MyBatisPlus系列第二篇:MyBatisPlus入门Hello World
文章目录
- 一、通用Mapper CRUD
-
- 1、提出问题?
- 2、Mapper CRUD
- 二、通用Mapper 插入操作
-
- 1、注解TbaleID&TableName使用
- 2、MP自增主键的获取
- 三、通用Mapper更新操作
- 四、通用Mapper查询操作
- 五、删除操作
- 六、MP启动注入SQL原理分析
- 七、全局策略配置
-
- 1、GlobalConfig
- 通用CRUD总结
一、通用Mapper CRUD
1、提出问题?
假设我们有一张员工表,有对应的实体类Employee、实现CRUD需要怎么操作?
实现方式:
1、基于mybatis:我们需要写一个EmployeeMapper接口、提供crud方法。再编写对应的EmployeeMapper.xml文件,编写每一个接口方法对应的SQL语句
2、基于MP:我们只需要写一个EmployeeMapper接口、继承BaseMapper接口。这就是需要使用MP完成所有的操作,甚至不需要创建SQL映射文件
2、Mapper CRUD
Mapper CRUD 接口封装的BaseMapper 为MP 提供了启动时自动解析实体表关系映射转换为mybatis的内部对象注入到容器
泛型T 为任意对象
参数 Serializable 为任意类型主键 Mybatis-Plus 不推荐使用复合主键约定每一张表都有自己的唯一 id 主键
对象 Wrapper 为 条件构造器
二、通用Mapper 插入操作
1、注解TbaleID&TableName使用
更多MP注解
//TableId value指定表中的主键列的列名、如果实体名与表的列名一致不用指定
//type:指定主键策略
@TableId(value = "id",type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
//MP会默认使用实体类的类名去数据库中找对应的表
//value:数据库表名、resultMap:xml中resultMap的id
@TableName(value = "tbl_employee")
public class Employee {
通用 Mapper接口
/**
*
* JavaBean和数据库表的字段对应,定义avaBean中成员变量时所使用的类型使用引用类型
* 因为每个基本类型都有个默认值:
* int==0
* Boolean==false
*/
public class Employee {
//TableId value指定表中的主键列的列名、如果实体名与表的列名一致不用指定
//type:指定主键策略
@TableId(value = "id",type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private Integer gender;
private Integer age;
package com.ming.mp.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.ming.mp.beans.Employee;
/**
* 基于mybatis实现,在mapper接口中编写crud相关的方法,还需要提供mapper接口提供的SQL映射文件和方法对应的sql语句
*
* 基于MP;让mapper接口去继承BaseMapper即可
* T:泛型我们指定的当前Mapper接口所操作的实体类类型
*
*
*/
public interface EmployeeMapper extends BaseMapper<Employee> {
}
测试:
private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper = context.getBean("employeeMapper",EmployeeMapper.class);
@Test
public void insertEmp(){
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setLastName("员工A");
employee.setEmail("[email protected]");
employee.setAge(18);
employee.setGender(1);
Integer count = employeeMapper.insert(employee);
}
2、MP自增主键的获取
Mybatis: 需要通过 useGeneratedKeys 以及 keyProperty 来设置
MP:自动将主键回写到实体类中,直接获取就行
@Test
public void insertEmp(){
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setLastName("员工A");
employee.setEmail("[email protected]");
employee.setAge(18);
employee.setGender(1);
Integer count = employeeMapper.insert(employee);
//获取主键
Integer id = employee.getId();
}
三、通用Mapper更新操作
@Test
public void updateByIdEmp(){
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(6);
employee.setLastName("MP");
///employee.setEmail("[email protected]");
employee.setAge(18);
employee.setGender(1);
//Integer count = employeeMapper.updateById(employee);
employeeMapper.updateAllColumnById(employee);
}
updateById:会对修改的属性做一个判断、为空的属性或者没有修改的属性(email)则不会出现在修改SQL语句中
Preparing: UPDATE tbl_employee SET last_name=?, gender=? WHERE id=?
updateAllColumnById:修改Entity所有的值,如果未设定(email),则会修改为null
Preparing: UPDATE tbl_employee SET last_name=?,email=?,gender=?,age=? WHERE id=?
四、通用Mapper查询操作
// 根据 ID 查询
T selectById(Serializable id);
// 根据 entity 条件,查询一条记录
T selectOne(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
// 查询(根据ID 批量查询)
List<T> selectBatchIds(@Param(Constants.COLLECTION) Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);
// 根据 entity 条件,查询全部记录
List<T> selectList(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
// 查询(根据 columnMap 条件)
List<T> selectByMap(@Param(Constants.COLUMN_MAP) Map<String, Object> columnMap);
// 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询全部记录
List<Map<String, Object>> selectMaps(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
// 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询全部记录。注意: 只返回第一个字段的值
List<Object> selectObjs(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
// 根据 entity 条件,查询全部记录(并翻页)
IPage<T> selectPage(IPage<T> page, @Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
// 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询全部记录(并翻页)
IPage<Map<String, Object>> selectMapsPage(IPage<T> page, @Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
// 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询总记录数
Integer selectCount(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
通用查询
selectOne:查询的时候只能返回一条数据,拼装查询的Entity时注意下条件唯一性
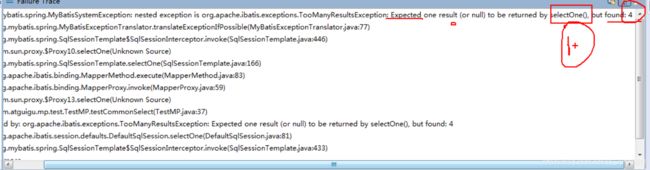
public void commonSelect() {
//1、selectById通过id查询(id 为主键)
//Preparing: SELECT id AS id,last_name AS lastName,email,gender,age FROM tbl_employee WHERE id=?
// Employee employee = employeeMapper.selectById(6);
// System.out.println(employee);
//2、selectOne通过多个列查询(id+name)参数T
// Employee employee = new Employee();
// employee.setId(6);
// employee.setLastName("MP");
// //Preparing: SELECT id AS id,last_name AS lastName,email,gender,age FROM tbl_employee WHERE id=? AND last_name=?
// Employee selectOne = employeeMapper.selectOne(employee);
//3、selectBatchIds:通过多个id查询
//SQL:SELECT id AS id,last_name AS lastName,email,gender,age FROM tbl_employee WHERE id IN ( ? , ? )
// List list = employeeMapper.selectBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1, 2));
// System.out.println(list);
//4、selectByMap
// LinkedHashMap map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// map.put("id","7");
// map.put("last_name","MP");
// List selectByMap = employeeMapper.selectByMap(map);
// System.out.println(selectByMap);
//5、分页查询 假分页内存分页 实现物理逻辑分页 要借助插件PageHelper
List<Employee> list = employeeMapper.selectPage(new Page<Employee>(2,2), null);
System.out.println(list);
//mybatis 分页工具PageHelper
@RequestMapping(value = "/getEmpList", method = {RequestMethod.GET})
public String getEmpList(HttpServletRequest request, @RequestParam(value = "pageNum", defaultValue = "1") Integer pageNum, Model model) {
PageHelper.startPage(pageNum, 5);
List<Emp> empList = iEepService.getEmpList();
PageInfo pageInfo = new PageInfo(empList, 5);
model.addAttribute("pageInfo", pageInfo);
return "empList";
}
}
五、删除操作
@Test
public void testCommonDelete(){
//1.根据主键id删除DELETE FROM tbl_employee WHERE id=?
// Integer id = employeeMapper.deleteById(6);
// System.out.println(id);
//2.deleteByMap: 根据 columnMap 条件、删除记录
// Map columnMap = new HashMap<>();
// columnMap.put("gender",0);
// Integer deleteByMap = employeeMapper.deleteByMap(columnMap);
// System.out.println(deleteByMap);
//3.删除(根据ID 批量删除)Preparing: DELETE FROM tbl_employee WHERE id IN ( ? , ? , ? , ? )
Integer integer = employeeMapper.deleteBatchIds(Arrays.asList(3, 5, 7, 8));
System.out.println(integer);
}
六、MP启动注入SQL原理分析
问题?
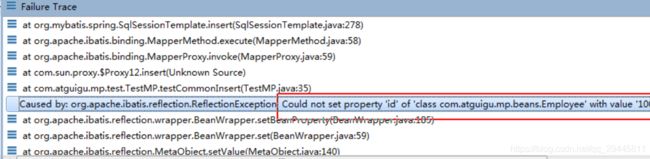
XXMapper继承了BaseMapper< T> ,BaseMapper中提供了通用的CRUD方法,方法来源我们的BaseMapper,有方法就必须有SQL语句,因为MyBatis 最终还是通过SQL语句操作数据
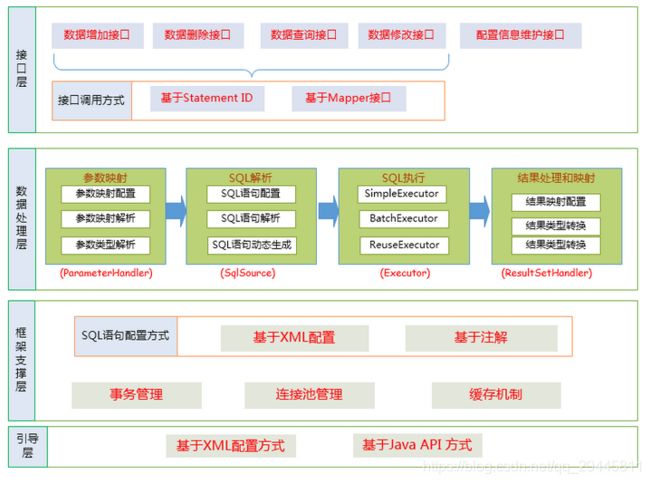
前置知识:mybatis源码中比较重要的一些对象 ,对mybatis框架执行流程configuration MappedStatement

分析SQL注入原理:
通过现象看到本质的东西
1、employeeMapper.deleteById(6) 以debug的方式查看
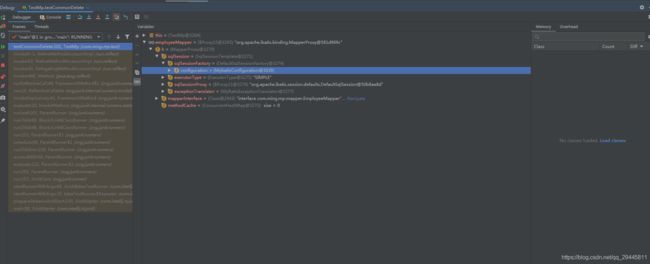
employeeMapper的本质:org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperProxy@581d969c 以jdk动态代理的方式
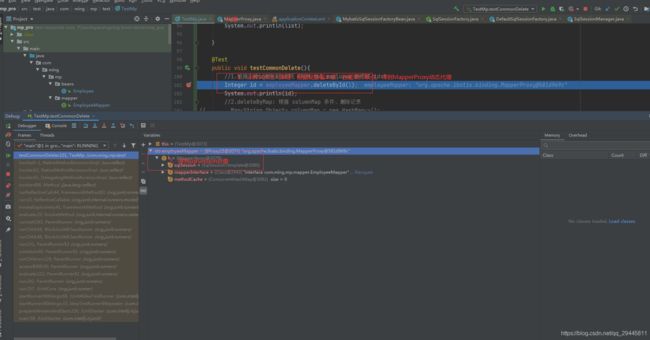
2、MapperProxy中sqlSession中的sqlSessionFactory
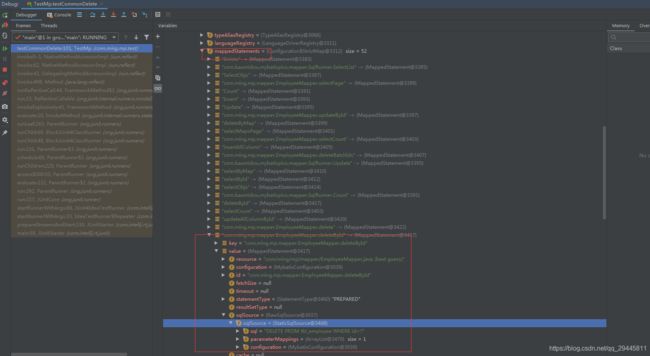
3、sqlSessionFactory中有一个configuration对象就是mybatis的全局配置、configuration里面有个MappedStatements都表示mapper接口中的一个方法与mapper映射文件的一个SQL语句对应
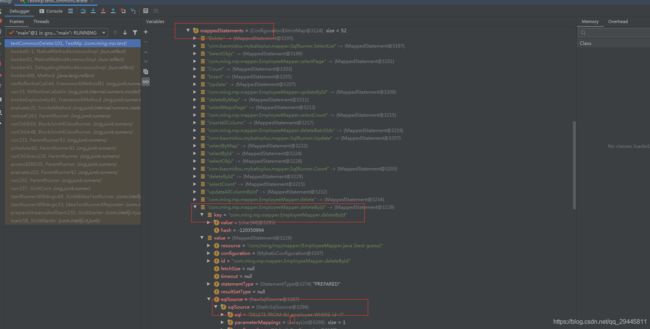
mybatisPlus 在启动就会分析xxMapper中的方法、并且将SQL语句处理好,保存到configuration对象中的MappedStatements中
现象分析完了
4、本质:MP在启动的时候 就会把一个方法构造成一个MappedSatement

5、AutoSqlInjector(SQL 自动注入器)调用addMappedStatement()方法打断点
SqlMethod:枚举对象 MP支持的SQL方法 模板的SQL语句
TableInfo:数据库表的反射信息对象,获取数据库表的信息对象
SqlSource:SQL语句处理对象
MapperBuilderAssistant: builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(通过MapperBuilderAssistant将所有的mappedStatement添加到configuration全局配置中),作用:用于缓存 SQL参数,查询、返回结果集处理
构建SQL语句:注入删除 SQL 语句
protected void injectDeleteByIdSql(boolean batch, Class<?> mapperClass, Class<?> modelClass, TableInfo table) {
SqlMethod sqlMethod = SqlMethod.DELETE_BY_ID;
SqlSource sqlSource;
// 因为后面要通过get方法获取类型,所以这里要获取key的属性值
String idStr = table.getKeyProperty();
if (batch) {
sqlMethod = SqlMethod.DELETE_BATCH_BY_IDS;
StringBuilder ids = new StringBuilder();
ids.append("\n" );
ids.append("#{item}");
ids.append("\n");
idStr = ids.toString();
}
String sql = String.format(sqlMethod.getSql(), table.getTableName(), table.getKeyColumn(), idStr);
sqlSource = languageDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, sql, modelClass);
this.addDeleteMappedStatement(mapperClass, sqlMethod.getMethod(), sqlSource);
}
删除
/**
* 删除
*/
public MappedStatement addDeleteMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperClass, String id, SqlSource sqlSource) {
return this.addMappedStatement(mapperClass, id, sqlSource, SqlCommandType.DELETE, null, null, Integer.class,
new NoKeyGenerator(), null, null);
}
通过MapperBuilderAssistant将所有的mappedStatement添加到mybatis的configuration全局配置中
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperClass, String id, SqlSource sqlSource,
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType, Class<?> parameterClass, String resultMap, Class<?> resultType,
KeyGenerator keyGenerator, String keyProperty, String keyColumn) {
String statementName = mapperClass.getName() + "." + id;
if (hasMappedStatement(statementName)) {
System.err.println("{" + statementName
+ "} Has been loaded by XML or SqlProvider, ignoring the injection of the SQL.");
return null;
}
/** 缓存逻辑处理 */
boolean isSelect = false;
if (sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT) {
isSelect = true;
}
return builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, StatementType.PREPARED, sqlCommandType, null, null, null,
parameterClass, resultMap, resultType, null, !isSelect, isSelect, false, keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn,
configuration.getDatabaseId(), languageDriver, null);
}
步骤:xxxMapper–>sqlSession—>sqlSessionFactory->confgiuration–>mappedStatements(所有的BaseMapper接口的方法)
七、全局策略配置
1、GlobalConfig
GlobalConfig
<bean id="sqlSessionFactoryBean" class="com.baomidou.mybatisplus.spring.MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!-- 数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"></property>
<!-- 别名处理 -->
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.ming.mp.beans"></property>
<!-- 注入全局MP策略配置 -->
<property name="globalConfig" ref="globalConfiguration"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 定义MybatisPlus的全局策略配置-->
<bean id ="globalConfiguration" class="com.baomidou.mybatisplus.entity.GlobalConfiguration">
<!-- 在2.3版本以后,dbColumnUnderline 默认值就是true 表名、字段名、是否使用下划线命名(默认 true: 数据库下划线命名) -->
<property name="dbColumnUnderline" value="true"></property>
<!-- 全局的主键策略 -->
<property name="idType" value="0"></property>
<!-- 全局的表前缀策略配置 -->
<property name="tablePrefix" value="tbl_"></property>
</bean>
通用CRUD总结
1、通用CRUD操作,需要继承BaseMapper< T>接口就可以实现大部分表的CRUD操作,方便的实现单一、批量
分页操作
2、提出需求
我们要分页查询Employee表中、年龄在19-50之间、性别为男性且姓名为xxx的用户,这个时候怎么实现?
Mybatis:需要在SQL映射文件中编写带条件的查询的SQL并基于PageHelper插件完成分页。实现事宜需求我们需要做很多重复单调的工作,普通的Mapper能够解决这类痛点吗?
MP:依旧不用编写SQL语句、MP提供了强大的条件构造器EntityWrapper