6、Java入门教程【数组】
数组是用于存储同种类型的多个数据的容器。
一、声明
//语法
dataType[] arrayRefVar; // 首选的方法
或
dataType arrayRefVar[]; // 效果相同,但不是首选方法
//示例
double[] myList; // 首选的方法
或
double myList[]; // 效果相同,但不是首选方法
二、创建数组
//语法
dataType[] arrayRefVar = new dataType[arraySize];
dataType[] arrayRefVar = new dataType[]{value0, value1, ..., valuek};
dataType[] arrayRefVar = {value0, value1, ..., valuek};
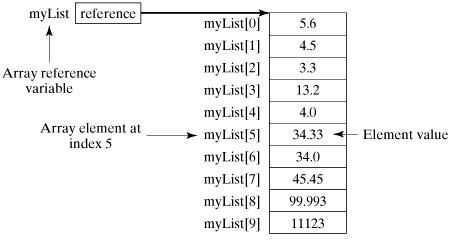
数组的元素是通过索引访问的。数组索引从 0 开始,所以索引值从 0 到 arrayRefVar.length-1。
//示例
public class TestArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 数组大小
int size = 10;
// 定义数组
double[] myList = new double[size];
myList[0] = 5.6;
myList[1] = 4.5;
myList[2] = 3.3;
myList[3] = 13.2;
myList[4] = 4.0;
myList[5] = 34.33;
myList[6] = 34.0;
myList[7] = 45.45;
myList[8] = 99.993;
myList[9] = 11123;
// 计算所有元素的总和
double total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
total += myList[i];
}
System.out.println("总和为: " + total);
}
}
注:采用new dataType[arraySize]的方式创建的数组,每一项都会有默认值,不同的类型默认值不一样:
- byte、short、int、char、long类型数组的元素默认值都是
0 - float、double类型数组元素的默认值都是
0.0 - boolean类型数组的元素默认值是
false,String类型数组的元素的默认值是null
三、数组遍历
使用myList.length可以获取数组的长度,结合for循环,我们可以对数组进行遍历,以便对数组中的每一项进行处理。
//方式一
public class TestArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] myList = {1.9, 2.9, 3.4, 3.5};
// 打印所有数组元素
for (int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++) {
System.out.println(myList[i] + " ");
}
// 计算所有元素的总和
double total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++) {
total += myList[i];
}
System.out.println("Total is " + total);
// 查找最大元素
double max = myList[0];
for (int i = 1; i < myList.length; i++) {
if (myList[i] > max) max = myList[i];
}
System.out.println("Max is " + max);
}
}
//方式二
for(type element: array)
{
System.out.println(element);
}
四、函数参数是数组
public static void printArray(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
}
五、函数的返回值是数组
public static int[] reverse(int[] list) {
int[] result = new int[list.length];
for (int i = 0, j = result.length - 1; i < list.length; i++, j--) {
result[j] = list[i];
}
return result;
}
六、多维数组
String[][] str = new String[3][4];
七、工具类Arrays
1、判断相等-equals
如果两个数组以相同顺序包含相同的元素,则两个数组是相等的。
package com.itfeiniu.hello;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a1 = {12, 56, 42};
//声明创建一个数组
int[] a2 = new int[3];//先定义数组长度
a2[0] = 12;
a2[1] = 56;
a2[2] = 42;
//给数组赋值
int[] a3 = {42, 56, 12};//a3元素和a1相同,顺序不同
if (Arrays.equals(a1, a2)) {
System.out.println("a1和a2相等");
} else {
System.out.println("a1和a2不相等");
}
if (Arrays.equals(a1, a3)) {
System.out.println("a1和a3相等");
} else {
System.out.println("a1和a3不相等");
}
}
}
//a1和a2相等
//a1和a3不相等
2、正序排序-sort
package com.itfeiniu.hello;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] myList = new int[3];
myList[0] = 3;
myList[1] = 1;
myList[2] = 2;
Arrays.sort(myList);
for (int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++) {
System.out.println(myList[i]);
}
}
}
//1
//2
//3
3、填充-fill
package com.itfeiniu.hello;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] myList = new int[3];
Arrays.fill(myList, 10);
for (int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++) {
System.out.println(myList[i]);
}
}
}
//10
//10
//10
4、查找-binarySearch
package com.itfeiniu.hello;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] myList = new int[3];
myList[0] = 30;
myList[1] = 10;
myList[2] = 20;
Arrays.sort(myList);//必须先做排序
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(myList, 20));
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(myList, 1));
}
}
//1
//-1
用二分查找算法在给定数组中搜索给定值的对象(Byte,Int,double等)。数组在调用前必须排序好的。如果查找值包含在数组中,则返回搜索键的索引;否则返回 (-(插入点) - 1)。
5、转换成字符串-toString
package com.itfeiniu.hello;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] myList = new int[3];
myList[0] = 30;
myList[1] = 10;
myList[2] = 20;
Arrays.sort(myList);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(myList));
}
}
//[10, 20, 30]
八、数组存储
JVM中包含三种内存区域:
- 方法区
- 栈内存
- 堆内存
变量和数组的存储案例说明:int a=20;int[] arr=new int[3];
- a是变量,直接放在【栈中】,a变量中存储的数据就是20这个值
- new int[3]是创建一个数组对象,会在【堆内存】中开辟区域存储3个整数
- arr是变量,在【栈中】,arr中存储的是数组对象在堆内存中的地址值
多个变量指向同一个数组:
package com.itfeiniu.hello;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr1 = {11, 22, 33};
int[] arr2 = arr1;
arr2[1] = 222;//改了arr2,arr1也同时改变。引用类型。
System.out.println(arr1[1]);
System.out.println(arr2[1]);//引用类型,arr2存储在栈中,存储了arr1的内存地址值
}
}
//222
//222
如果某个数组变量存储的地址是
null,那么该变量将不再指向任何数组对象。