【LeetCode热题100】打卡第43天:会议室II&完全平方数
文章目录
- 【LeetCode热题100】打卡第43天:会议室II&完全平方数
-
- ⛅前言
- 会议室II
-
- 题目
- 题解
- 完全平方数
-
- 题目
- 题解
【LeetCode热题100】打卡第43天:会议室II&完全平方数
⛅前言
大家好,我是知识汲取者,欢迎来到我的LeetCode热题100刷题专栏!
精选 100 道力扣(LeetCode)上最热门的题目,适合初识算法与数据结构的新手和想要在短时间内高效提升的人,熟练掌握这 100 道题,你就已经具备了在代码世界通行的基本能力。在此专栏中,我们将会涵盖各种类型的算法题目,包括但不限于数组、链表、树、字典树、图、排序、搜索、动态规划等等,并会提供详细的解题思路以及Java代码实现。如果你也想刷题,不断提升自己,就请加入我们吧!QQ群号:827302436。我们共同监督打卡,一起学习,一起进步。
PS:作者水平有限,如有错误或描述不当的地方,恳请及时告诉作者,作者将不胜感激
会议室II
题目
原题链接:253.会议室II
题解
-
解法一:优先队列
import java.util.PriorityQueue; /** * @author ghp * @title */ class Solution { public int minMeetingRooms(int[][] intervals) { if (intervals.length == 0) { return 0; } // 升序队列,队头到队尾的元素是从小到大排序的,存储活动的结束时间 PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(intervals.length, (a, b) -> a - b); // 往队列中添加第一场会议的结束时间 queue.offer(intervals[0][1]); // 遍历会议的起始时间 for (int i = 1; i < intervals.length; i++) { // 判断当前会议开始时刻,之前开始的会议中是否存在已经结束的会议 if (intervals[i][0] >= queue.peek()) { // 之前开始的会议中存在已经结束的会议,则将结束的会议从队列中移除 queue.poll(); } queue.offer(intervals[i][1]); } // 所有会议都已经开始了,此时队列中剩余的会议就是存在时间冲突的,需要单独安排会议室 return queue.size(); } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O ( n + m ) O(n+m) O(n+m)
其中 n n n 为会议的数量,即数组的行,m为数组的列,也就是2
-
解法二:暴力
感觉这个暴力比优先队列还要难以理解,本题解参考:[中等] 253. 会议室 II - 简书 (jianshu.com)
个人感觉难以理解的是 end 数组,这个暴力我感觉有点巧妙,end数组表示会议室的数量,还同时记录会议的结束时间,同时表示当前已结束的会议
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; /** * @author ghp * @title */ class Solution { public int minMeetingRooms(int[][] intervals) { // 记录已结束会议的结束时间 List<Integer> end = new ArrayList<>(); // 按开始时间升序 Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]); // 遍历所有的会议 for (int[] meeting : intervals) { boolean isExit = false; // 遍历已结束的会议,判断其中是否存在结束时间早于当前会议起始时间的会议 for (int i = 0; i < end.size(); i++) { int endTime = end.get(i); if (endTime <= meeting[0]) { // 存在结束时间早于当前会议起始时间的会议,需要更新会议的结束时间 end.set(i, meeting[1]); // 找到了当前会议起始时间之前结束的会议,说明不需要新增会议室 isExit = true; break; } } if (!isExit) { // 不存在,说明当前的会议时间与其他会议存在冲突,需要新增会议室 end.add(meeting[1]); } } // end中存在的会议都是与其它至少一个会议有冲突的,所以end的大小就是至少需要的会议室数量 return end.size(); } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
其中 n n n 为数组中元素的个数
拓展内容
前面我们在解法一中使用优先队列一下就解决了问题,感觉意犹未尽,这里我们提高对自己的要求,我们参考PriorityQueue的源码,直接自己手动实现一个优先队列,顺便学习一下优先队列是如何实现的
class MyPriorityQueue {
/**
* 存储队列中的元素
*/
private int[] arr;
/**
* 队列的容量
*/
private int capacity;
/**
* 队列中元素的个数
*/
private int size;
public MyPriorityQueue(int capacity) {
this.arr = new int[capacity];
this.capacity = capacity;
this.size = 0;
}
/**
* 添加元素
* @param val
*/
public void offer(int val) {
arr[size] = val;
size++;
// 把新加入的元素进行向上调整
siftUp(arr, size - 1);
}
/**
* 向上调整元素
* @param arr
* @param index
*/
private static void siftUp(int[] arr, int index) {
int child = index;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0) {
if (arr[parent] < arr[child]) {
// 当前不符合大堆结构,就进行调整
int temp = arr[parent];
arr[parent] = arr[child];
arr[child] = temp;
} else {
// 发现当前父节点比子节点大,这时说明整个数组已经符合堆的要求了
break;
}
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
}
/**
* 移除队尾元素
* @return
*/
public int poll() {
// 下标为0,即队首元素,删除堆顶元素,还要保证剩下的结构依旧为堆
// 先将队首元素保存下来,先将队首元素保存下来,
int result = arr[0];
arr[0] = arr[size - 1];
size--;
// 针对队首元素进行向下调整
siftDown(arr, size, 0);
// 返回保存的队首元素
return result;
}
private static void siftDown(int[] arr, int size, int index) {
int parent = index;
// 通过parent找到child的下标
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < size) {
//比较左右子树找到较大值
if (child + 1 < size && arr[child + 1] > arr[child]) {
child = child + 1;
}
// 经过上面的比较已经不知道child是左子树,还是右子树了
// 但是child下标一定对应左右子树中的较大值下标
//拿child位置元素与parent位置元素比较
if (arr[child] > arr[parent]) {
// 不符合就交换父子节点
int temp = arr[child];
arr[child] = arr[parent];
arr[parent] = temp;
} else {
// 调整完毕,不需要再调整
break;
}
// 更新parent和child节点,处理下一层数据
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
}
/**
* 查看队头元素
* @return
*/
public int peek() {
return arr[0];
}
/**
* 判断队列是否为空
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
}
完全平方数
题目
原题链接:279.完全平方数
题解
-
解法一:DFS(超时 502 / 588 )
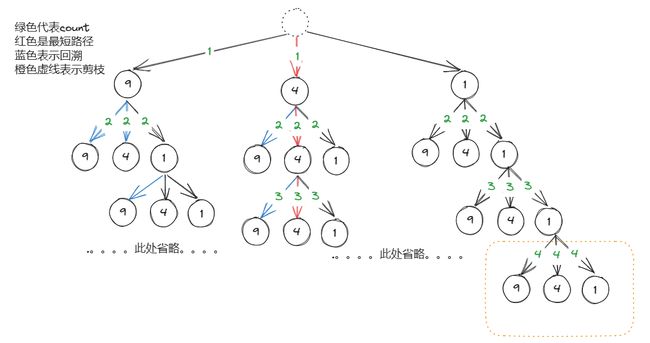
暴力DFS思路很简单,我们需要提前对数据进行处理,使得这个题目转换成一个求最短路径的问题
这里举一例例子:
比如当我们要计算和为12的完全平方数的个数时,我们可以按照以下思路
- 计算完全平方数的个数。我们先对12求平方根,可以得出3,这个3就是能够组成和为12的完全平方根的个数
- 计算完全平方数。然后根据这个3,我们可以提前计算出12可以由哪些完全平方数组成,很容易可以得到 能够组成12 的完全平方数有:1,4,9
- 利用DFS寻找最小组合数,下方是我画的一个比较简单的图解,希望对你的理解有所帮助
/** * @author ghp * @title */ class Solution { // 记录当前和为n的完全平方数的最少数量 private int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; public int numSquares(int n) { // 计算完全平方数的个数 int sqrt = (int) Math.sqrt(n); // 计算完全平方数 int[] square = new int[sqrt]; for (int i = 1; i <= sqrt; i++) { square[i - 1] = i * i; } // 利用DFS搜寻最短路径 dfs(square, n, sqrt - 1, 0, 0); return min == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : min; } private void dfs(int[] square, int target, int index, int sum, int count) { if (sum == target) { // 寻找一种方案,更新min min = Math.min(min, count); return; } if (sum > target || count >= min) { // 剪枝。当前和已经超过目标值 或 当前参与求和平方数的个数已经大于等于最小值了 return; } for (int i = square.length - 1; i > 0; i--) { dfs(square, target, i, sum + square[i], count + 1); } } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( 2 n ) O(2^n) O(2n),由于引入了剪枝操作实际的耗时会比理论上的低
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
其中 n n n 为square数组中元素的个数
代码优化:(优化后还是超时 551 / 588)
- 去除了count和isFind等成员变量,直接采用变量的引用传递。直接进行变量的引用传递通常比使用成员变量要更好,因为这样可以减少对成员变量的访问开销,并且可以避免多线程环境下的竞争和同步问题。而且,使用引用传递可以使代码更清晰和易读。
- 在dfs方法中增加了一个剪枝条件,当当前步数count已经大于等于min时,停止继续搜索
- 在dfs方法中增加了一个next变量,记录下一层最大的值,优化了循环次数(核心优化)
这个 next 能够使得快速定位到下一个数,比如:square=1,4,9,target=12,第一遍index=2,sum=0,此时 next= (12-0)/9=1,下一层遍历就直接从索引为1开始,直接对索引大于1的进行了一个剪枝
/** * @author ghp * @title */ class Solution { // 记录当前和为n的完全平方数的最少数量 private int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; public int numSquares(int n) { // 计算完全平方数的个数 int sqrt = (int) Math.sqrt(n); // 计算完全平方数 int[] square = new int[sqrt]; for (int i = 1; i <= sqrt; i++) { square[i - 1] = i * i; } // 利用DFS搜寻最短路径 dfs(square, n, sqrt - 1, 0, 0); return min == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : min; } private void dfs(int[] square, int target, int index, int sum, int count) { if (sum == target) { // 寻找一种方案,更新min min = Math.min(min, count); return; } if (index < 0 || count >= min) { // 剪枝。已经到最底层了 或 当前参与求和平方数的个数已经大于等于最小值了 return; } // 计算下一层的最大节点 int maxCount = (target - sum) / square[index]; for (int i = maxCount; i > 0; i--) { dfs(square, target, index - 1, sum + i * square[index], count + i); } } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( 2 n ) O(2^n) O(2n),由于引入了剪枝操作实际的耗时会比理论上的低
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
其中 n n n 为square数组中元素的个数
代码优化:(过啦)
我们可以发现之前那种先把所有能够组成n的平方和求出的方式比较蠢,既浪费了空间又浪费了时间,我们完全可以在一边DFS遍历的时候,一遍计算平方和,从最大数到最小数开始搜索。解题的图解和前面的是一致的,就是节约了求取平方和的操作,从而大大节约的时间,但是可以发现这样子,能过,提交后空间占比超过该90%,时间占比只超过5%,所以说这一题DFS并不是终极解法
class Solution { private int minCount = Integer.MAX_VALUE; public int numSquares(int n) { dfs(n, 0); return minCount; } private void dfs(int target, int count) { if (count >= minCount) { // 如果当前数量已经超过最小数量,则直接返回 return; } if (target == 0) { // 如果目标数为0,更新最小数量并返回 minCount = Math.min(minCount, count); return; } for (int i = (int) Math.sqrt(target); i > 0; i--) { // 尝试使用完全平方数进行递归搜索 dfs(target - i * i, count + 1); } } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( 2 n ) O(2^n) O(2n),由于引入了剪枝操作实际的耗时会比理论上的低
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
其中 n n n 为square数组中元素的个数
-
解法二:BFS(超时 502 / 588 )
一般DFS的题目都可以使用BFS解决,同时对于最短路径问题,一般BFS要比DFS要更加快。这里吸取前面的经验,来使用BFS实现
import java.util.Deque; import java.util.LinkedList; /** * @author ghp * @title */ class Solution { public int numSquares(int n) { Deque<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(new int[]{0, 0}); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // 上一层节点的状态 int[] pre = queue.poll(); int sum = pre[0]; int count = pre[1]; if (sum == n || count == min) { // BFS一层一层往下搜,最先等于n的,一定是最段路径,所以这里直接就返回了 return count; } // 遍历下一层 for (int i = (int) Math.sqrt(n); i > 0; i--) { if (sum + i * i <= n) { queue.offer(new int[]{sum + i * i, count + 1}); } } } return -1; } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n 1.5 ) O(n^{1.5}) O(n1.5),在每一层中,内层循环的次数是随着当前节点的值而减少的,即与n有关的次数。每个节点最多可以生成n个节点,因此总共的节点个数是n^1.5级别的。
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n),主要是用来存储队列和集合的空间消耗,并且最坏情况下,所有的数都需要存储在vis集合中
其中 n n n 为square数组中元素的个数
对于最短路径问题,一般BFS要比DFS能容易找到答案
代码优化:(过啦)
直接暴力BFS不能过,我们可以进行记忆化搜索从而实现剪枝效果,
import java.util.Deque; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Set; class Solution { public int numSquares(int n) { Deque<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>(); // 记录搜索的状态 Set<Integer> vis = new HashSet<>(); queue.offer(new int[]{0, 0}); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // 上一层节点的状态 int[] pre = queue.poll(); int sum = pre[0]; int count = pre[1]; if (sum == n || count == min) { // BFS一层一层往下搜,最先等于n的,一定是最段路径,所以这里直接就返回了 return count; } // 遍历下一层 for (int i = (int) Math.sqrt(n); i > 0; i--) { int curSum = sum + i * i; if (!vis.contains(curSum) && curSum <= n) { // 当前层的状态并没有出现,并且当前和也要小于目标值,则可以往下遍历 queue.offer(new int[]{curSum, count + 1}); // 将当前状态添加到vis集合中 vis.add(curSum); } } } return -1; } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n 1.5 ) O(n^{1.5}) O(n1.5),在每一层中,内层循环的次数是随着当前节点的值而减少的,即与n有关的次数。每个节点最多可以生成n个节点,因此总共的节点个数是n^1.5级别的。
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n),主要是用来存储队列和集合的空间消耗,并且最坏情况下,所有的数都需要存储在vis集合中
其中 n n n 为square数组中元素的个数
这里再提供一种方法,参考这位大佬的,我感觉这个BFS解法相当优雅,这里是直接通过 sqrt 计算出下一层节点的最大值,从而不需要遍历所有的可能,不需要像上面那种方法还单独拿一个 vis 去记录状态,使用 sqrt计算后 压根就不需要去当心会有重复状态的出现,它相当于是跳跃式的遍历,这个有点类似与我之前 DFS 中的方法,至少在DFS我想到了,在这里我又没想到w(゚Д゚)w
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; class Solution { public int numSquares(int n) { // 队列记录剩余值 Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.add(n); int count = 0; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { count++; for (int size = queue.size(); size > 0; size--) { // 回溯到上一个节点 int pre = queue.poll(); // 计算下一层最大的值 int next = (int) Math.sqrt(pre); if (next * next == pre) { return count; } for (int i = next; i > 0; i--) { queue.add(pre - i * i); } } } return -1; } } -
解法三:动态规划
本题本质是一个完全背包问题,我们完全可以参考完全背包问题的解法进行求解
题解参考:【宫水三叶】详解完全背包一维空间优化推导(附背包问题攻略) - 完全平方数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
import java.util.Arrays; class Solution { int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; public int numSquares(int n) { // 计算出所有可能用到的完全平方数 int m = (int) Math.sqrt(n); int[] square = new int[m]; for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { square[i - 1] = i * i; } // f[i][j] 代表考虑前 i 个物品,凑出 j 所使用到的最小元素个数 int[][] f = new int[m + 1][n + 1]; // 当没有任何数时,除了 f[0][0] 为 0(花费 0 个数值凑出 0),其他均为无效值 Arrays.fill(f[0], INF); f[0][0] = 0; // 处理剩余数的情况 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { int x = square[i - 1]; for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) { // 对于不选第 i 个数的情况 f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j]; // 对于选 k 次第 i 个数的情况 for (int k = 1; k * x <= j; k++) { // 能够选择 k 个 x 的前提是剩余的数字 j - k * x 也能被凑出 if (f[i - 1][j - k * x] != INF) { f[i][j] = Math.min(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - k * x] + k); } } } } return f[m][n]; } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n 2 ∗ n ) O(n^2*\sqrt{n}) O(n2∗n)
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ∗ n ) O(n*\sqrt{n}) O(n∗n)
其中 n n n 为square数组中元素的个数
代码优化:空间优化
备注:这里我先把题解放这里,今天就先把DFS和BFS的两个解法给消化吸收了,这个动态规划,我把题解和链接先放这里,后面二刷或者后面有时间的时候再来看一看,同样的这个题解也来自【宫水三叶】大佬
二维转一维
class Solution { public int numSquares(int n) { int[] f = new int[n + 1]; Arrays.fill(f, 0x3f3f3f3f); f[0] = 0; for (int t = 1; t * t <= n; t++) { int x = t * t; for (int j = x; j <= n; j++) { f[j] = Math.min(f[j], f[j - x] + 1); } } return f[n]; } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ∗ n ) O(n^*\sqrt{n}) O(n∗n)
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(\sqrt{n}) O(n)
其中 n n n 为square数组中元素的个数
-
解法四:四平方和定理
这是本题的究极解法了,感兴趣的可以去LeetCode官方看看(果然算法的尽头就是数学)
class Solution { public int numSquares(int n) { if (isPerfectSquare(n)) { return 1; } if (checkAnswer4(n)) { return 4; } for (int i = 1; i * i <= n; i++) { int j = n - i * i; if (isPerfectSquare(j)) { return 2; } } return 3; } // 判断是否为完全平方数 public boolean isPerfectSquare(int x) { int y = (int) Math.sqrt(x); return y * y == x; } // 判断是否能表示为 4^k*(8m+7) public boolean checkAnswer4(int x) { while (x % 4 == 0) { x /= 4; } return x % 8 == 7; } } 作者:LeetCode-Solution 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/perfect-squares/solution/wan-quan-ping-fang-shu-by-leetcode-solut-t99c/ 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(\sqrt{n}) O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
参考题解:
- 完全平方数 - 完全平方数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 画解算法:279. 完全平方数 - 完全平方数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 【宫水三叶】详解完全背包一维空间优化推导(附背包问题攻略) - 完全平方数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 标准的 BFS 题解 - 完全平方数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
在此致谢各位LeetCode的大佬