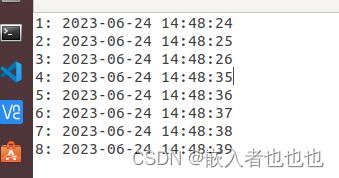
一、向文件中输出时间,并且是每一秒更新一次,按ctrl+c停止输出后,下次再运行./a.out会继续想文件中接着输出;
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("text.txt","a+"); //追加方式打开文件
//打印文件打开出错信息
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
//计算文件行数
int line = 0;
char buf[128];
while((fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),fp)) != NULL )
{
if(buf[strlen(buf)-1] == '\n')
line++;
}
time_t last_time,now_time; //定义时间类型变量
time(&last_time); //获取当前时间last_time
struct tm *t; //struct tm类型的结构体指针
while(1)
{
time(&now_time); //获取当前时间now_time
//比较last_time 和 now_time
if(last_time != now_time)
{
//秒数转变成struct tm类型的结构体指针
t = localtime(&now_time);
//向text.txt文件里打印
fprintf(fp,"%d: %4d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d\n",\
++line,t->tm_year+1900,t->tm_mon+1,t->tm_mday,\
t->tm_hour,t->tm_min,t->tm_sec);
last_time = now_time; //时间更新
fflush(fp); //刷新缓冲区
}
}
fclose(fp); //关闭文件
return 0;
}
二、使用fread、fwrite完成两个文件的拷贝;
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE *srcfp,*tarfp;
srcfp = fopen("text.txt","r"); //只读打开text.txt
if(NULL == srcfp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
tarfp = fopen("text1.txt","w"); //只写打开text1.txt
if(NULL == tarfp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
char buf[1024]; //定义数组空间
int k = fread(buf,1,sizeof(buf),srcfp); //fread读取数据到buf数组中
fwrite(buf,k,1,tarfp); //fwrite读取数据放到文件中
puts("拷贝成功");
fclose(srcfp);//关闭文件
fclose(tarfp);
return 0;
}

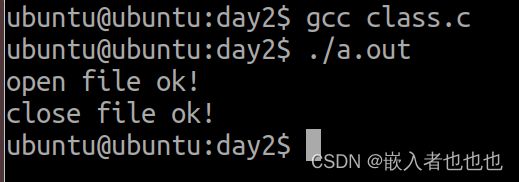
1.文件的打开和关闭(fopen,fclose);
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("text.txt","r");//只读打开文件
if(NULL == fp)
puts("open file error!");
else
puts("open file ok!");
//关闭文件
if(fclose(fp) != 0)
puts("close file error");
else
puts("close file ok!");
return 0;
}
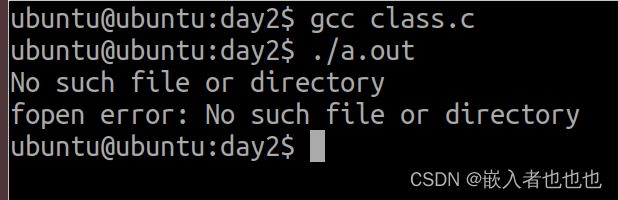
2.将错误码转换为错误信息(strerror,perror);
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("text1.txt","r");//只读打开不存在的文件
if(NULL == fp)
{
//将错误码转变为错误信息
strerror(errno); //strerror函数打印
printf("%s\n",strerror(errno));
perror("fopen error"); //perror函数打印
return -1;
}
fclose(fp); //关闭文件
return 0;
}
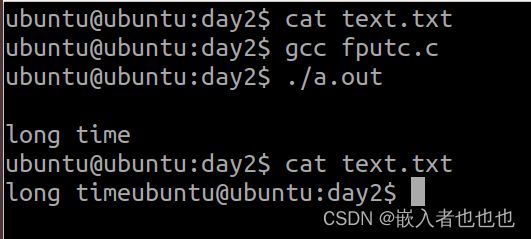
3.向文件写入字符,从文件获取字符(fputc,fgetc);
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("text.txt","w");//只写权限打开文件
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
//向文件中写入long time
fputc('l',fp);
fputc('o',fp);
fputc('n',fp);
fputc('g',fp);
fputc(' ',fp);
fputc('t',fp);
fputc('i',fp);
fputc('m',fp);
fputc('e',fp);
puts("");
fclose(fp); //关闭文件
fp = fopen("text.txt","r");//只读权限打开文件
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
char ch; //从文件中获取字符
while((ch=fgetc(fp)) != EOF )
printf("%c",ch);
puts("");
fclose(fp); //关闭文件
return 0;
}
4.使用fgetc和fputc统计一个文件的行数,文件可以是外部传入 ;
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//判断输入文件个数
if(argc != 2)
{
printf("输入文件错误!\n");
printf("用法:./a.out filename\n");
return -1;
}
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen(argv[1],"r"); //只读打开文件数组的第二个文件
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
int line_num = 0; //行数
char ch;
//获取文件字符统计行数
while((ch=fgetc(fp)) != EOF)
{
if(ch == '\n')
line_num++;
}
fclose(fp); //关闭文件
printf("该文件一共有%d行\n",line_num);
return 0;
}

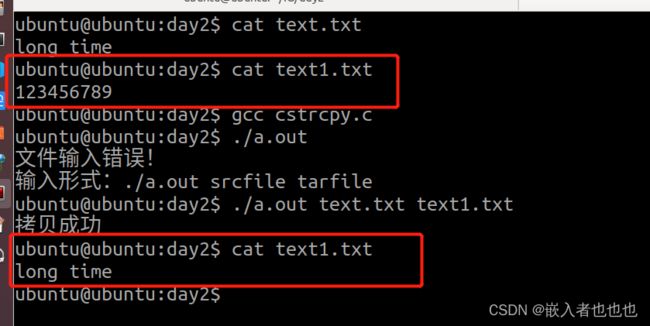
5.使用fgetc和fputc实现两个文件的拷贝;
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//判断输入文件个数
if(argc != 3)
{
printf("文件输入错误!\n");
printf("输入形式:./a.out srcfile tarfile\n");
return -1;
}
FILE *srcfp,*tarfp;
srcfp = fopen("text.txt","r"); //只读打开源文件
if(NULL == srcfp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
tarfp = fopen("text1.txt","w"); //只写打开目标文件
if(NULL == tarfp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
char ch;
while((ch=fgetc(srcfp)) != EOF)
{
fputc(ch,tarfp); //把读取的字符放入目标文件
}
//关闭两个文件
fclose(srcfp);
fclose(tarfp);
puts("拷贝成功");
return 0;
}
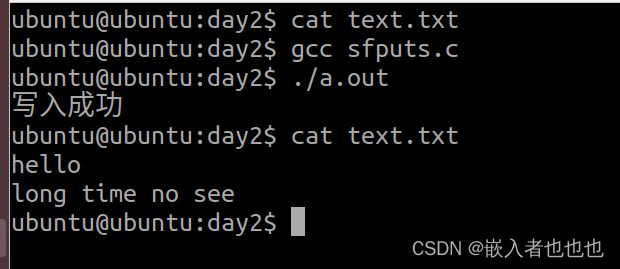
6.向指定文件写入字符串(fputs);
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("text.txt","w"); //只写打开文件
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
//向指定文件写入字符串
fputs("hello\n",fp);
fputs("long time ",fp);
fputs("no see\n",fp);
fclose(fp); //关闭文件
puts("写入成功");
return 0;
}
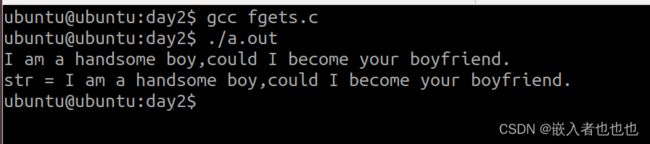
7.从标准输入文件中读取数据到s中(fgets);
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char str[128];
//从标准输入文件读取数据到数组中
fgets(str,sizeof(str),stdin);
str[strlen(str)-1] = '\0'; //让最后一个'\n'转换成'\0'
printf("str = %s\n",str);
return 0;
}
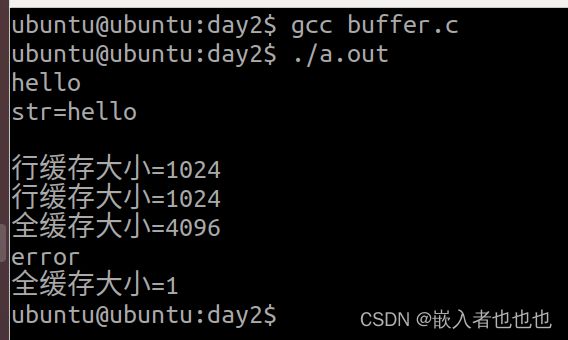
8.验证缓冲区,行缓存、全缓存、不缓存的大小;
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//验证行缓存大小
char str[128];
fgets(str,sizeof(str),stdin);
printf("str=%s\n",str);
printf("行缓存大小=%ld\n",stdin->_IO_buf_end - stdin->_IO_buf_base);
printf("行缓存大小=%ld\n",stdout->_IO_buf_end - stdout->_IO_buf_base);
//验证全缓存大小
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("text.txt","w");
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
fputs("hello world",fp);
printf("全缓存大小=%ld\n",fp->_IO_buf_end - fp->_IO_buf_base);
fclose(fp);
//验证不缓存大小
fputs("error\n",stderr); //向标准出错中写入数据
printf("全缓存大小=%ld\n",stderr->_IO_buf_end - stderr->_IO_buf_base);
return 0;
}
9.获取当前系统时间(time函数,localtime函数);
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
time_t sys_tem; //定义时间类型变量保存秒数
time(&sys_tem); //调用time函数,获取秒数
struct tm *t = localtime(&sys_tem); //将秒数转换为时间指针
//输出系统时间
printf("%4d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d\n",\
t->tm_year+1900,t->tm_mon+1,t->tm_mday,\
t->tm_hour,t->tm_min,t->tm_sec);
return 0;
}
10.将时间格式串放到buf指向的数组中(sprintf函数);
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
time_t sys_tem; //定义时间类型变量保存秒数
time(&sys_tem); //调用time函数,获取秒数
struct tm *t = localtime(&sys_tem); //将秒数转换为时间指针
//将时间格式串放到buf指向的数组中
char buf[128];
sprintf(buf,"%4d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d\n",\
t->tm_year+1900,t->tm_mon+1,t->tm_mday,\
t->tm_hour,t->tm_min,t->tm_sec);
//输出系统时间
printf("%s",buf);
return 0;
}

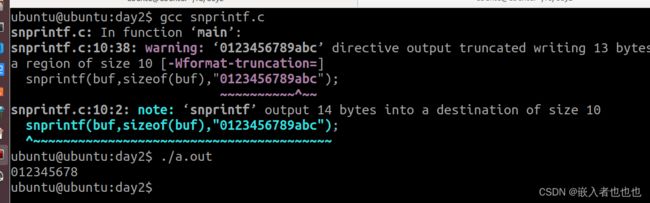
11.将字符串放入buf指向的数组中(snprintf);
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char buf[10];
//将字符串放入buf指向的数组中
//会警告,但可以运行
snprintf(buf,sizeof(buf),"0123456789abc");
printf("%s\n",buf);
return 0;
}
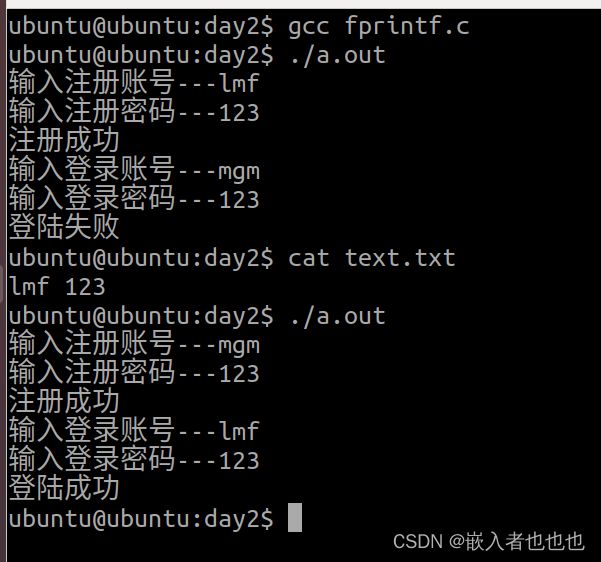
12.向文件输入注册账号密码,比对登录账号密码(fprintf fscanf);
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
char username[20];//注册账号密码
char pwd[20];
char login[20];//登录账号密码
char password[20];
fp = fopen("text.txt","a"); //追加权限打开文件
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
//输入账号密码
printf("输入注册账号---");
scanf("%s",username);
printf("输入注册密码---");
scanf("%s",pwd);
fprintf(fp,"%s %s\n",username,pwd);
fclose(fp);
puts("注册成功");
fp = fopen("text.txt","r"); //只读权限打开文件
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
//登录账号密码
printf("输入登录账号---");
scanf("%s",login);
printf("输入登录密码---");
scanf("%s",password);
//从指针文件读取数据,与登录数据进行比对
while(fscanf(fp,"%s %s",username,pwd) != EOF)
{
if(strcmp(username,login)==0 && strcmp(pwd,password)==0)
{
puts("登陆成功");
fclose(fp);
return 2;
}
}
puts("登陆失败");
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
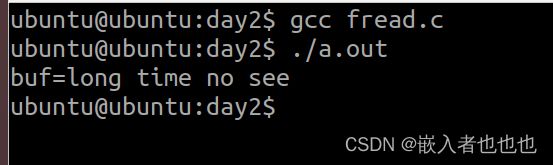
13.读写字符串(fread,fwrite函数);
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("text.txt","a+"); //追加打开文件
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
//把字符串写入到fp中
char str[] = "long time no see";
fwrite(str,sizeof(str),1,fp);
fclose(fp);
fp = fopen("text.txt","r"); //只读打开文件
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
//以fread读取数据放到缓冲区中
char buf[1024];
fread(buf,sizeof(buf),1,fp);
printf("buf=%s\n",buf);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
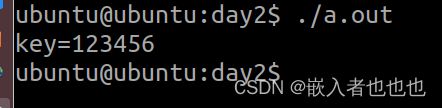
14.读写整型变量(fread,fwrite函数);
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("text.txt","w"); //只写打开文件
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
//用fwrite把整数写入到fp中
int num = 123456;
fwrite(&num,sizeof(num),1,fp);
fclose(fp);
fp = fopen("text.txt","r"); //只读打开文件
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
//以fread读取数据
int key = 0;
fread(&key,sizeof(key),1,fp);
//打印数据
printf("key=%d\n",key);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
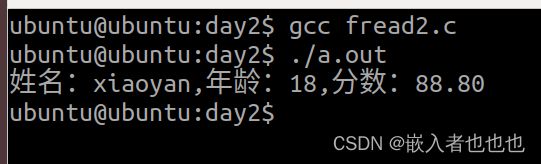
15.结构体数据的读写(fread,fwrite函数);
#include
#include
#include
//定义学生信息结构体
struct Stu
{
char name[20];
int age;
float score;
};
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("text.txt","w"); //只写方式打开文件
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen errro");
return -1;
}
//定义两个结构体变量
struct Stu s[2] = {{"xiaoyan",18,88.8},{"tangsan",19,99.9}};
//向文件写入两个学生大小的数据
fwrite(s,sizeof(struct Stu),2,fp);
fclose(fp);
fp = fopen("text.txt","r"); //只读形式打开文件
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen errro");
return -1;
}
struct Stu buf;
fread(&buf,sizeof(struct Stu),1,fp); //读取第一位学生信息
printf("姓名:%s,年龄:%d,分数:%.2lf\n",buf.name,buf.age,buf.score);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
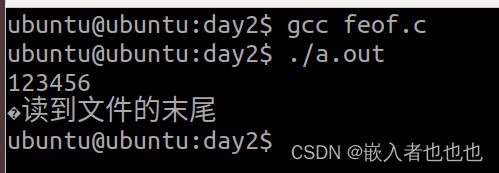
16.判断读取文件字符结束的原因(feof,ferror函数);
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("text.txt","r"); //只读形式打开文件
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
char ch;
while(1)
{
ch = fgetc(fp);
printf("%c",ch);
if(feof(fp))
{
puts("读到文件的末尾");
break;
}else if(ferror(fp))
{
puts("读取文件失败");
break;
}
}
fclose(fp); //关闭文件
return 0;
}
17.重新定位光标,读取结构体中第二名学生信息(fseek函数);
#include
#include
#include
//定义学生信息结构体
struct Stu
{
char name[20];
int age;
float score;
};
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("text.txt","w"); //只写方式打开文件
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen errro");
return -1;
}
//定义两个结构体变量
struct Stu s[2] = {{"xiaoyan",18,88.8},{"tangsan",19,99.9}};
//向文件写入两个学生大小的数据
fwrite(s,sizeof(struct Stu),2,fp);
fclose(fp);
fp = fopen("text.txt","r"); //只读形式打开文件
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen errro");
return -1;
}
struct Stu stu;
//定位光标,读取第二名学生信息
fseek(fp,sizeof(struct Stu),SEEK_SET);
//以fread进行读取数据
fread(&stu,sizeof(struct Stu),1,fp);
printf("姓名:%s,年龄:%d,分数:%.2lf\n",stu.name,stu.age,stu.score);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
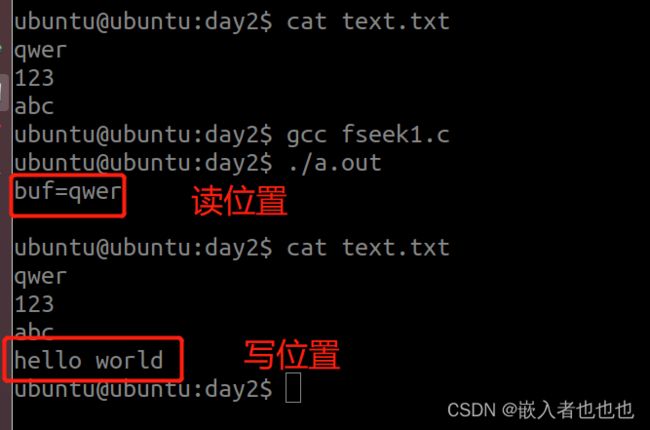
18.验证,以a+的形式打开文件,开头读,结尾写,使用fseek可以更改读指针的位置,但是,不能更改写指针位置;
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("text.txt","a+");
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
//将光标移动到文件开头
fseek(fp,0,SEEK_SET);
//验证写指针位置,结果无法在指针进行写数据
fputs("hello world\n",fp);
fclose(fp); //写操作结束关闭文件
fp = fopen("text.txt","a+"); //重新打开文件
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen error");
return -1;
}
//将光标移动到文件开头
fseek(fp,0,SEEK_SET);
char buf[128] = "";
//验证读指针位置,结果可以在指针光标位置进行数据读取
fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),fp);
printf("buf=%s\n",buf);
return 0;
}