前端 | ( 十三)CSS3简介及基本语法(下)| 伸缩盒模型 | 尚硅谷前端html+css零基础教程2023最新
学习来源:尚硅谷前端html+css零基础教程,2023最新前端开发html5+css3视频
系列笔记:
- 【HTML4】(一)前端简介
- 【HTML4】(二)各种各样的常用标签
- 【HTML4】(三)表单及HTML4收尾
- 【CSS2】(四)CSS基础及CSS选择器
- 【CSS2】(五)CSS三大特性及常用属性
- 【CSS2】(六)CSS盒子模型
- 【CSS2】(七)浮动
- 【CSS2】( 八)定位与布局
- 【实操】( 九)尚品汇实操练习
- 【HTML5】( 十)HTML5简介及相关新增属性
- 【CSS3】( 十一)CSS3简介及基本语法(上)| 相关新增属性
- 【CSS3】( 十二)CSS3简介及基本语法(中)| 变换、过渡与动画
- 【CSS3】 (十三)CSS3简介及基本语法(下)| 伸缩盒模型
文章目录
- 伸缩盒模型
-
- 伸缩盒模型简介
- 伸缩容器、伸缩项目
- 主轴方向
- 主轴换行方式
- flex-flow
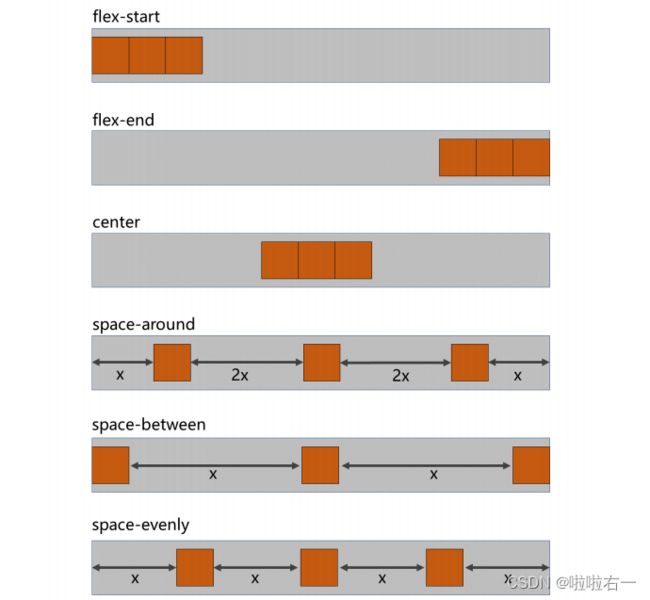
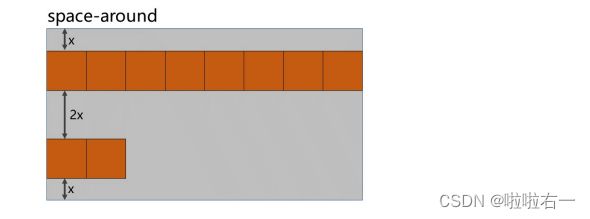
- 主轴对齐方式
- 侧轴对齐方式
- flex实现水平垂直居中
- 伸缩性
- flex复合属性
- 项目排序和单独对齐(了解)
- 案例
- 相应式布局
- BFC
⭐️前文回顾:前端 | ( 十二)CSS3简介及基本语法(中)| 变换、过渡与动画 | 尚硅谷前端html+css零基础教程2023最新
⭐️前文对应p178-p183,本文对应p183-p200
⭐️补充网站:W3school,MDN
伸缩盒模型
伸缩盒模型简介
伸缩容器、伸缩项目
主轴: 伸缩项目沿着主轴排列,主轴默认是水平的,默认方向是:从左到右(左边是起点,右边是终点)。侧轴: 与主轴垂直的就是侧轴,侧轴默认是垂直的,默认方向是:从上到下(上边是起点,下边是终点)。
主轴方向
主轴换行方式
flex-flow
主轴对齐方式
侧轴对齐方式
flex实现水平垂直居中
方法一:父容器开启 flex 布局,随后使用 justify-content 和 align-items 实现水平垂直居中
.outer {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: #888;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.inner {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: orange;
}
方法二:父容器开启 flex 布局,随后子元素 margin: auto
.outer {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: #888;
display: flex;
}
.inner {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: orange;
margin: auto;
}
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>元素水平垂直居中title>
<style>
.outer {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: #888;
display: flex;
/* 方案一 */
/* justify-content: center; */
/* align-items: center; */
}
.inner {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: orange;
/* 方案二 */
margin: auto;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="inner">div>
div>
body>
html>
伸缩性
.inner {
/* 设置伸缩项目在主轴上的基准长度,若主轴是横向的宽失效,若主轴是纵向的高失效 */
flex-basis: 300px;
}
伸
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>伸缩项目_伸title>
<style>
.outer {
width: 1000px;
height: 900px;
background-color: #888;
margin: 0 auto;
/* 伸缩盒模型相关属性-start */
/* 将该元素变为了伸缩容器(开启了flex布局) */
display: flex;
/* 调整主轴方向,水平从左到右,默认 */
flex-direction: row;
/* 主轴换行方式,换行 */
flex-wrap: wrap;
/* 主轴的对齐方式,主轴的起始位置 */
justify-content: flex-start;
}
.inner {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: skyblue;
border: 1px solid black;
box-sizing: border-box;
flex-grow: 0;
}
/* 瓜分比例:1/6 */
.inner1 {
flex-grow: 1;
}
/* 1/3 */
.inner2 {
flex-grow: 2;
width: 300px;
}
/* 1/2 */
.inner3 {
flex-grow: 3;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="inner inner1">1div>
<div class="inner inner2">2div>
<div class="inner inner3">3div>
div>
body>
html>
缩
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>伸缩项目_缩title>
<style>
.outer {
width: 400px;
height: 900px;
background-color: #888;
margin: 0 auto;
/* 伸缩盒模型相关属性-start */
/* 将该元素变为了伸缩容器(开启了flex布局) */
display: flex;
/* 调整主轴方向,水平从左到右,默认 */
flex-direction: row;
/* 主轴换行方式,换行 */
/* 想缩就别说这玩意,不然直接就换行处理了 */
/* flex-wrap: wrap; */
/* 主轴的对齐方式,主轴的起始位置 */
justify-content: flex-start;
/* 侧轴的对齐方式 */
align-content: flex-start;
}
.inner {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: skyblue;
/* border: 1px solid black; */
/* box-sizing: border-box; */
flex-grow: 1;
}
.inner1 {
flex-shrink: 1;
}
.inner2 {
flex-shrink: 2;
width: 300px;
}
.inner3 {
flex-shrink: 3;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="inner inner1">
<div style="width: 50px;height:50px;background-color: green;">1div>
div>
<div class="inner inner2">2div>
<div class="inner inner3">3div>
div>
body>
html>
带上边框,浏览器计算的时候会有一些
误差。实际应用shrink默认就是1,就不写了。简化!
flex复合属性
项目排序和单独对齐(了解)
order属性定义项目的排列顺序。数值越小,排列越靠前,默认为 0 。- 通过
align-self属性,可以单独调整某个伸缩项目的对齐方式 - 默认值为
auto,表示继承父元素的align-items属性。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>项目排序与单独对齐title>
<style>
.outer {
width: 600px;
height: 900px;
background-color: #888;
margin: 0 auto;
/* 伸缩盒模型相关属性-start */
/* 将该元素变为了伸缩容器(开启了flex布局) */
display: flex;
/* 调整主轴方向,水平从左到右,默认 */
flex-direction: row;
/* 主轴换行方式,换行 */
/* flex-wrap: wrap; */
/* 主轴的对齐方式,主轴的起始位置 */
justify-content: flex-start;
/* 侧轴的对齐方式 */
align-content: flex-start;
}
.inner {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: skyblue;
border: 1px solid black;
box-sizing: border-box;
/* 可以拉伸 可以压缩 设置基准长度为0,可简写为:flex:1 */
flex: 1 1 0;
}
.inner1 {
order: 3;
}
.inner2 {
order: 2;
}
.inner3 {
order: 1;
}
.inner2 {
align-self: center;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="inner inner1">1div>
<div class="inner inner2">2div>
<div class="inner inner3">3div>
div>
body>
html>
案例
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>尚硅谷官网title>
<style>
* {
font-family: Arial;
font-size: 14px;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
border: none;
}
a { text-decoration: none; }
ul { list-style: none; }
html,body {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
body {
/* 背景铺满 */
background-image: url('../images/bg.jpg');
/* 背景图不重复 */
background-repeat: no-repeat;
/* 当图片和背景不适配时的最优解 */
background-size: cover;
}
.page-header {
height: 70px;
/* 需要设置透明度 */
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7);
/* 设置伸缩盒子 */
display: flex;
/* 主轴两边定格 */
justify-content: space-between;
/* 侧轴对齐方式 */
align-items: center;
padding: 0 20px;
}
.header-nav {
display: flex;
}
.header-nav li a {
color: white;
font-size: 20px;
border: 1px solid white;
/* 圆角8px */
border-radius: 8px;
padding: 10px;
margin-right: 20px;
}
.header-nav li:last-child a {
margin-right: 0;
}
.page-content {
display: flex;
/* calc进行数值计算 */
height: calc(100vh - 70px);
}
.content-nav {
width: 1000px;
height: 300px;
/* 垂直居中 */
margin: auto;
display: flex;
/* 主轴对齐方式:均分 */
justify-content: space-evenly;
/* 侧轴 */
align-items: center;
}
.content-nav .item {
width: 180px;
height: 200px;
background-color: orange;
display: flex;
/* 转换主轴 */
flex-direction: column;
/* 侧轴 */
align-items: center;
/* 主轴均分 */
justify-content: space-evenly;
transition: 0.2s linear;
cursor: pointer;
}
.content-nav .item:hover {
/* 边框阴影 */
box-shadow: 0px 0px 20px black;
}
.content-nav .item span {
font-size: 20px;
color: white;
}
.content-nav .item:nth-child(1) {
background-color:#595CA8;
}
.content-nav .item:nth-child(2) {
background-color:#FF9D2E;
}
.content-nav .item:nth-child(3) {
background-color:#01A6DE;
}
.content-nav .item:nth-child(4) {
background-color:#015E91;
}
.content-nav .item:nth-child(5) {
background-color:#1DC128;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<header class="page-header">
<a href="#">
<img src="../images/logo.png" alt="logo">
a>
<ul class="header-nav">
<li><a href="#">国内校区a>li>
<li><a href="#">澳洲校区a>li>
<li><a href="#">英国校区a>li>
<li><a href="#">美国校区a>li>
ul>
header>
<div class="page-content">
<div class="content-nav">
<div class="item">
<img src="../images/item1.png" alt="">
<span>我的邮箱span>
div>
<div class="item">
<img src="../images/item2.png" alt="">
<span>云服务span>
div>
<div class="item">
<img src="../images/item3.png" alt="">
<span>手机课堂span>
div>
<div class="item">
<img src="../images/item4.png" alt="">
<span>微信服务span>
div>
<div class="item">
<img src="../images/item5.png" alt="">
<span>在线客服span>
div>
div>
div>
body>
html>
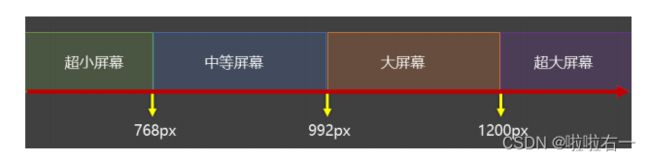
相应式布局
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>01_媒体查询_媒体类型title>
<style>
h1 {
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
line-height: 400px;
background-image: linear-gradient(30deg,red,yellow,green);
margin: 0 auto;
text-align: center;
font-size: 100px;
color: white;
text-shadow: 0 0 10px black;
}
/* 只有在打印机或打印预览才应用的样式 */
@media print {
h1 {
background: transparent;
}
}
/* 只有在屏幕上才应用的样式 */
@media screen {
h1 {
font-family: "翩翩体-简";
}
}
/* 一直都应用的样式 */
@media all {
h1 {
color: red;
}
}
style>
head>
<body>
<h1>新年快乐h1>
body>
html>
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>媒体查询_媒体特性title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
h1 {
height: 200px;
background-color: gray;
text-align: center;
line-height: 200px;
font-size: 100px;
}
/* 检测到视口的宽度为800px时,应用如下样式 */
@media (width:800px) {
h1 {
background-color: green;
}
}
/* 检测到视口的宽度小于等于700px时,应用如下样式 */
@media (max-width:700px) {
h1 {
background-color: orange;
}
}
/* 检测到视口的宽度大于等于900px时,应用如下样式 */
@media (min-width:900px) {
h1 {
background-color: deepskyblue;
}
}
style>
head>
<body>
<h1>你好啊h1>
body>
html>
BFC
更加通俗的理解:
- BFC是
Block Formatting Context (块级格式上下文),可以理解成元素的一个“特异功能”。 - 该 “特异功能”,在默认的情况下处于关闭状态;当元素满足了某些条件后,该“特异功能”被激活。
- 所谓激活“特异功能”,专业点说就是:该元素创建了 BFC (又称:开启了 BFC )。

- 元素开启 BFC 后,其子元素不会再产生 margin 塌陷问题。
- 元素开启 BFC 后,自己不会被其他浮动元素所覆盖。
- 元素开启 BFC 后,就算其子元素浮动,元素自身高度也不会塌陷。