ffplay.c学习-4-⾳频输出和⾳频重采样
目录
- ⾳频输出模块
- 打开SDL⾳频设备
- 打开⾳频设备audio_open
- 回调函数逻辑sdl_audio_callback
- 回调函数读取数据
- ⾳频重采样
- 重采样逻辑
- 样本补偿
1. ⾳频输出模块
- ffplay的⾳频输出通过SDL实现。
- ⾳频输出的主要流程:
- 打开SDL⾳频设备,设置参数
- 启动SDL⾳频设备播放
- SDL⾳频回调函数读取数据,这个时候我们就要从FrameQueue读取frame填充回调函数提供的buffer空间。
- audio的输出在SDL下是被动的,即在开启SDL⾳频后,当SDL需要数据输出时则通过回调函数的⽅式告诉应⽤者需要传⼊多少数据,但这⾥存在⼀些问题:
- ffmpeg解码⼀个AVPacket的⾳频到AVFrame后,在AVFrame中存储的⾳频数据⼤⼩与SDL回调所需要的数据不⼀定相等 (回调函数每次要获取的数据量都是固定);
- 特别是如果要实现声⾳变速播放功能,那每帧AVFrame做变速后的数据⼤⼩⼤概率和SDL回调锁需要的数据⼤⼩不⼀致。
- 这就需要再增加⼀级缓冲区解决问题,即是从FrameQueue队列读取到Frame的数据后,先缓存到⼀个buffer⾥,然后再从该buffer读取数据给到SDL回调函数。
- 在audio输出时,主要模型如下图:
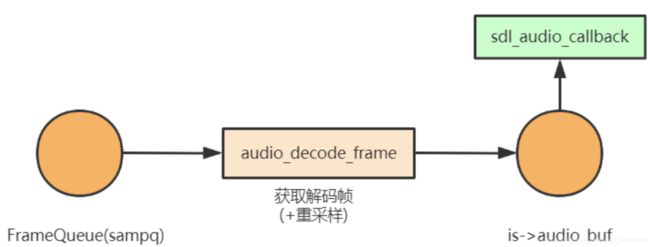
- 在这个模型中,sdl通过sdl_audio_callback函数向ffplay要⾳频数据,ffplay将sampq中的数据通过audio_decode_frame 函数取出,放⼊ is->audio_buf ,然后送出给sdl。在后续回调时先找audio_buf 要数据,数据不⾜的情况下,再调⽤ audio_decode_frame 补充 audio_buf
- 注意 audio_decode_frame 这个函数名很具有迷惑性,实际上,这个函数是没有解码功能的。这个函数主要是处理sampq到audio_buf的过程,最多只是执⾏了重采样(数据源和输出参数不⼀致时则做重采样)。
1. 打开SDL⾳频设备
- SDL⾳频输出的参数是⼀开始就设置好的,当码流的解出来的⾳频参数和预设的输出参数不⼀致时,则需要重采样成预设参数⼀致数据,这样才能正常播放。
- ⾳频设备的打开实际是在解复⽤线程中实现的。解复⽤线程中先打开⾳频设备(设定⾳频回调函数供SDL⾳频播放线程回调),然后再创建⾳频解码线程。调⽤链如下:
main() -->
stream_open() -->
read_thread() -->
stream_component_open() -->
audio_open(is, channel_layout, nb_channels, sample_rate, &is->audio_tgt);
- 先看打开sdl⾳频输出的代码(stream_component_open函数):
#else
sample_rate = avctx->sample_rate;
nb_channels = avctx->channels;
channel_layout = avctx->channel_layout;
#endif
if ((ret = audio_open(is, channel_layout, nb_channels, sample_rate, &is->audio_tgt)) < 0)
goto fail;
is->audio_hw_buf_size = ret;
is->audio_src = is->audio_tgt;
is->audio_buf_size = 0;
is->audio_buf_index = 0;
- 由于不同的⾳频输出设备⽀持的参数不同,⾳轨的参数不⼀定能被输出设备⽀持(此时就需要重采样了), audio_tgt 就保存了输出设备参数。
- audio_open是ffplay封装的函数,会优先尝试请求参数能否打开输出设备,尝试失败后会⾃动查找最佳的参数重新尝试。不再具体分析。
- audio_src ⼀开始与 audio_tgt 是⼀样的,如果输出设备⽀持⾳轨参数,那么 audio_src 可以⼀直保持与 audio_tgt ⼀致,否则将在后⾯代码中⾃动修正为⾳轨参数,并引⼊重采样机制。
- 最后初始化了⼏个audio_buf相关的参数。这⾥介绍下audio_buf相关的⼏个变量:
audio_buf: 从要输出的AVFrame中取出的⾳频数据(PCM),如果有必要,则对该数据重采样。
audio_buf_size: audio_buf的总⼤⼩
audio_buf_index: 下⼀次可读的audio_buf的index位置。
audio_write_buf_size:audio_buf剩余的buffer⻓度,即audio_buf_size - audio_buf_index
- 在 audio_open 函数内,通过通过 SDL_OpenAudioDevice 注册 sdl_audio_callback 函数为⾳频输出的回调函数。那么,主要的⾳频输出的逻辑就在 sdl_audio_callback 函数内了。
2. 打开⾳频设备audio_open
- audio_open()函数填⼊期望的⾳频参数,打开⾳频设备后,将实际的⾳频参数存⼊输出参数is->audio_tgt中,后⾯⾳频播放线程⽤会⽤到此参数,使⽤此参数将原始⾳频数据重采样,转换为⾳频设备⽀持的格式。
static int audio_open(void *opaque, int64_t wanted_channel_layout,
int wanted_nb_channels, int wanted_sample_rate,
struct AudioParams *audio_hw_params) {
SDL_AudioSpec wanted_spec, spec;
const char *env;
static const int next_nb_channels[] = {0, 0, 1, 6, 2, 6, 4, 6};
static const int next_sample_rates[] = {0, 44100, 48000, 96000, 192000};
int next_sample_rate_idx = FF_ARRAY_ELEMS(next_sample_rates) - 1;
env = SDL_getenv("SDL_AUDIO_CHANNELS");
if (env) {
wanted_nb_channels = atoi(env);
wanted_channel_layout = av_get_default_channel_layout(wanted_nb_channels);
}
if (!wanted_channel_layout || wanted_nb_channels != av_get_channel_layout_nb_channels(wanted_channel_layout)) {
wanted_channel_layout = av_get_default_channel_layout(wanted_nb_channels);
wanted_channel_layout &= ~AV_CH_LAYOUT_STEREO_DOWNMIX;
}
wanted_nb_channels = av_get_channel_layout_nb_channels(wanted_channel_layout);
wanted_spec.channels = wanted_nb_channels;
wanted_spec.freq = wanted_sample_rate;
if (wanted_spec.freq <= 0 || wanted_spec.channels <= 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Invalid sample rate or channel count!\n");
return -1;
}
while (next_sample_rate_idx && next_sample_rates[next_sample_rate_idx] >= wanted_spec.freq)
next_sample_rate_idx--;
wanted_spec.format = AUDIO_S16SYS;
wanted_spec.silence = 0;
wanted_spec.samples = FFMAX(SDL_AUDIO_MIN_BUFFER_SIZE,
2 << av_log2(wanted_spec.freq / SDL_AUDIO_MAX_CALLBACKS_PER_SEC));
wanted_spec.callback = sdl_audio_callback;
wanted_spec.userdata = opaque;
while (!(audio_dev = SDL_OpenAudioDevice(NULL, 0, &wanted_spec, &spec,
SDL_AUDIO_ALLOW_FREQUENCY_CHANGE | SDL_AUDIO_ALLOW_CHANNELS_CHANGE))) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_WARNING, "SDL_OpenAudio (%d channels, %d Hz): %s\n",
wanted_spec.channels, wanted_spec.freq, SDL_GetError());
wanted_spec.channels = next_nb_channels[FFMIN(7, wanted_spec.channels)];
if (!wanted_spec.channels) {
wanted_spec.freq = next_sample_rates[next_sample_rate_idx--];
wanted_spec.channels = wanted_nb_channels;
if (!wanted_spec.freq) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"No more combinations to try, audio open failed\n");
return -1;
}
}
wanted_channel_layout = av_get_default_channel_layout(wanted_spec.channels);
}
if (spec.format != AUDIO_S16SYS) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"SDL advised audio format %d is not supported!\n", spec.format);
return -1;
}
if (spec.channels != wanted_spec.channels) {
wanted_channel_layout = av_get_default_channel_layout(spec.channels);
if (!wanted_channel_layout) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"SDL advised channel count %d is not supported!\n", spec.channels);
return -1;
}
}
audio_hw_params->fmt = AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16;
audio_hw_params->freq = spec.freq;
audio_hw_params->channel_layout = wanted_channel_layout;
audio_hw_params->channels = spec.channels;
audio_hw_params->frame_size = av_samples_get_buffer_size(NULL, audio_hw_params->channels,
1, audio_hw_params->fmt, 1);
audio_hw_params->bytes_per_sec = av_samples_get_buffer_size(NULL, audio_hw_params->channels,
audio_hw_params->freq,
audio_hw_params->fmt, 1);
if (audio_hw_params->bytes_per_sec <= 0 || audio_hw_params->frame_size <= 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "av_samples_get_buffer_size failed\n");
return -1;
}
return spec.size;
}
3. 回调函数逻辑sdl_audio_callback
- 再来看 sdl_audio_callback
static void sdl_audio_callback(void *opaque, Uint8 *stream, int len) {
VideoState *is = opaque;
int audio_size, len1;
audio_callback_time = av_gettime_relative();
while (len > 0) {
if (is->audio_buf_index >= is->audio_buf_size) {
audio_size = audio_decode_frame(is);
if (audio_size < 0) {
is->audio_buf = NULL;
is->audio_buf_size = SDL_AUDIO_MIN_BUFFER_SIZE / is->audio_tgt.frame_size
* is->audio_tgt.frame_size;
} else {
if (is->show_mode != SHOW_MODE_VIDEO)
update_sample_display(is, (int16_t *) is->audio_buf, audio_size);
is->audio_buf_size = audio_size;
}
is->audio_buf_index = 0;
}
len1 = is->audio_buf_size - is->audio_buf_index;
if (len1 > len)
len1 = len;
if (!is->muted && is->audio_buf && is->audio_volume == SDL_MIX_MAXVOLUME)
memcpy(stream, (uint8_t *) is->audio_buf + is->audio_buf_index, len1);
else {
memset(stream, 0, len1);
if (!is->muted && is->audio_buf)
SDL_MixAudioFormat(stream, (uint8_t *) is->audio_buf + is->audio_buf_index,
AUDIO_S16SYS, len1, is->audio_volume);
}
len -= len1;
stream += len1;
is->audio_buf_index += len1;
}
is->audio_write_buf_size = is->audio_buf_size - is->audio_buf_index;
if (!isnan(is->audio_clock)) {
set_clock_at(&is->audclk, is->audio_clock -
(double) (2 * is->audio_hw_buf_size + is->audio_write_buf_size)
/ is->audio_tgt.bytes_per_sec,
is->audio_clock_serial,
audio_callback_time / 1000000.0);
sync_clock_to_slave(&is->extclk, &is->audclk);
}
}
- sdl_audio_callback 函数是⼀个典型的缓冲区输出过程,看代码和注释应该可以理解。具体看3个细节:
- 输出audio_buf到stream,如果audio_volume为最⼤⾳量,则只需memcpy复制给stream即可。否则,可以利⽤SDL_MixAudioFormat进⾏⾳量调整和混⾳
- 如果audio_buf消耗完了,就调⽤ audio_decode_frame 重新填充audio_buf。接下来会继续分析audio_decode_frame函数
- set_clock_at更新audclk时,audio_clock是当前audio_buf的显示结束时间(pts+duration),由于audio driver本身会持有⼀⼩块缓冲区,典型地会是两块交替使⽤,所以有 2 * is->audio_hw_buf_size,⾄于为什么还要 audio_write_buf_size,⼀图胜千⾔。
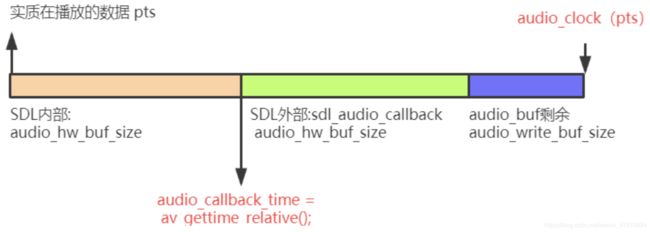
- 我们先来is->audio_clock是在audio_decode_frame赋值:is->audio_clock = af->pts + (double) af->frame->nb_samples / af->frame->sample_rate;
- 从这⾥可以看出来,这⾥的时间戳是audio_buf结束位置的时间戳,⽽不是audio_buf起始位置的时间戳,所以当audio_buf有剩余时,那实际数据的pts就变成is->audio_clock - (double)(is->audio_write_buf_size) / is->audio_tgt.bytes_per_sec,即是
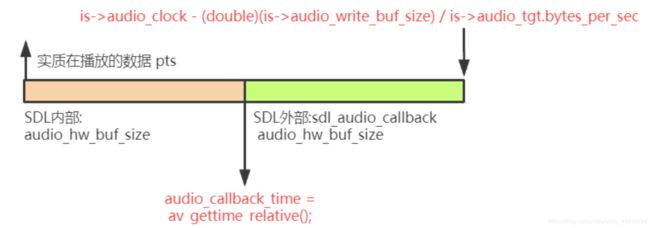
- 再考虑到,实质上audio_hw_buf_size*2这些数据实际都没有播放出去,所以就有is->audio_clock - (double)(2 * is->audio_hw_buf_size + is->audio_write_buf_size) / is->audio_tgt.bytes_per_sec。
- 再加上我们在SDL回调进⾏填充
 时,实际上
时,实际上  是有开始被播放,所以我们这⾥采⽤的相对时间是,刚回调产⽣的,就是内部
是有开始被播放,所以我们这⾥采⽤的相对时间是,刚回调产⽣的,就是内部  在播放的时候,那相对时间实际也在⾛.
在播放的时候,那相对时间实际也在⾛.
- 最终
set_clock_at(&is->audclk, is->audio_clock - (double)(2 * is->audio_hw_buf_size + is-
>audio_write_buf_size) / is->audio_tgt.bytes_per_sec, is->audio_clock_serial,
audio_callback_time / 1000000.0);
4. 回调函数读取数据
- 接下来看下 audio_decode_frame :
static int audio_decode_frame(VideoState *is)
{
int data_size, resampled_data_size;
int64_t dec_channel_layout;
av_unused double audio_clock0;
int wanted_nb_samples;
Frame *af;
if (is->paused)
return -1;
do {
#if defined(_WIN32)
while (frame_queue_nb_remaining(&is->sampq) == 0) {
if ((av_gettime_relative() - audio_callback_time) > 1000000LL * is->audio_hw_buf_size / is->audio_tgt.bytes_per_sec / 2)
return -1;
av_usleep (1000);
}
#endif
if (!(af = frame_queue_peek_readable(&is->sampq)))
return -1;
frame_queue_next(&is->sampq);
} while (af->serial != is->audioq.serial);
data_size = av_samples_get_buffer_size(NULL,
af->frame->channels,
af->frame->nb_samples,
af->frame->format, 1);
dec_channel_layout =
(af->frame->channel_layout &&
af->frame->channels == av_get_channel_layout_nb_channels(af->frame->channel_layout)) ?
af->frame->channel_layout : av_get_default_channel_layout(af->frame->channels);
wanted_nb_samples = synchronize_audio(is, af->frame->nb_samples);
if (af->frame->format != is->audio_src.fmt ||
dec_channel_layout != is->audio_src.channel_layout ||
af->frame->sample_rate != is->audio_src.freq ||
(wanted_nb_samples != af->frame->nb_samples && !is->swr_ctx)
) {
....
}
if (is->swr_ctx) {
const uint8_t **in = (const uint8_t **)af->frame->extended_data;
uint8_t **out = &is->audio_buf1;
int out_count = (int64_t)wanted_nb_samples * is->audio_tgt.freq / af->frame->sample_rate
+ 256;
int out_size = av_samples_get_buffer_size(NULL, is->audio_tgt.channels,
out_count, is->audio_tgt.fmt, 0);
int len2;
if (out_size < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "av_samples_get_buffer_size() failed\n");
return -1;
}
if (wanted_nb_samples != af->frame->nb_samples) {
int sample_delta = (wanted_nb_samples - af->frame->nb_samples) * is->audio_tgt.freq
/ af->frame->sample_rate;
int compensation_distance = wanted_nb_samples * is->audio_tgt.freq / af->frame->sample_rate;
if (swr_set_compensation(is->swr_ctx,
sample_delta,
compensation_distance) < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "swr_set_compensation() failed\n");
return -1;
}
}
av_fast_malloc(&is->audio_buf1, &is->audio_buf1_size, out_size);
if (!is->audio_buf1)
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
len2 = swr_convert(is->swr_ctx, out, out_count, in, af->frame->nb_samples);
if (len2 < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "swr_convert() failed\n");
return -1;
}
if (len2 == out_count) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_WARNING, "audio buffer is probably too small\n");
if (swr_init(is->swr_ctx) < 0)
swr_free(&is->swr_ctx);
}
is->audio_buf = is->audio_buf1;
resampled_data_size = len2 * is->audio_tgt.channels * av_get_bytes_per_sample(is->audio_tgt.fmt);
} else {
is->audio_buf = af->frame->data[0];
resampled_data_size = data_size;
}
audio_clock0 = is->audio_clock;
if (!isnan(af->pts))
is->audio_clock = af->pts + (double) af->frame->nb_samples / af->frame->sample_rate;
else
is->audio_clock = NAN;
is->audio_clock_serial = af->serial;
#ifdef DEBUG
{
static double last_clock;
printf("audio: delay=%0.3f clock=%0.3f clock0=%0.3f\n",
is->audio_clock - last_clock,
is->audio_clock, audio_clock0);
last_clock = is->audio_clock;
}
#endif
return resampled_data_size;
}
- audio_decode_frame 并没有真正意义上的 decode 代码,最多是进⾏了重采样。主流程有以下步骤:
- 从sampq取⼀帧,必要时丢帧。如发⽣了seek,此时serial会不连续,就需要丢帧处理
- 计算这⼀帧的字节数。通过av_samples_get_buffer_size可以⽅便计算出结果
- 获取这⼀帧的数据。对于frame格式和输出设备不同的,需要重采样;如果格式相同,则直接拷⻉指针输出即可。总之,需要在audio_buf中保存与输出设备格式相同的⾳频数据
- 更新audio_clock,audio_clock_serial。⽤于设置audclk.
2. ⾳频重采样
- FFmpeg解码得到的⾳频帧的格式未必能被SDL⽀持,在这种情况下,需要进⾏⾳频重采样,即将⾳频帧格式转换为SDL⽀持的⾳频格式,否则是⽆法正常播放的。
- ⾳频重采样涉及两个步骤:
- 打开⾳频设备时进⾏的准备⼯作:确定SDL⽀持的⾳频格式,作为后期⾳频重采样的⽬标格式。这⼀部分内容参考⾳频输出模块
- ⾳频播放线程中,取出⾳频帧后,若有需要(⾳频帧格式与SDL⽀持⾳频格式不匹配)则进⾏重采样,否则直接输出
1. 重采样逻辑
- ⾳频重采样在 audio_decode_frame() 中实现, audio_decode_frame() 就是从⾳频frame队列中取出⼀个frame,按指定格式经过重采样后输出(解码不是在该函数进⾏)。
- 重采样的细节很琐碎,直接看注释:
static int audio_decode_frame(VideoState *is)
{
int data_size, resampled_data_size;
int64_t dec_channel_layout;
av_unused double audio_clock0;
int wanted_nb_samples;
Frame *af;
if (is->paused)
return -1;
do {
#if defined(_WIN32)
while (frame_queue_nb_remaining(&is->sampq) == 0) {
if ((av_gettime_relative() - audio_callback_time) > 1000000LL * is->audio_hw_buf_size / is->audio_tgt.bytes_per_sec / 2)
return -1;
av_usleep (1000);
}
#endif
if (!(af = frame_queue_peek_readable(&is->sampq)))
return -1;
frame_queue_next(&is->sampq);
} while (af->serial != is->audioq.serial);
data_size = av_samples_get_buffer_size(NULL,
af->frame->channels,
af->frame->nb_samples,
af->frame->format, 1);
dec_channel_layout =
(af->frame->channel_layout &&
af->frame->channels == av_get_channel_layout_nb_channels(af->frame->channel_layout)) ?
af->frame->channel_layout : av_get_default_channel_layout(af->frame->channels);
wanted_nb_samples = synchronize_audio(is, af->frame->nb_samples);
if (af->frame->format != is->audio_src.fmt ||
dec_channel_layout != is->audio_src.channel_layout ||
af->frame->sample_rate != is->audio_src.freq ||
(wanted_nb_samples != af->frame->nb_samples && !is->swr_ctx)
) {
swr_free(&is->swr_ctx);
is->swr_ctx = swr_alloc_set_opts(NULL,
is->audio_tgt.channel_layout,
is->audio_tgt.fmt,
is->audio_tgt.freq,
dec_channel_layout,
af->frame->format,
af->frame->sample_rate,
0, NULL);
if (!is->swr_ctx || swr_init(is->swr_ctx) < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"Cannot create sample rate converter for conversion of %d Hz %s %d channels to %d Hz %s %d channels!\n",
af->frame->sample_rate, av_get_sample_fmt_name(af->frame->format), af->frame->channels,
is->audio_tgt.freq, av_get_sample_fmt_name(is->audio_tgt.fmt), is->audio_tgt.channels);
swr_free(&is->swr_ctx);
return -1;
}
is->audio_src.channel_layout = dec_channel_layout;
is->audio_src.channels = af->frame->channels;
is->audio_src.freq = af->frame->sample_rate;
is->audio_src.fmt = af->frame->format;
}
if (is->swr_ctx) {
const uint8_t **in = (const uint8_t **)af->frame->extended_data;
uint8_t **out = &is->audio_buf1;
int out_count = (int64_t)wanted_nb_samples * is->audio_tgt.freq / af->frame->sample_rate
+ 256;
int out_size = av_samples_get_buffer_size(NULL, is->audio_tgt.channels,
out_count, is->audio_tgt.fmt, 0);
int len2;
if (out_size < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "av_samples_get_buffer_size() failed\n");
return -1;
}
if (wanted_nb_samples != af->frame->nb_samples) {
int sample_delta = (wanted_nb_samples - af->frame->nb_samples) * is->audio_tgt.freq
/ af->frame->sample_rate;
int compensation_distance = wanted_nb_samples * is->audio_tgt.freq / af->frame->sample_rate;
if (swr_set_compensation(is->swr_ctx,
sample_delta,
compensation_distance) < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "swr_set_compensation() failed\n");
return -1;
}
}
av_fast_malloc(&is->audio_buf1, &is->audio_buf1_size, out_size);
if (!is->audio_buf1)
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
len2 = swr_convert(is->swr_ctx, out, out_count, in, af->frame->nb_samples);
if (len2 < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "swr_convert() failed\n");
return -1;
}
if (len2 == out_count) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_WARNING, "audio buffer is probably too small\n");
if (swr_init(is->swr_ctx) < 0)
swr_free(&is->swr_ctx);
}
is->audio_buf = is->audio_buf1;
resampled_data_size = len2 * is->audio_tgt.channels * av_get_bytes_per_sample(is->audio_tgt.fmt);
} else {
is->audio_buf = af->frame->data[0];
resampled_data_size = data_size;
}
audio_clock0 = is->audio_clock;
if (!isnan(af->pts))
is->audio_clock = af->pts + (double) af->frame->nb_samples / af->frame->sample_rate;
else
is->audio_clock = NAN;
is->audio_clock_serial = af->serial;
#ifdef DEBUG
{
static double last_clock;
printf("audio: delay=%0.3f clock=%0.3f clock0=%0.3f\n",
is->audio_clock - last_clock,
is->audio_clock, audio_clock0);
last_clock = is->audio_clock;
}
#endif
return resampled_data_size;
}
2. 样本补偿
- swr_set_compensation说明
int swr_set_compensation(struct SwrContext *s, int sample_delta, int compensation_distance);



 时,实际上
时,实际上  是有开始被播放,所以我们这⾥采⽤的相对时间是,刚回调产⽣的,就是内部
是有开始被播放,所以我们这⾥采⽤的相对时间是,刚回调产⽣的,就是内部  在播放的时候,那相对时间实际也在⾛.
在播放的时候,那相对时间实际也在⾛.