【Vue3】BEM 架构和 Sass 语法
1. BEM 架构
BEM(Block, Element, Modifier)是一种命名约定,用于在编写 CSS 和 HTML 类名时创建可维护和可重用的样式。BEM 是一种常用的 CSS 命名规范,它的目的是减少样式之间的耦合,增加样式的可读性,并提高样式的复用性。
BEM 的三个主要概念:
- Block(块):Block 是一个独立的、可复用的组件或模块,它代表一个完整的功能单元。块是一个顶层的元素,它本身应该有意义并且可以独立存在。
- Element(元素):Element 是块的组成部分,它不能单独存在,必须依赖于块。Element 是块的一部分,它只有在块的上下文中才有意义。
- Modifier(修饰符):Modifier 是用于改变块或元素外观、状态或行为的标志。通过添加修饰符类名,可以修改块或元素的样式,从而实现不同的变体。
BEM 的优点:
- 可读性:BEM 的类名规范清晰明了,易于理解和阅读,使其他开发者更容易理解代码结构和样式的用途。
- 可维护性:BEM 通过将样式与组件封装在一起,降低了样式之间的耦合性,使样式更易于维护和修改。
- 可重用性:BEM 鼓励将样式抽象为可复用的块和元素,提高了样式的复用性,减少了重复编写样式的工作。
以element-plus中input和button元素的样式为例:
BEM 的命名约定(以element-plus为例):
el:namespace(element-plus所有样式都是el开头)-:block(代表块级区域)__:element(连接元素内容)--:modifier(修饰内容)
2. Sass 常用语法
2.1. 嵌套规则 (Nested Rules)
Sass 允许将一套 CSS 样式嵌套进另一套样式中,内层的样式将它外层的选择器作为父选择器,避免了重复输入父选择器。
例如:
#main p {
color: #00ff00;
width: 97%;
.redbox {
background-color: #ff0000;
color: #000000;
}
}
编译为:
#main p {
color: #00ff00;
width: 97%;
}
#main p .redbox {
background-color: #ff0000;
color: #000000;
}
2.2. 父选择器 & (Referencing Parent Selectors: &)
在嵌套 CSS 规则时,有时也需要直接使用嵌套外层的父选择器。
例如,当给某个元素设定 hover 样式时,或者当 body 元素有某个 classname 时,可以用 & 代表嵌套规则外层的父选择器。
a {
font-weight: bold;
text-decoration: none;
&:hover { text-decoration: underline; }
body.firefox & { font-weight: normal; }
}
编译为
a {
font-weight: bold;
text-decoration: none;
}
a:hover {
text-decoration: underline;
}
body.firefox a {
font-weight: normal;
}
如果含有多层嵌套,最外层的父选择器会一层一层向下传递:
#main {
color: black;
a {
font-weight: bold;
&:hover { color: red; }
}
}
编译为
#main {
color: black;
}
#main a {
font-weight: bold;
}
#main a:hover {
color: red;
}
2.3. 变量 ## (Variables: ## )
SassScript 最普遍的用法就是变量,变量以美元符号开头,赋值方法与 CSS 属性的写法一样:
$width: 5em;
直接使用即调用变量:
#main {
width: $width;
}
编译为
#main {
width: 5em;
}
2.4. 插值语句 #{} (Interpolation: #{})
通过 #{} 插值语句可以在选择器或属性名中使用变量:
$name: foo;
$attr: border;
/* 动态类名必须结合插值语句 */
p.#{$name} {
#{$attr}-color: blue;
}
编译为
p.foo {
border-color: blue;
}
2.5. @at-root
子级跳出父级的嵌套
例如:
.parent {
...
@at-root .child { ... }
}
编译为:
.parent { ... }
.child { ... }
/* 如果没有@at-root则编译为: */
/* .parent {...} */
/* .parent .child (...) */
2.6. 定义混合指令 @mixin (Defining a Mixin: @mixin)
公共的、常用的样式使用@mixin进行封装
@mixin large-text {
font: {
family: Arial;
size: 20px;
weight: bold;
}
color: #ff0000;
}
.page-title {
@include large-text;
padding: 4px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
编译为:
.page-title {
font-family: Arial;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
color: #ff0000;
padding: 4px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
2.7. 参数 (Arguments)
参数用于给混合指令中的样式设定变量,并且赋值使用。在定义混合指令的时候,按照变量的格式,通过逗号分隔,将参数写进圆括号里。引用指令时,按照参数的顺序,再将所赋的值对应写进括号:
/* 很类似于js中的函数 */
@mixin sexy-border($color, $width) {
border: {
color: $color;
width: $width;
style: dashed;
}
}
p { @include sexy-border(blue, 1in); }
/* 1in:1英寸 */
编译为
p {
border-color: blue;
border-width: 1in;
border-style: dashed;
}
3. 编写BEM架构和全局Sass文件
bem.scss
$namespace: 'el' !default;
$block-sel: '-' !default;
$elem-sel: '__' !default;
$mod-sel: '--' !default;
// block
// 定义变量生成此规则
@mixin b($block) {
$B:#{$namespace + $block-sel + $block};
.#{$B} {
@content; //相当于一个占位符
}
}
// element
// .el-block__inner{} 定义变量生成此规则
@mixin e($el) {
$selector: &;
@at-root {
#{$selector + $elem-sel + $el} {
@content;
}
}
}
// modifier
@mixin m($m) {
$selector: &;
@at-root {
#{$selector + $mod-sel + $m} {
@content;
}
}
}
vite.config.ts
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
import vue from '@vitejs/plugin-vue'
// https://vitejs.dev/config/
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [vue()],
// 通过配置变为全局通用样式
css: {
preprocessorOptions: {
scss: {
additionalData: '@import "./src/bem.scss";',
},
},
}
})
App.vue
test
inner
modify
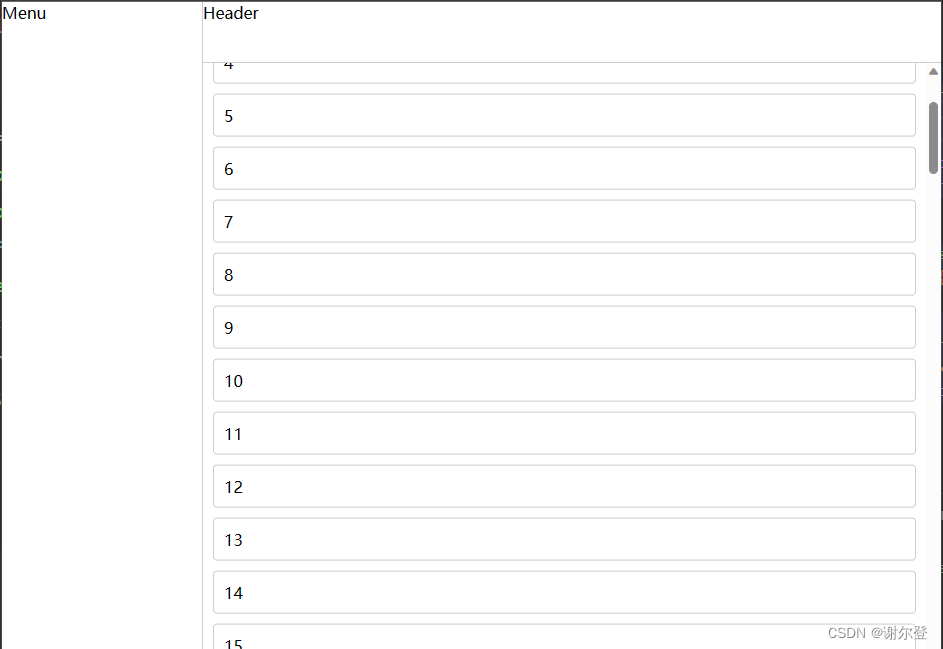
4. 小案例(Layout布局)
bem.scss
$namespace: 'el' !default;
$block-sel: '-' !default;
$elem-sel: '__' !default;
$mod-sel: '--' !default;
// BFC(Block Formatting Context)块格式化上下文
@mixin bfc {
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
}
// block
// 定义变量生成此规则
@mixin b($block) {
$B:#{$namespace + $block-sel + $block};
.#{$B} {
@content; //相当于一个占位符
}
}
// element
// .el-block__inner{} 定义变量生成此规则
@mixin e($el) {
$selector: &;
@at-root {
#{$selector + $elem-sel + $el} {
@content;
}
}
}
// modifier
@mixin m($m) {
$selector: &;
@at-root {
#{$selector + $mod-sel + $m} {
@content;
}
}
}
App.vue
index.vue …\Content
{{ item }}
index.vue …\Header
Header
index.vue …\Menu
index.vue …\Layout