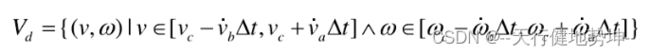路径规划-DWA算法(C++实现)
1、简单介绍
DWA算法(dynamic window approach),其原理主要是在速度空间(v,w)中采样多组速度,并模拟出这些速度在一定时间内的运动轨迹,并通过评价函数对这些轨迹进行评价(其中包括距离障碍物距离,距离目标点距离等等进行评价),选取最优轨迹对应的(v,w)驱动机器人运动。
2、原理
2.1、运动学模型
1)非全向运动:只能前进和旋转(相邻时刻码盘采样,近似直线v*detaT)
x = x + V Δ t cos ( θ t ) x = x+V\Delta t \cos(\theta_{t}) x=x+VΔtcos(θt).
y = y + V Δ t sin ( θ t ) y = y+V\Delta t \sin(\theta_{t}) y=y+VΔtsin(θt).
θ t = θ t + w Δ t \theta_{t} =\theta_{t}+w\Delta t θt=θt+wΔt.
2) 全向运动:存在y上的速度
需要把y轴的移动距离投影到世界坐标系即可
Δ x = v y Δ t cos ( θ t + π / 2 ) = − v y Δ t sin ( θ t ) \Delta x = v_{y}\Delta t\cos(\theta_{t}+\pi/2) = -v_{y}\Delta t\sin(\theta_{t}) Δx=vyΔtcos(θt+π/2)=−vyΔtsin(θt)
Δ y = v y Δ t sin ( θ t + π / 2 ) = v y Δ t cos ( θ t ) \Delta y = v_{y}\Delta t\sin(\theta_{t}+\pi/2) = v_{y}\Delta t\cos(\theta_{t}) Δy=vyΔtsin(θt+π/2)=vyΔtcos(θt)
把y的投影加上上方的的公式
x = x + V Δ t cos ( θ t ) − v y Δ t sin ( θ t ) x = x+V\Delta t \cos(\theta_{t})-v_{y}\Delta t\sin(\theta_{t}) x=x+VΔtcos(θt)−vyΔtsin(θt).
y = y + V Δ t sin ( θ t ) + v y Δ t cos ( θ t ) y = y+V\Delta t \sin(\theta_{t})+v_{y}\Delta t\cos(\theta_{t}) y=y+VΔtsin(θt)+vyΔtcos(θt).
θ t = θ t + w Δ t \theta_{t} =\theta_{t}+w\Delta t θt=θt+wΔt.
需要补充说明的是,令 v ( t ) v_{(t)} v(t)=0,上式与1)中公式表达式完全相同,故ROS中采用2)中的公式进行计算,所以DWA算法适用于两轮差速和全向移动机器人。
2.2 、速度空间(v,w)
机器人的轨迹运动模型有了,根据速度就可以推算出轨迹。因此只需采样很多速度,推算轨迹,然后评价这些轨迹好不好就行了
- 移动机器人受障碍的影响
为了能在碰到障碍物前停下来,在最大减速度的条件下,速度满足以下条件:
其中dist(v,w)为(v,w)对应的轨迹上里障碍物最近的距离。
在上述三条约束条件的限制下,速度空间(v,w)会有一定的范围,另外会随着电机的线加速度、角加速度进行变换,速度空间会动态变化,我们将其称为动态窗口。在满足约束条件的情况下,进行采样(v,w),可以得到相应的轨迹:

2.3、评价函数
在速度空间(v,w)中采样,根据运动学模型推测对应的轨迹,接下来引入评价函数,对轨迹进行打分,选取最优的轨迹。
一般来说,评价函数如下:
其中,heading(v,w)为方位角评价函数:评价机器人在当前的设定的速度下,轨迹末端朝向与目标点之间的角度差距;dist(v,w) 主要的意义为机器人处于预测轨迹末端点位置时与地图上最近障碍物的距离,对于靠近障碍物的采样点进行惩罚,确保机器人的避障能力,降低机器人与障碍物发生碰撞的概率;velocity(v,w)为当前机器人的线速度,为了促进机器人快速到达目标; α , β , γ \alpha , \beta,\gamma α,β,γ为权重。当然,可以对评价函数进行优化,添加更多的评价函数指标。
2.4 、注意事项
- 如果是出小车一直后退,可以通过设置最小速度来避免
- 如果出现,小车无法行走,应该检查一些最大加速度在给定的时间间隔内是否大于最小速度,若不大于最小速度则无法得到有效速度。
- 如果,小车遇到障碍物无法躲避应该把预测时间调大一些试试
2.5 、应用场景
计算复杂度低: 只考虑安全的轨迹,每次采样的时间较短,可以实时避障
应用模型: 适用于两轮差分和全向移动模型、不能用在阿克曼模型。
缺点:
(1)前瞻性不足: 只模拟并评价了下一步,如在机器人前段遇见“C”字形障碍时,不能很好的避障
(2)非全局最优路径: 每次都选择下一步的最佳路径,而非全局最优路径
以上理论参考参考
3、C++实现
代码中的变量设置需要进行修改
#ifndef DWA_H
#define DWA_H
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define PI 3.1415926
struct Car
{
float max_speed = 0.4;
float min_speed = 0.05;
float max_angular_speed = 14 * PI / 180.0; // 0.26
float min_angular_speed = -14 * PI / 180.0;
float max_accel = 0.6;
float max_angular_speed_rate = 7 * PI / 180; // 0.122
float v_resolution = 0.01; // 速度采样分辨率
float yaw_rate_resolution = PI / 180;
float dt = 0.1; //运动学模型预测时间
float predict_time = 6.0;
float goal_cost_gain = 0.15;
float speed_cost_gain = 1.0;
float obstacle_cost_gain = 1.0;
float dis_cost_gain = 0.2;
float radius = 0.3;
};
struct State
{
float x;
float y;
float yaw;
float speed;
float angular_speed;
State(){};
State(float x_, float y_, float yaw_, float speed_, float angular_speed_)
: x(x_), y(y_), yaw(yaw_), speed(speed_), angular_speed(angular_speed_)
{
}
};
class DWA2
{
public:
DWA2();
vector dwaControl(const State &CState);
void dwaControl(const std::vector &robotState,
const std::vector &goal,
const std::vector> &obstacle,
vector &bestSpeed,
std::vector> &nextpath,
const int type = 1);
void dwaControl(
const std::vector &robotState, const std::vector &goal,
std::queue>>> &obstacle,
vector &bestSpeed, std::vector> &nextpath,
const int type = 1);
private:
vector calcDw(const State &CState);
void calcBestSpeed(const State &CState, const vector &dw,
const int type = 1);
void calcBestSpeed(const State &CState, const vector &dw,
const std::vector> &obstacle,
vector &bestSpeed,
std::vector> &nextpath,
const int type = 1);
void calcBestSpeed(
const State &CState, const vector &dw,
std::queue>>> &obstacle,
vector &bestSpeed, std::vector> &nextpath,
const int type = 1);
void predictTrajectory(const State &CState, const float &speed,
const float &angular_speed, vector &trajectory,
const int type = 1);
State motionModel(const State &CState, const float &speed,
const float &angular_speed, const int type = 1);
float calcGoalCost(const vector &trajectory);
float calcObstacleCost(const vector &trajectory);
float calcObstacleCost(const vector &trajectory,
const std::vector> &obstacle,
bool &flag);
float calcObstacleCost(
const vector &trajectory,
std::queue>>> &obstacle_,
bool &flag);
double getAng(double now_x, double now_y, double tar_x, double tar_y,
double now_ang);
Car car;
vector> trajectory;
State destinationState;
bool aaa = false;
int leftTrun = 0;
int rightTrun = 0;
};
#endif // DWA_H
//动态窗口法
void DWA2::dwaControl(const std::vector &robotState,
const std::vector &goal,
const std::vector> &obstacle,
vector &bestSpeed,
std::vector> &nextpath, const int type)
{
State currentState(robotState[0], robotState[1], robotState[2], robotState[3],
robotState[4]);
destinationState.x = goal[0];
destinationState.y = goal[1];
vector dw(
4); // dw[0]为最小速度,dw[1]为最大速度,dw[2]为最小角速度,dw[3]为最大角速度
//计算动态窗口
dw = calcDw(currentState);
//计算最佳(v, w)
calcBestSpeed(currentState, dw, obstacle, bestSpeed, nextpath, type);
return;
}
void DWA2::dwaControl(
const std::vector &robotState, const std::vector &goal,
std::queue>>> &obstacle,
vector &bestSpeed, std::vector> &nextpath,
const int type)
{
State currentState(robotState[0], robotState[1], robotState[2], robotState[3],
robotState[4]);
destinationState.x = goal[0];
destinationState.y = goal[1];
// dw[0]为最小速度,dw[1]为最大速度,dw[2]为最小角速度,dw[3]为最大角速度
vector dw(4);
//计算动态窗口
dw = calcDw(currentState);
//计算最佳(v, w)
calcBestSpeed(currentState, dw, obstacle, bestSpeed, nextpath, type);
return;
}
// 计算动态窗口
vector DWA2::calcDw(const State &CState)
{
// 机器人速度属性限制的动态窗口
vector dw_robot_state{car.min_speed, car.max_speed,
car.min_angular_speed, car.max_angular_speed};
// 机器人模型限制的动态窗口
vector dw_robot_model(4);
dw_robot_model[0] = CState.speed - car.max_accel * car.dt;
dw_robot_model[1] = CState.speed + car.max_accel * car.dt;
dw_robot_model[2] =
CState.angular_speed - car.max_angular_speed_rate * car.dt;
dw_robot_model[3] =
CState.angular_speed + car.max_angular_speed_rate * car.dt;
vector dw{
max(max(dw_robot_state[0], dw_robot_model[0]), car.min_speed),
min(dw_robot_state[1], dw_robot_model[1]),
max(dw_robot_state[2], dw_robot_model[2]),
min(dw_robot_state[3], dw_robot_model[3])};
// std::cout<<"dw : "< &dw,
const std::vector> &obstacle,
vector &bestSpeed,
std::vector> &nextpath,
const int type)
{
vector best_speed{0, 0};
vector trajectoryTmp;
vector trajectory;
float min_cost = 10000;
float final_cost;
float goal_cost;
float speed_cost = 0;
float obstacle_cost = 0;
float distance_cost = 0;
std::vector> temobs = obstacle;
for (float i = dw[0]; i < dw[1]; i += car.v_resolution)
{
for (float j = dw[2]; j < dw[3]; j += car.yaw_rate_resolution)
{
//预测轨迹
trajectoryTmp.clear();
predictTrajectory(CState, i, j, trajectoryTmp, type);
//计算代价
goal_cost = car.goal_cost_gain * calcGoalCost(trajectoryTmp);
speed_cost =
car.speed_cost_gain * (car.max_speed - trajectoryTmp.back().speed);
bool flag = true;
obstacle_cost = car.obstacle_cost_gain *
calcObstacleCost(trajectoryTmp, obstacle, flag);
distance_cost = car.dis_cost_gain *
sqrt(pow(destinationState.x - trajectoryTmp.back().x, 2) +
pow(destinationState.y - trajectoryTmp.back().y, 2));
final_cost = goal_cost + speed_cost + obstacle_cost + distance_cost;
if (final_cost < min_cost && flag)
{
min_cost = final_cost;
best_speed[0] = i;
best_speed[1] = j;
trajectory = trajectoryTmp;
}
if (best_speed[0] < 0.001 && CState.speed < 0.001)
{
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
for (auto ob : temobs)
{
float dis = sqrt(pow(ob[0] - trajectory[trajectory.size() - 1].x, 2) +
pow(ob[1] - trajectory[trajectory.size() - 1].y, 2));
if (dis > car.radius + 0.1)
{
continue;
}
// double ang = getAng(CState.x,CState.y, ob[0], ob[1],
// CState.yaw);
double ang = getAng(trajectory[trajectory.size() - 1].x,
trajectory[trajectory.size() - 1].y, ob[0], ob[1],
CState.yaw);
if (ang > 0)
{
left++;
}
else
{
right++;
}
}
if (left >= right)
{
std::cout << "in left" << std::endl;
best_speed[1] = -(car.max_angular_speed_rate * 0.5) * type;
}
else
{
std::cout << "in right" << std::endl;
best_speed[1] = (car.max_angular_speed_rate * 0.5) * type;
}
std::cout << "*********" << std::endl;
}
}
}
cout << "best_speed:" << best_speed[0] << " , " << best_speed[1] << endl;
bestSpeed = best_speed;
nextpath.clear();
for (auto nextpoint : trajectory)
{
nextpath.push_back(std::vector{nextpoint.x, nextpoint.y});
}
return;
}
void DWA2::calcBestSpeed(
const State &CState, const vector &dw,
std::queue>>> &obstacle,
vector &bestSpeed, std::vector> &nextpath,
const int type)
{
vector best_speed{0, 0};
vector trajectoryTmp;
vector trajectory;
float min_cost = 10000;
float final_cost;
float goal_cost;
float speed_cost = 0;
float obstacle_cost = 0;
float distance_cost = 0;
std::queue>>> temobs = obstacle;
for (float i = dw[0]; i < dw[1]; i += car.v_resolution)
{
for (float j = dw[2]; j < dw[3]; j += car.yaw_rate_resolution)
{
//预测轨迹
trajectoryTmp.clear();
predictTrajectory(CState, i, j, trajectoryTmp, type);
//计算代价
goal_cost = car.goal_cost_gain * calcGoalCost(trajectoryTmp);
speed_cost =
car.speed_cost_gain * (car.max_speed - trajectoryTmp.back().speed);
bool flag = true;
obstacle_cost = car.obstacle_cost_gain *
calcObstacleCost(trajectoryTmp, obstacle, flag);
distance_cost = car.dis_cost_gain *
sqrt(pow(destinationState.x - trajectoryTmp.back().x, 2) +
pow(destinationState.y - trajectoryTmp.back().y, 2));
final_cost = goal_cost + speed_cost + obstacle_cost + distance_cost;
if (final_cost < min_cost && flag)
{
min_cost = final_cost;
best_speed[0] = i;
best_speed[1] = j;
trajectory = trajectoryTmp;
}
if (best_speed[0] < 0.001 && CState.speed < 0.001)
{
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
int queue_size = temobs.size();
for (int i = 0; i < queue_size; i++)
{
std::vector>> obsvec = temobs.front();
temobs.push(obsvec);
temobs.pop();
for (auto obs : obsvec)
{
for (auto ob : obs)
{
float dis = sqrt(
pow(ob[0] - trajectoryTmp[trajectoryTmp.size() - 1].x, 2) +
pow(ob[1] - trajectoryTmp[trajectoryTmp.size() - 1].y, 2));
if (dis > car.radius + 0.1)
{
continue;
}
// double ang = getAng(CState.x,CState.y, ob[0], ob[1],
// CState.yaw);
double ang = getAng(trajectoryTmp[trajectoryTmp.size() - 1].x,
trajectoryTmp[trajectoryTmp.size() - 1].y,
ob[0], ob[1], CState.yaw);
if (ang > 0)
{
left++;
}
else
{
right++;
}
}
}
}
if (left >= right)
{
std::cout << "in left" << std::endl;
best_speed[1] = -(car.max_angular_speed_rate * 0.8);
}
else
{
std::cout << "in right" << std::endl;
best_speed[1] = (car.max_angular_speed_rate * 0.8);
}
std::cout << "xxxxxxxx" << std::endl;
}
}
}
cout << "best_speed:" << best_speed[0] << ", " << best_speed[1] << endl;
bestSpeed = best_speed;
nextpath.clear();
for (auto nextpoint : trajectory)
{
nextpath.push_back(std::vector{nextpoint.x, nextpoint.y});
}
return;
}
// 在一段时间内预测轨迹
void DWA2::predictTrajectory(const State &CState, const float &speed,
const float &angular_speed,
vector &trajectory, const int type)
{
float time = 0;
State nextState = CState;
nextState.speed = speed;
nextState.angular_speed = angular_speed;
while (time < car.predict_time)
{
nextState = motionModel(nextState, speed, angular_speed, type);
if (aaa)
cout << "nextState:(" << nextState.x << ", " << nextState.y << ", "
<< nextState.yaw * 180 / PI << ")" << nextState.speed << " "
<< nextState.angular_speed << endl;
trajectory.push_back(nextState);
time += car.dt;
}
}
double DWA2::getAng(double now_x, double now_y, double tar_x, double tar_y,
double now_ang)
{
double x = cos(now_ang) * (tar_x - now_x) + sin(now_ang) * (tar_y - now_y);
double y = -sin(now_ang) * (tar_x - now_x) + cos(now_ang) * (tar_y - now_y);
double ang = atan2(y, x);
return ang;
// var angle = 180 / Math.PI * radian; // 根据弧度计算角度
}
//根据动力学模型计算下一时刻状态
State DWA2::motionModel(const State &CState, const float &speed,
const float &angular_speed, const int type)
{
State nextState;
float nowx = CState.x;
float nowy = CState.y;
float nowang = nextState.yaw;
nextState.x = CState.x + speed * car.dt * cos(CState.yaw);
nextState.y = CState.y + speed * car.dt * sin(CState.yaw);
nextState.yaw = CState.yaw + angular_speed * car.dt;
nextState.speed = CState.speed;
nextState.angular_speed = CState.angular_speed;
return nextState;
}
// 计算方位角代价
float DWA2::calcGoalCost(const vector &trajectory)
{
float error_yaw = atan2(destinationState.y - trajectory.back().y,
destinationState.x - trajectory.back().x);
float goal_cost = error_yaw - trajectory.back().yaw;
// cout << "error_yaw :" << error_yaw << " yaw:" <<
// trajectory.back().yaw;
goal_cost = atan2(sin(goal_cost), cos(goal_cost));
// cout << " final:" << goal_cost << endl;
if (goal_cost >= 0)
return goal_cost;
else
return -goal_cost;
}
// 计算障碍代价
float DWA2::calcObstacleCost(const vector &trajectory,
const std::vector> &obstacle,
bool &flag)
{
float distance;
for (auto obs : obstacle)
{
for (int j = 0; j < trajectory.size() - 1; j++)
{
distance = sqrt(pow(obs[0] - trajectory[j].x, 2) +
pow(obs[1] - trajectory[j].y, 2));
if (distance <= car.radius)
{
flag = false;
return 10000.0;
}
}
}
return 0;
// return minDis;
}
float DWA2::calcObstacleCost(
const vector &trajectory,
std::queue>>> &obstacle_,
bool &flag)
{
float distance;
float minDis = FLT_MAX;
while (!obstacle_.empty())
{
std::vector>> obstacle = obstacle_.front();
obstacle_.pop();
for (auto obs1 : obstacle)
{
for (auto obs : obs1)
{
for (int j = 0; j < trajectory.size() - 1; j++)
{
distance = sqrt(pow(obs[0] - trajectory[j].x, 2) +
pow(obs[1] - trajectory[j].y, 2));
if (distance <= car.radius)
{
flag = false;
return 10000.0;
}
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
dwa2->dwaControl(
std::vector{now_x, now_y, now_ang, control_opt[0], control_opt[1]},
std::vector{robot_x, robot_y}, obsBoxQueue, control_opt,
trajectory_opt);
return 0;
}