾还有\0结束符
import sys sum = 10 sum1 = " " print(sys.getsizeof(sum1)) #运行结果 49 Process finished with exit code 0
2 类型转换
num = 100 num2 = "100" name = 'alex' num3 = int(num2) print(type(num3),num3) #运行结果 <class 'int'> 100 num1 = str(num) print(type(num1),num1) #运行结果 <class 'str'> 100 print(len(name)) #运行结果 4
3 字符串拼接的两种方式
a = "lao" b = 'wang' c = a + b print(c) #运行结果 laowang A = 10 B = 2 C = A + B print(C) #运行结果 12
#####################第一种方式 e = "===" + a + b + "===" print(e) #####################第二种方式 f = "===%s==="%(a+b) print(f) #运行结果 ===laowang=== ===laowang=== Process finished with exit code 0
4 字符串的下标
name = "abcdef" print(name[0]) print(name[5]) #运行结果 a f ####### 越界
print(name[6])
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "D:/DPJ-1/Demo/其他/other.py", line 324, in
print(name[6])
IndexError: string index out of range
########[-3][-2][-1]
print(name[len(name)-1])
print(name[-1])
print(name[-2])
print(name[-3])
#运行结果
f
f
e
d
Process finished with exit code 0
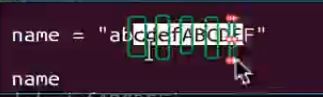
5 切片
# 正向切片---顾头不顾尾 name = "abcdefABCDEF" print(name[2:5]) #实质[2:4] print(name[2:6])#实质[2:5] #运行结果 cde cdef #反向切片 print(name[2:-2]) #[2: cdefABCDEF # :-2] abcdefABCD #结果 cdefABCD print(name[2:-1]) print(name[2:0]) print(name[2:]) #运行结果 cdefABCD cdefABCDE ""#空 cdefABCDEF
1 实质:[起始位置:终止位置:步长]
name = "abcdefABCDEF" print(name[2:-1]) cdefABCDE print(name[2:-1:2]) ceACE print(name[2:-1:1]) cdefABCDE print(name[2:-1]) #默认步长为1 cdefABCDE
2 字符串的逆序(倒序)?
name = "abcdefABCDEF" ##### 正序 print(name[0:]) #abcdefABCDEF print(name[-1:]) #F print(name[-1:0]) #""空值 #####倒序(面试必考) print(name[-1:0:-1]) #FEDCBAfedcb print(name[-1::-1]) #FEDCBAfedcba print(name[::-1]) #FEDCBAfedcba
6 字符串的常见操作
知道方向,不要去背
In [57]: my_str = "hello world python adn pythonxxxxcpp" In [59]: my_str. my_str.capitalize my_str.isalnum my_str.join my_str.rsplit my_str.casefold my_str.isalpha my_str.ljust my_str.rstrip my_str.center my_str.isdecimal my_str.lower my_str.split my_str.count my_str.isdigit my_str.lstrip my_str.splitlines my_str.encode my_str.isidentifier my_str.maketrans my_str.startswith my_str.endswith my_str.islower my_str.partition my_str.strip my_str.expandtabs my_str.isnumeric my_str.replace my_str.swapcase my_str.find my_str.isprintable my_str.rfind my_str.title my_str.format my_str.isspace my_str.rindex my_str.translate my_str.format_map my_str.istitle my_str.rjust my_str.upper my_str.index my_str.isupper my_str.rpartition my_str.zfill
1 find,index查找
my_str = "hello world python and pythonxxxcpp" print(my_str.find("world")) #6 #w的下标 print(my_str.find("python"))#从左边开始find #12 print(my_str.rfind("python"))#从右边开始find #23 print(my_str.find("redhat"))#没有find out 返回-1 #-1 ######index print(my_str.index("python")) #12 print(my_str.rindex("python")) #23 print(my_str.index("redhat")) Traceback (most recent call last): File "D:/-1/Demo/其他/other.py", line 364, inprint(my_str.index("redhat"))#没找到报错 ValueError: substring not found
2 count 和 replace
#count() 方法用于统计字符串里某个字符出现的次数。
#replace() 方法把字符串中的 old(旧字符串) 替换成 new(新字符串),如果指定第三个参数max,则替换不超过 max 次。
my_str = "hello world python and pythonxxxcpp"
######count print(my_str.count("python")) #2 print(my_str.count("world")) #1 print(my_str.count("redhat")) #0 ######replace print(my_str.replace("world","WORLD")) #hello WORLD python and pythonxxxcpp print(my_str.replace("python","redhat",1)) #替换第一个 #hello world redhat and pythonxxxcpp #数字,元组,字符串,都是不可变类型
3 split 分割(数据清洗)
#split() 通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片,如果参数 num 有指定值,则仅分隔 num 个子字符串
print(my_str.split(" ")) #['hello', 'world', 'python', 'and', 'pythonxxxcpp']
4 capitalize 和 title 首字母大写
#capitalize()将字符串的第一个字母变成大写,其他字母变小写。
#title() 方法返回"标题化"的字符串,就是说所有单词都是以大写开始,其余字母均为小写(见 istitle())。
print(my_str.capitalize()) #Hello world python and pythonxxxcpp print(my_str.title()) #Hello World Python And Pythonxxxcpp
5 startswitch endswith 开头结尾
#startswith() 方法用于检查字符串是否是以指定子字符串开头,如果是则返回 True,否则返回 False。如果参数 beg 和 end 指定值,则在指定范围内检查。
#endswith() 方法用于判断字符串是否以指定后缀结尾,如果以指定后缀结尾返回True,否则返回False。可选参数"start"与"end"为检索字符串的开始与结束位置。
#上传文件名称的判断 file_name = 'abc.txt' print(file_name.endswith(".txt")) #True print(file_name.startswith("abc")) #True #对文件内容 的审查,模块 上传病毒
6 lower, upper 转换为大小写(用户输入同一格式)
name = "Abc" print(name.lower()) #全部小写 #abc print(name.upper())#全部大写 #ABC
7 center,ljust,rjust 居中显示,(网易云歌词)
# center() 方法返回一个指定的宽度 width 居中的字符串,fillchar 为填充的字符,默认为空格。
lyric = "想要陪你一起看大海" print(lyric.center(50)) # 想要陪你一起看大海 print(lyric.ljust(50)) #想要陪你一起看大海 # print(lyric.rjust(50)) # 想要陪你一起看大海
8 strip 去除空格,\n,\t
#strip() 方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列。 lyric = " 想要陪你一起看大海" print(lyric.lstrip()) #去除左\n,\t #想要陪你一起看大海 print(lyric.rstrip())#去除右\n,\t # 想要陪你一起看大海 print(lyric.strip())#trip() 方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列。 #想要陪你一起看大海
9 partition,rparttition 分割
my_str = "hello world python and pythonxxxcpp" #跟split差不多,切割字符串。 print(my_str.partition("python"))#默认从左向右切割 #('hello world ', 'python', ' and pythonxxxcpp') print(my_str.rpartition("python")) #rparttition 表示从右向左 切割 #('hello world python and ', 'python', 'xxxcpp')
10 splitlines 按行\n分割
my_line = "hello\nworld\nxx\nyy\nzz" print(my_line) hello world xx yy zz print(my_line.splitlines()) #['hello', 'world', 'xx', 'yy', 'zz']
11 isdigit,isalpha,isalnum 注册时,必须是字母与数字的组合
s为字符串
s.isalnum() 所有字符都是数字或者字母
s.isalpha() 所有字符都是字母
s.isdigit() 所有字符都是数字
s.islower() 所有字符都是小写
s.isupper() 所有字符都是大写
s.istitle() 所有单词都是首字母大写,像标题
s.isspace() 所有字符都是空白字符、\t、\n、\r
#####数字整数 isdigit num = input("输入数字") if num.isdigit(): num = int(num) print("是数字:",num) #运行结果 输入数字1 是数字: 1 ######字母 isalpha num = input("输入内容:") if num.isalpha(): print("是字母",num) #运行结果 输入内容:a 是字母 a ####注册页面,必须是数字与字母的组合 num = '1q' print(num.isdigit())#判断是否是数字 #False print(num.isalpha())#判读是否是字母 #False print(num.isalnum())#alpha,number。判断是否是数字与字母 #True
######数字字母组合
num = input("输入内容:")
if num.isalnum():
print("是字母和数字",num)
#运行结果
输入内容:1q
是字母和数字 1q
12 join 构建字符串
#join() 方法用于将序列中的元素以指定的字符连接生成一个新的字符串。 a = ["aa","bb","cc"] print(a) #['aa', 'bb', 'cc'] b = "=" print(b.join(a)) #aa=bb=cc b = " " print(b.join(a)) #aa bb cc
13 format :格式化输出
#格式化输出1 s = "myname is {0}, i am {1}" print(s.format("alex",22)) #myname is alex, i am 22 #格式化输出2 s = "myname is {name}, i am {age}" print(s.format("alex",22))#格式错误会报错 Traceback (most recent call last): File "D:/1/Demo/其他/other.py", line 444, inprint(s.format("alex",22)) KeyError: 'name' print(s.format(name='alex',age=22)) #myname is alex, i am 22
7 面试题:给定一个字符串str,去除所有的空格和\t,返回字符串
(面试题)给定一个字符串Str, 去除所有的 空格和'\t',返回字符串
test_str = "hello world nihao \t heihie \t woshi nide\tpython \n ll\ndu"
###解答 test_str = "hello world nihao \t heihie \t woshi nide\tpython \n ll\ndu" print(test_str.split()) #['hello', 'world', 'nihao', 'heihie', 'woshi', 'nide', 'python', 'll', 'du']
####字符串拼接 test_str = "hello world nihao \t heihie \t woshi nide\tpython \n ll\ndu" res = test_str.split() print(" ".join(res)) #hello world nihao heihie woshi nide python ll du print("".join(res)) #helloworldnihaoheihiewoshinidepythonlldu