2021SC@SDUSC-Zxing(七):解码关键类详解-Reader
2021SC@SDUSC
文章目录
-
- 一、Reader方法
- 二、万能解码类 —— MultiFormatReader
- 三、ORCode解码类—— QRCodeReader
-
-
- 一、二维码介绍
- 二、解码流程图
- 三、QRCodeReader中的方法
-
- 三、总结
之前的文章都是对图片的处理工作,这篇文章开始介绍核心的解码类,接口Reade的实现类有很多,仅解释部分种类的解码过程,其余种类的码如果有时间再详细介绍。

一、Reader方法
此接口的实现可以将某种格式的条形码图像解码为其编码的字符串。例如,com.google.zxing.qrcode.QRCodeReader可以解码二维码。解码器可选择性地从调用者接收提示,这可帮助其更快或更准确地解码。
| 方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| decode(BinaryBitmap image) | 在图像中以某种格式定位和解码条形码。image要解码的条形码图像;返回值为条形码编码的返回字符串(封装为result,将会在下一篇博客讲解)。抛出异常:如果未找到潜在的条形码,则引发NotFoundException;如果找到潜在条形码但未通过其校验和,则引发ChecksumException;如果找到可能的条形码但格式无效,则引发FormatException |
| decode(BinaryBitmap image, Map |
在图像中以某种格式定位和解码条形码。此方法还接受提示,每个提示可能与某些数据关联,这可能有助于实现解码。image要解码的条形码图像;hints作为Map从 DecodeHintType传递给任意数据。数据的含义取决于提示类型。实现可能使用这些提示,也可能不使用这些提示。 返回值为条形码编码的返回字符串(封装为result,将会在下一篇博客讲解)。抛出异常:如果未找到潜在的条形码,则引发NotFoundException;如果找到潜在条形码但未通过其校验和,则引发ChecksumException;如果找到可能的条形码但格式无效,则引发FormatException |
| reset() | 重置解码后实现的任何内部状态,以准备重用。void类型,无返回值 |
二、万能解码类 —— MultiFormatReader
MultiFormatReader是一个工厂类,是大多数应用程序库的主要入口点。默认情况下,它尝试解码库支持的所有条形码格式。
通过这个类引用的包就可以看出它确实是个比较综合的类别,几乎涵盖了Zxing所能解析的所有码的类型(BarcodeFormat中有的所有类型,BarcodeFormat介绍见2021SC@SDUSC-Zxing(八)):
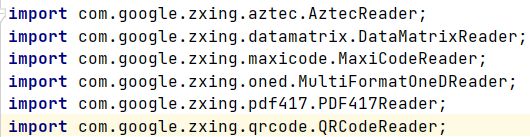
由于使用方便,javase和安卓的decode()调用的都是这个方法。
这个类最关键的方法就是确定码的类型以便调用相应的Reader的setHints方法。这个方法的代码思想如下图所示:

可见下图,二维码和条形码大小近似,但是优先扫描的是条形码。

此外,Zxing的作者在编写代码的时候,比起解码速度更加注重的的解码的准确性。代码中的DecodeHintType.TRY_HARDER表示的就是这个意思。
代码如下:
public void setHints(Map<DecodeHintType,?> hints) {
this.hints = hints;
boolean tryHarder = hints != null && hints.containsKey(DecodeHintType.TRY_HARDER);
//告诉编译器忽略 unchecked 警告信息,如使用List,ArrayList等未进行参数化产生的警告信息。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Collection<BarcodeFormat> formats =
hints == null ? null : (Collection<BarcodeFormat>) hints.get(DecodeHintType.POSSIBLE_FORMATS);
Collection<Reader> readers = new ArrayList<>();
if (formats != null) {
boolean addOneDReader =
formats.contains(BarcodeFormat.UPC_A) ||
formats.contains(BarcodeFormat.UPC_E) ||
formats.contains(BarcodeFormat.EAN_13) ||
formats.contains(BarcodeFormat.EAN_8) ||
formats.contains(BarcodeFormat.CODABAR) ||
formats.contains(BarcodeFormat.CODE_39) ||
formats.contains(BarcodeFormat.CODE_93) ||
formats.contains(BarcodeFormat.CODE_128) ||
formats.contains(BarcodeFormat.ITF) ||
formats.contains(BarcodeFormat.RSS_14) ||
formats.contains(BarcodeFormat.RSS_EXPANDED);
// 将条形码Reader提前置于“normal”模式
if (addOneDReader && !tryHarder) {
readers.add(new MultiFormatOneDReader(hints));
}
if (formats.contains(BarcodeFormat.QR_CODE)) {
readers.add(new QRCodeReader());
}
if (formats.contains(BarcodeFormat.DATA_MATRIX)) {
readers.add(new DataMatrixReader());
}
if (formats.contains(BarcodeFormat.AZTEC)) {
readers.add(new AztecReader());
}
if (formats.contains(BarcodeFormat.PDF_417)) {
readers.add(new PDF417Reader());
}
if (formats.contains(BarcodeFormat.MAXICODE)) {
readers.add(new MaxiCodeReader());
}
// 最后以“try harder”模式结束
if (addOneDReader && tryHarder) {
readers.add(new MultiFormatOneDReader(hints));
}
}
if (readers.isEmpty()) {
if (!tryHarder) {
readers.add(new MultiFormatOneDReader(hints));
}
readers.add(new QRCodeReader());
readers.add(new DataMatrixReader());
readers.add(new AztecReader());
readers.add(new PDF417Reader());
readers.add(new MaxiCodeReader());
if (tryHarder) {
readers.add(new MultiFormatOneDReader(hints));
}
}
this.readers = readers.toArray(EMPTY_READER_ARRAY);
}
三、ORCode解码类—— QRCodeReader
我们首先介绍一下在Reader介绍中出现的QRCodeReader类。这个实现类可以检测和解码图像中的QR码。
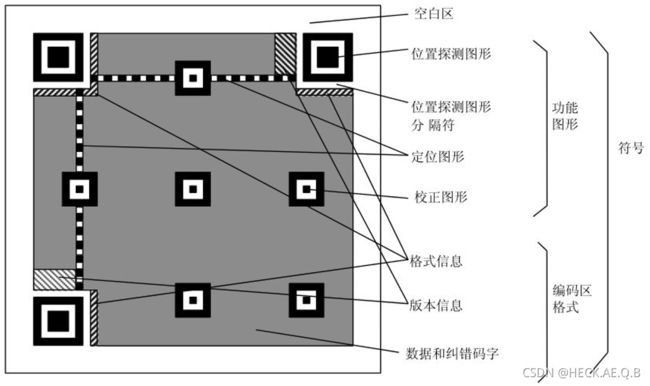
一、二维码介绍
功能图形:起到定位的作用
位置探测图形:由三个黑白相间的大正方形嵌套组成,分别位于二维码左上角、右上角、左下角,目的是为了确定二维码的大小和位置。
定位图形:由两条黑白相间的直线组成,便于确定二维码的角度,纠正扭曲。
校正图形:仅在版本2以上存在,由三个黑白相间的小正方形嵌套组成,便于确定中心,纠正扭曲。 数据区记录了具体的数据信息,纠错信息与版本信息。
数据和纠错码:记录了数据信息和相应的纠错码,纠错码的存在使得当二维码的数据出现允许范围内的错误时,也可以正确解码。
版本信息:仅在版本7以上存在,记录具体的版本信息。 格式信息:记录使用的掩码和纠错等级。
此外二维码的外围还留有一圈空白区,主要是为了便于识别而存在。其中不能有图样或标记,以保证QR码清晰可识别。
对于一些信息少的小型QR码,会按照规定的方式减少校正标志位,白边(静态区域)的大小也会缩小:

我觉得QR码的定位标志设置的非常巧妙,左上、左下、右下各一个“回”字标志,协助扫描软件定位。有了这些定位标志就可以让QR码在任意角度被扫描,这是一维条形码做不到的。也由于定位的功能,在不同的QR码中,“回”字标志的区域大小是固定的。

二、解码流程图
BitMatrix可视化输出:Zxing(九)-4.Reader
Detector讲解:Zxing(十一)
Dcoder讲解:Zxing(十二)
三、QRCodeReader中的方法
| 方法 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
| getDecoder() | Decoder实现二维码解码的主要类——与从图像中定位和提取二维码相对。 |
| decode(BinaryBitmap image) | 重写方法 |
| decode(BinaryBitmap image, Map |
重写方法 |
| reset() | 重写方法 |
| extractPureBits(BitMatrix image) | 该方法检测“纯”图像中的代码,即纯单色图像,该图像仅包含未旋转、未倾斜的代码图像,周围有一些白色边框。这是一种特殊的方法,在这种特殊情况下工作异常迅速。 |
| moduleSize(int[] leftTopBlack, BitMatrix image) | 获取二维码块的大小 |
decode(BinaryBitmap image, Map
public final Result decode(BinaryBitmap image, Map<DecodeHintType,?> hints)
throws NotFoundException, ChecksumException, FormatException {
// DecoderResult类介绍:封装解码位矩阵的结果。这通常适用于二维条形码格式。
// 目前,它包含获得的原始字节,以及这些字节的字符串解释。
DecoderResult decoderResult;
//ResultPoint将关注点封装在包含条形码的图像中。例如,这通常是查找器图案的位置或条形码的一角
ResultPoint[] points;
//初始化阶段
//这一步表示Reader不需借助Detector就可以定位二维码区域。如果hints不为空并且图像是码的纯单色图像。单色图像:黑白图像,黑1白0
if (hints != null && hints.containsKey(DecodeHintType.PURE_BARCODE)) {
// 定义bits为二值图像,捕获有白色边框的二维码区域
BitMatrix bits = extractPureBits(image.getBlackMatrix());
// 给decoderResult初始化
decoderResult = decoder.decode(bits, hints);
// 给points初始化
points = NO_POINTS;
} else {
// 这一步表示Reader需要借助Detector定位二维码。
// image.getBlackMatrix()是矩阵在第一次请求时按需创建,然后缓存。这个方法使用昂贵,不建议频繁调用
DetectorResult detectorResult = new Detector(image.getBlackMatrix()).detect(hints);
// 给decoderResult初始化
decoderResult = decoder.decode(detectorResult.getBits(), hints);
// 给points初始化
points = detectorResult.getPoints();
}
// If the code was mirrored: swap the bottom-left and the top-right points.
// 如果代码被镜像(由于图片是可以通过安卓端传递过来的,相机取景时有将图片镜像的可能):交换左下角点和右上角点。
//instanceof是Java中的二元运算符,左边是对象,右边是类;当对象是右边类或子类所创建对象时,返回true;否则,返回false。
if (decoderResult.getOther() instanceof QRCodeDecoderMetaData) {
((QRCodeDecoderMetaData) decoderResult.getOther()).applyMirroredCorrection(points);
}
// 返回解码得到的字符串
Result result = new Result(decoderResult.getText(), decoderResult.getRawBytes(), points, BarcodeFormat.QR_CODE);
// 返回结果中的字节段列表。如果没有,返回null
List<byte[]> byteSegments = decoderResult.getByteSegments();
if (byteSegments != null) {
result.putMetadata(ResultMetadataType.BYTE_SEGMENTS, byteSegments);
}
// 使用的错误更正级别的名称,没有返回null
String ecLevel = decoderResult.getECLevel();
if (ecLevel != null) {
result.putMetadata(ResultMetadataType.ERROR_CORRECTION_LEVEL, ecLevel);
}
// 如果代码格式支持结构化追加,并且当前扫描的代码是其中的一部分。
if (decoderResult.hasStructuredAppend()) {
//序列号随附
result.putMetadata(ResultMetadataType.STRUCTURED_APPEND_SEQUENCE,
decoderResult.getStructuredAppendSequenceNumber());
//码与码之间关系平等
result.putMetadata(ResultMetadataType.STRUCTURED_APPEND_PARITY,
decoderResult.getStructuredAppendParity());
}
// 条形码符号标识符。注:根据GS1规范,在条形码内容前加前缀时,标识符可能必须替换前导FNC1/GS字符。
result.putMetadata(ResultMetadataType.SYMBOLOGY_IDENTIFIER, "]Q" + decoderResult.getSymbologyModifier());
return result;
}
单色图像(纯黑白、0/1图像):二维码的本质就是一些按照特定规则排序的01码

extractPureBits(BitMatrix image)详解(已注释):
由decode方法我们知道,主要负责extractPureBits捕获有白色边框的二维码区域。这个方法会检测纯单色图像(该图像仅包含未旋转、未倾斜的代码图像,周围有一些白色边框),这是一种特殊的方法,在这种特殊的情况下识别异常迅速。
private static BitMatrix extractPureBits(BitMatrix image) throws NotFoundException {
int[] leftTopBlack = image.getTopLeftOnBit();
int[] rightBottomBlack = image.getBottomRightOnBit();
// NotFoundException.getNotFoundInstance():在图像中找不到条形码时引发。可能已部分检测到,但无法确认。
if (leftTopBlack == null || rightBottomBlack == null) {
throw NotFoundException.getNotFoundInstance();
}
float moduleSize = moduleSize(leftTopBlack, image);
int top = leftTopBlack[1];
int bottom = rightBottomBlack[1];
int left = leftTopBlack[0];
int right = rightBottomBlack[0];
// 检查
if (left >= right || top >= bottom) {
throw NotFoundException.getNotFoundInstance();
}
if (bottom - top != right - left) {
// 特殊情况下,右下角的模块不是黑色的
// 假设它是正方形,那么使用高度作为宽度
right = left + (bottom - top);
if (right >= image.getWidth()) {
// 如果这样做没有意义,请中止--关闭图像
throw NotFoundException.getNotFoundInstance();
}
}
int matrixWidth = Math.round((right - left + 1) / moduleSize);
int matrixHeight = Math.round((bottom - top + 1) / moduleSize);
if (matrixWidth <= 0 || matrixHeight <= 0) {
throw NotFoundException.getNotFoundInstance();
}
if (matrixHeight != matrixWidth) {
// 仅可能解码方形区域
throw NotFoundException.getNotFoundInstance();
}
//将“边框”推到模块宽度的一半,这样我们就开始在模块中间进行采样。以防图像有点失真,这将有助于恢复。
int nudge = (int) (moduleSize / 2.0f);
top += nudge;
left += nudge;
//但请注意,这不会从边缘采样。“right”是最右边的有效像素位置——right+1不一定是。
//这是正的,因为下面的内部x循环太大
int nudgedTooFarRight = left + (int) ((matrixWidth - 1) * moduleSize) - right;
if (nudgedTooFarRight > 0) {
if (nudgedTooFarRight > nudge) {
// 两种方式都不合适;中止
throw NotFoundException.getNotFoundInstance();
}
left -= nudgedTooFarRight;
}
// 参见上面的逻辑
int nudgedTooFarDown = top + (int) ((matrixHeight - 1) * moduleSize) - bottom;
if (nudgedTooFarDown > 0) {
if (nudgedTooFarDown > nudge) {
// 两种方式都不合适;中止
throw NotFoundException.getNotFoundInstance();
}
top -= nudgedTooFarDown;
}
// 现在只需读出这些信息
BitMatrix bits = new BitMatrix(matrixWidth, matrixHeight);
for (int y = 0; y < matrixHeight; y++) {
int iOffset = top + (int) (y * moduleSize);
for (int x = 0; x < matrixWidth; x++) {
if (image.get(left + (int) (x * moduleSize), iOffset)) {
bits.set(x, y);
}
}
}
return bits;
}
三、总结
通过UML我们可以看出decode是解码的核心,这部分我们会在后面章节单独介绍
拓展知识:
二维码较条形码优点
- 存储大容量信息
传统的条形码只能处理20位左右的信息量,与此相比,QR码可处理条形码的几十倍到几百倍的信息量。 - 在小空间内打印
QR码使用纵向和横向两个方向处理数据,如果是相同的信息量,QR码所占空间为条形码的十分之一左右。

- 有效表现各种字母
QR码是日本国产的二维码,因此非常适合处理日文字母和汉字。QR码字集规格定义是按照日本标准“JIS第一级和第二级的汉字”制定的,因此在日语处理方面,每一个全角字母和汉字都用13比特的数据处理,效率较高,与其他二维码相比,可以多存储20%以上的信息。

欢迎提出宝贵意见,感谢观看!
参考:
ZxingAPI
二维码知识介绍
二维码(QR code)基本结构及生成原理