动态代理AOP机制分析
有一个接口Vehicle,接口里有个run方法,有一个汽车类和一个轮船类,实现了这个接口。
要求在运行Car对象的run方法或运行ship对象的run方法前输出一些日志。
交通工具开始运行了…
轮船在海上running
交通工具停止运行了…交通工具开始运行了…
轮船在海上running
交通工具停止运行了…
我们可以使用动态代理解决这个问题
定义接口
public interface Vehicle {
void run();
String fly(int height);
}
汽车类
public class Car implements Vehicle{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("小汽车在公路running....");
}
@Override
public String fly(int height) {
return "小车飞翔的高度 " + height;
}
}
轮船类
public class Ship implements Vehicle{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("轮船在海上running");
}
@Override
public String fly(int height) {
return "轮船飞翔的高度 " + height;
}
}
定义代理类
public class VehicleProxyProvider {
//定义一个属性
//target_vehicle表示真正要执行的对象
private Vehicle target_vehicle;
public VehicleProxyProvider(Vehicle target_vehicle) {
this.target_vehicle = target_vehicle;
}
public Vehicle getProxy() {
//得到类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = target_vehicle.getClass().getClassLoader();
Class<?>[] interfaces = target_vehicle.getClass().getInterfaces();
//匿名内部类
InvocationHandler invocationHandler = new InvocationHandler() {
/**
* @param proxy the proxy instance that the method was invoked on
* @param method the {@code Method} instance corresponding to
* the interface method invoked on the proxy instance. The declaring
* class of the {@code Method} object will be the interface that
* the method was declared in, which may be a superinterface of the
* proxy interface that the proxy class inherits the method through.
* @param args an array of objects containing the values of the
* arguments passed in the method invocation on the proxy instance,
* or {@code null} if interface method takes no arguments.
* Arguments of primitive types are wrapped in instances of the
* appropriate primitive wrapper class, such as
* {@code java.lang.Integer} or {@code java.lang.Boolean}.
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
//使用反射+动态代理
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("交通工具开始运行了....");
System.out.println(method);
Object result = method.invoke(target_vehicle, args);
System.out.println("交通工具停止运行了");
return result;
}
};
Vehicle proxy = (Vehicle) Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader,interfaces,invocationHandler);
return proxy;
}
}
测试
public class Main {
@Test
public void proxyRun() {
Vehicle vehicle = new Ship();
ProxyProvider proxyProvider = new ProxyProvider(vehicle);
Vehicle proxy = proxyProvider.getProxy();
proxy.run();
Vehicle car = new Car();
ProxyProvider proxyProvider1 = new ProxyProvider(car);
Vehicle proxy1 = proxyProvider1.getProxy();
String fly = proxy1.fly(100);
System.out.println(fly);
}
}
无独有偶
我们可以在最为核心的invoke方法前后打印输出日志,这也就是AOP的底层机制所在之处。
先定义一个接口
public interface SmartAnimal {
int getSum(int a, int b);
int getSub(int a, int b);
}
再定义接口的实现类
public class Sum implements SmartAnimal {
@Override
public int getSum(int a, int b) {
int sum = a + b;
return sum;
}
@Override
public int getSub(int a, int b) {
int c = a - b;
return c;
}
}
定义动态代理类
public class ProxyProvider {
private final SmartAnimal smartAnimal;
public ProxyProvider(SmartAnimal smartAnimal) {
this.smartAnimal = smartAnimal;
}
public SmartAnimal getProxy() {
ClassLoader classLoader = smartAnimal.getClass().getClassLoader();
Class<?>[] interfaces = smartAnimal.getClass().getInterfaces();
InvocationHandler invocationHandler = new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
SpaAop.before(proxy,method,args);
Object result = method.invoke(smartAnimal, args);
SpaAop.after(method,result);
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("方法执行异常-日志-方法名-" + method.getName() + "-异常类型=" + e.getClass().getName());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {//不管是否出现异常方法最终都会执行到finally
System.out.println("方法最终结束-日志-方法名-" + method.getName());
}
}
};
SmartAnimal proxy =(SmartAnimal) Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, invocationHandler);
return proxy;
}
}
把要输出的日志封装的一个类的静态方法中,这样就可以通过类名.方法名来调用实现了解耦,同时也可以在方法中获取参数
public class SpaAop {
public static void before(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {
System.out.println("before方法执行前日志-方法名" +method.getName() + "-参数-"+ Arrays.toString(args));
}
public static void after(Method method, Object result) {
System.out.println("after日志-方法名" + method.getName() + "-结果result=" + result);
}
}
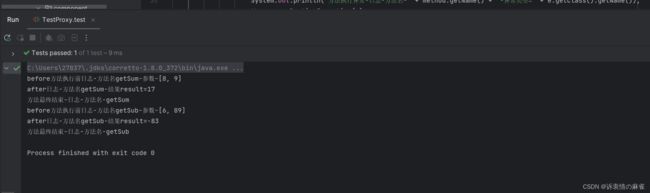
测试 运行截图
public class TestProxy {
@Test
public void test() {
Sum sum = new Sum();
ProxyProvider proxyProvider = new ProxyProvider(sum);
SmartAnimal proxy = proxyProvider.getProxy();
proxy.getSum(8, 9);
proxy.getSub(6,89);
}
}