【网络】HTTP协议
目录
一、URL
二、HTTP协议
1、HTTP请求格式
2、HTTP响应格式
3、HTTP的方法
4、HTTP的状态码
5、HTTP常见Header
三、实现简单的HTTP服务器
1、基础版本
2、增加web目录
3、目标文件中包含多种资源
4、添加状态码
4.1、客户端错误状态码
4.2、重定向状态码
5、设置Cookie
HTTP协议又称超文本传输协议。用于网络中资源的相互传输。
一、URL
经过之前的学习,我们知道想要访问服务器,就必须要知道该服务器的IP与端口号。
平时我们俗称的 "网址" 其实就是说的 URL(统一资源定位符),拿到一个网站的URL后,会首先对域名进行解析服务:
现在我们经常能看得的URL比如:
只能看到协议名与服务器地址,而没有其他部分。
这是因为现在的网站进入时一般不需要登录,所以直接删除了登录信息。server端的端口号必须是众所周知的且不能随意更改,所以端口号和成熟的应用层协议是一一对应的。即协议名称与端口号,一对一,强相关。http协议的端口号是80,https协议的端口号是443。用户登陆网站时,会根据协议名自动找到端口号,不需要写出来。
带层次的文件路径表明我们想要访问什么资源。第一个 "/" 是web根目录。
"?" 是区分URL左侧和右侧的分隔符。 "?" 的右侧跟的都是参数,这些参数最终会交给访问的资源。参数都是kv的,k和v通过"="连接,多个kv之间通过"&"连接。
"#" 是片段分隔符,现在已经很少见了,不做考虑。
如果用户的访问内容本身带有 "?、#、/" 等特殊字符,则会被浏览器或某种客户端自动转换成对应的16进制格式,以与URL的固定字符做区分。这个过程叫做URL的encode编码,主要用于解决URL中出现特殊符号的问题。一般的httpserver收到这些16进制格式后,需要进行decode,把它们转换回原有的字符。
转义的规则如下:
将需要转码的字符转为16进制,然后从右到左,取4位(不足4位直接处理),每2位做一位,前面加上%,编码成%XY格式。
二、HTTP协议
1、HTTP请求格式
- 请求行:[方法] + [url] + [版本]
- 请求报头Header:请求的属性,冒号分割的键值对。每组属性之间使用\n分隔。遇到空行表示Header部分结束。
- 空行。
- 有效载荷Body:空行后面的内容都是Body。Body允许为空字符串。如果Body存在, 则在Header中会有一个Content-Length属性来标识Body的长度。
2、HTTP响应格式
- 请求行:[版本号] + [状态码] + [状态码解释]
- 请求报头Header:请求的属性,冒号分割的键值对。每组属性之间使用\n分隔。遇到空行表示Header部分结束。
- 有效载荷Body:空行后面的内容都是Body。Body允许为空字符串。如果Body存在,则在Header中会有一个Content-Length属性来标识Body的长度。如果服务器返回了一个html页面,那么html页面内容就是在body中。
3、HTTP的方法
其中最常用的就是GET方法和POST方法。
- GET能获取一个静态网页(server->client),也可以通过URL的方式提交参数(client->server)。
- POST方法用于提交参数(client->server),但是是通过正文部分提交的。
GET方法提交参数,不私秘,因为这样会把参数回显到浏览器的URL部分。
POST方法提交参数比较私秘一些,所以所有的登录、注册、支付等等行为,都要使用POST方法。但是POST方法也是不安全的,因为正文部分也会被抓包抓到。所以还需要把参数做一些加密工作。
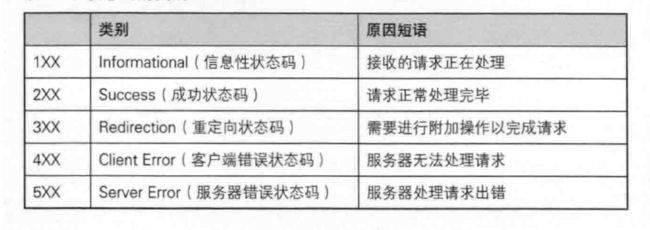
4、HTTP的状态码
最常见的状态码,比如 200(OK),404(Not Found),403(Forbidden),302(Redirect,重定向),504(Bad Gateway)。
5、HTTP常见Header
- Content-Type:数据类型(text/html等)
- Content-Length:Body的长度
- Host:客户端告知服务器, 所请求的资源是在哪个主机的哪个端口上;
- User-Agent:声明用户的操作系统和浏览器版本信息;
- referer:当前页面是从哪个页面跳转过来的;
- location:搭配3xx状态码使用, 告诉客户端接下来要去哪里访问;
- Cookie:用于在客户端存储少量信息. 通常用于实现会话(session)的功能
关于http的会话保持功能:
http本身是无状态的,即无法记录之前的访问状态,因为http的本职工作是进行超文本传输,但是http也参与了会话保持功能(比如浏览器访问网站登录账号后,下次再访问就不需要登陆了)。
http的会话保持功能是通过cookie实现的。当用户第一次登录账号,登陆成功后,服务器会把用户名、密码等私人信息携带到http响应里。当浏览器收到携带Set-Cookie选项的信息时,会将响应中的cookie信息在本地进行保存,保存方案有内存级和文件级。下一次再访问同样的网站时,浏览器所构建的请求都会有一个cookie属性,把保存的历史cookie信息携带上,不用用户手动操作。
因为cookie中存储的信息一般都很重要,且存在被盗取的风险,所以需要一层保护保护,即在服务器端形成session对象。
用户第一次登录,服务器认证成功后,会在服务器内部形成session对象,并用当前用户的基本信息做填充,同时生成一个唯一的session id。之后服务器在http响应里携带的Set-Cookie属性中就只包含session id了。浏览器在收到响应后,把session id保存到本地的cookie属性中。此时浏览器本地的cookie信息只包含session id与session id的有效期。用户下次访问时,浏览器会把session id包含到cookie中构建请求发送到服务器,服务器拿到session id在自己的本地查找对比,找到了相同的就直接允许访问了。
三、实现简单的HTTP服务器
1、基础版本
//HttpServer.hpp
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "Sock.hpp"
static const uint16_t defaultport = 8888;
using func_t = std::function;
class HttpServer;
class ThreadData
{
public:
ThreadData(int sock, std::string ip, uint16_t port, HttpServer *tsvrp)
: _sock(sock), _ip(ip), _port(port), _tsvrp(tsvrp)
{
}
uint16_t _sock;
std::string _ip;
uint16_t _port;
HttpServer *_tsvrp;
};
class HttpServer
{
public:
HttpServer(func_t func, uint16_t port = defaultport)
: _func(func), _port(port)
{
}
void InitServer()
{
_listensock.Socket();
_listensock.Bind(_port);
_listensock.Listen();
}
void HandlerHttpRequest(int sock)
{
char buffer[4096];
std::string request;
ssize_t s = recv(sock, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1, 0);
if (s > 0)
{
buffer[s] = 0;
request = buffer;
std::string response = _func(request);
send(sock, response.c_str(), response.size(), 0);
}
else
{
logMessage(INFO, "client quit...");
}
}
static void *threadRoutine(void *args)
{
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
ThreadData *td = static_cast(args);
td->_tsvrp->HandlerHttpRequest(td->_sock);
close(td->_sock);
delete td;
return nullptr;
}
void Start()
{
while (1)
{
std::string clientip;
uint16_t clientport;
int sock = _listensock.Accept(&clientip, &clientport);
if (sock < 0)
continue;
ThreadData *td = new ThreadData(sock, clientip, clientport, this);
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, td);
}
}
~HttpServer()
{
}
private:
uint16_t _port;
Sock _listensock;
func_t _func;
};
//main.cc
#include "HttpServer.hpp"
#include
#include "error.hpp"
std::string SEP="\r\n";
std::string HandlerHttp(const std::string& request)
{
std::cout << "============================" << std::endl;
std::cout << request << std::endl;
std::string body = " this is a test
";
std::string response = "HTTP/1.0 200 OK" + SEP;
response += "Content-Length: " + std::to_string(body.size()) + SEP;
response += "Content-Type: test/html" + SEP;
response += SEP;
response += body;
return response;
}
int main()
{
uint16_t port = 8081;
std::unique_ptr tsvr(new HttpServer(HandlerHttp, port));
tsvr->InitServer();
tsvr->Start();
return 0;
} 2、增加web目录
因为响应的body部分可能经常需要更改,因此不方便直接编写进代码中,此时就需要以文件的形式存储body的内容。
同时,我们希望根据用户指明的web目录,来获取指定的资源。所以可以通过反序列化以及请求分析的方法截取解读url部分内容。
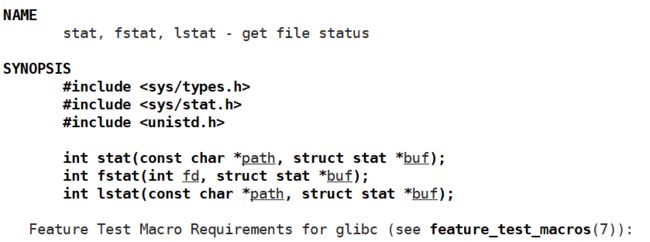
使用到的接口方法:
int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);通过 stat 结构体,可以获取文件的相关属性。
编写代码:
//Util.hpp
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "log.hpp"
class Util
{
public:
static bool ReadFile(const std::string& path, std::string* fileContent)
{
//1.获取文件本身大小
struct stat st;
int n = stat(path.c_str(), &st);
if(n < 0)
return false;
int size = st.st_size;
//2.调整string空间
fileContent->resize(size);
//3.读取
int fd = open(path.c_str(), O_RDONLY);
if(fd < 0)
return false;
read(fd, (char*)fileContent->c_str(), size);
close(fd);
logMessage(INFO, "read file %s done", path.c_str());
}
static std::string ReadOneLine(std::string& message, const std::string& sep)
{
auto pos = message.find(sep);
if(pos == std::string::npos)
return "";
std::string s = message.substr(0, pos);
message.erase(0, pos+sep.size());
return s;
}
static bool ParseRequestLine(std::string& line, std::string* method, std::string* url, std::string* httpVersion)
{
std::stringstream ss(line);
ss >> *method >> *url >> *httpVersion;
return true;
}
};
//main.cc
#include "HttpServer.hpp"
#include
#include
#include "error.hpp"
#include "Util.hpp"
std::string SEP="\r\n";
//一个webserver不做特殊说明,如果用户直接默认访问"/",不能把整站都发给对方
//需要添加默认首页,而且不能让用户访问wwwroot里面的任何一个目录本身,也可以给每一个目录都带上一个目录首页。
const std::string defaultHomePage = "index.html";
const std::string webRoot = "./wwwroot"; //web根目录
class HttpRequest
{
public:
HttpRequest(std::string path = webRoot)
:_path(path)
{}
~HttpRequest(){}
void Print()
{
logMessage(DEBUG, "method: %s, url: %s, version: %s",
_method.c_str(), _url.c_str(), _httpVersion.c_str());
logMessage(DEBUG, "path: %s", _path.c_str());
}
public:
std::string _method;
std::string _url;
std::string _httpVersion;
std::vector _body;
std::string _path;
};
HttpRequest Deserialize(std::string& message)
{
HttpRequest req;
std::string line = Util::ReadOneLine(message, SEP);
Util::ParseRequestLine(line, &req._method, &req._url, &req._httpVersion);
while(!message.empty())
{
line = Util::ReadOneLine(message, SEP);
req._body.push_back(line);
}
req._path += req._url;
if(req._path[req._path.size() - 1] == '/')
req._path += defaultHomePage;
return req;
}
std::string HandlerHttp(std::string& message)
{
//1.读取请求
std::cout << "============================" << std::endl;
// std::cout << message << std::endl;
//2.反序列化和分析请求
HttpRequest req = Deserialize(message);
req.Print();
//3.处理请求
std::string body;
Util::ReadFile(req._path, &body);
std::string response = "HTTP/1.0 200 OK" + SEP;
response += "Content-Length: " + std::to_string(body.size()) + SEP;
response += "Content-Type: test/html" + SEP;
response += SEP;
response += body;
return response;
}
int main()
{
uint16_t port = 8081;
std::unique_ptr tsvr(new HttpServer(HandlerHttp, port));
tsvr->InitServer();
tsvr->Start();
return 0;
} 3、目标文件中包含多种资源
如果用户访问的资源中包含多种资源,包括文本、图片、音频、视频等,就需要根据资源的后缀名来判断资源类型,并进行转化。因此在请求结构体中需要增加一个后缀字段,并在请求反序列化与请求分析阶段提取后缀保存起来。
class HttpRequest
{
public:
HttpRequest(std::string path = webRoot)
: _path(path)
{
}
~HttpRequest() {}
void Print()
{
logMessage(DEBUG, "method: %s, url: %s, version: %s",
_method.c_str(), _url.c_str(), _httpVersion.c_str());
// for(const auto& line:_body)
// {
// logMessage(DEBUG, "-%s", line.c_str());
// }
logMessage(DEBUG, "path: %s", _path.c_str());
}
public:
std::string _method;
std::string _url;
std::string _httpVersion;
std::vector _body;
std::string _path;
std::string _suffix;
};
HttpRequest Deserialize(std::string &message)
{
HttpRequest req;
std::string line = Util::ReadOneLine(message, SEP);
Util::ParseRequestLine(line, &req._method, &req._url, &req._httpVersion);
while (!message.empty())
{
line = Util::ReadOneLine(message, SEP);
req._body.push_back(line);
}
req._path += req._url;
if (req._path[req._path.size() - 1] == '/')
req._path += defaultHomePage;
auto pos = req._path.rfind(".");
if ((pos == std::string::npos))
req._suffix = ".html";
else
req._suffix = req._path.substr(pos);
return req;
} 在服务器响应时,也就不能直接把资源类型定义成固定类型了,而是应该根据后缀来选择。
std::string GetContentType(const std::string &suffix)
{
std::string content_type = "Content-Type: ";
if (suffix == ".html" || suffix == ".htm")
return content_type + "text/html";
else if (suffix == ".css")
return content_type + "text/css";
else if (suffix == ".js")
return content_type + "applicate/x-javascript";
else if (suffix == ".png")
return content_type + "image/png";
else if (suffix == ".jpg")
return content_type + "image/jpeg";
}
std::string HandlerHttp(std::string &message)
{
// 1.读取请求
std::cout << "============================" << std::endl;
// std::cout << message << std::endl;
// 2.反序列化和分析请求
HttpRequest req = Deserialize(message);
req.Print();
// 3.处理请求
std::string body;
Util::ReadFile(req._path, &body);
std::string response = "HTTP/1.0 200 OK" + SEP;
response += "Content-Length: " + std::to_string(body.size()) + SEP;
response += GetContentType(req._suffix) + SEP;
response += SEP;
response += body;
return response;
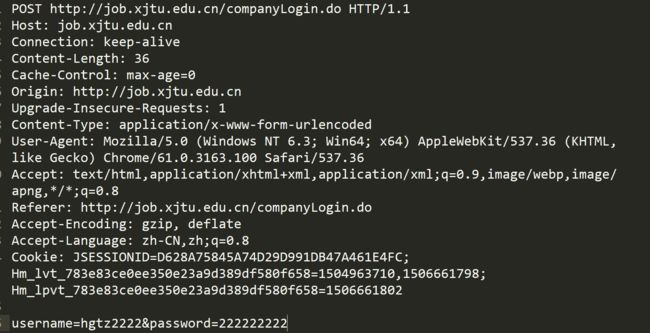
}模拟浏览器登录:
4、添加状态码
4.1、客户端错误状态码
//main.cc
const std::string page_404 = "./wwwroot/err_404.html";
std::string HandlerHttp(std::string &message)
{
// 1.读取请求
std::cout << "============================" << std::endl;
// std::cout << message << std::endl;
// 2.反序列化和分析请求
HttpRequest req = Deserialize(message);
req.Print();
// 3.处理请求
std::string body;
std::string response;
// Util::ReadFile(req._path, &body);
//判断读取是否成功,读取失败就进入404页面
if (true == Util::ReadFile(req._path, &body))
{
response = "HTTP/1.0 200 OK" + SEP;
response += "Content-Length: " + std::to_string(body.size()) + SEP;
response += GetContentType(req._suffix) + SEP;
response += SEP;
response += body;
}
else
{
response = "HTTP/1.0 404 Not Found" + SEP;
Util::ReadFile(page_404, &body);
response += "Content-Length: " + std::to_string(body.size()) + SEP;
response += GetContentType(".html") + SEP;
response += SEP;
response += body;
}
return response;
}说明:状态码并不是浏览器解释内容的唯一要素,因此状态码的编写可以是非常随意的。这就导致现在几乎都看不到 5 开头的服务器状态错误码了,就是因为程序员都不愿意在自己的服务器上写这种错误码,一方面是怕被别人抓到这个错误并复现,另一方面是嫌丢人。
4.2、重定向状态码
3XX 状态码是关于重定向的,常见的状态码有:301,302,303,304,307 和 308。这些状态码大致可以分为三类,其中包括:
- 永久重定向:301,308
- 临时重定向:302,303, 307
- 其他重定向:304
临时重定向不更改浏览器的任何地址信息。永久重定向会更改浏览器的本地书签。
不论是临时重定向,还是永久重定向,都需要server端在返回状态码的同时也要返回重定向的地址,即在报头中添加 Location 字段。
编写代码:
std::string HandlerHttp(std::string &message)
{
// 1.读取请求
std::cout << "============================" << std::endl;
// std::cout << message << std::endl;
//重定向测试
std::string response;
response = "HTTP/1.0 302 Found" + SEP;
response += "Location: https://www.baidu.com/" + SEP;
response += SEP;
return response;
}5、设置Cookie
class Session
{
public:
std::string name;
std::string passwd;
uint64_t loginTime;
};
std::unordered_map sessions;
bool Login(std::string& message)
{
std::string name;
std::string passwd;
if(check(name, passwd))
{
Session* session = new Session(name, passwd);
int random = rand();
sessions.insert(std::pair(random, session));
}
//构建resonse响应
//Set-Cookie:sessionid
}