mybatis - 注解开发 构建SQL
一.Mybatis注解开发单表操作
1.1 MyBatis的常用注解
这几年来注解开发越来越流行,Mybatis也可以使用注解开发方式,这样我们就可以减少编写Mapper
映射文件了。我们先围绕一些基本的CRUD来学习,再学习复杂映射多表操作。
@Insert:实现新增
@Update:实现更新
@Delete:实现删除
@Select:实现查询
@Result:实现结果集封装
@Results:可以与@Result 一起使用,封装多个结果集
@One:实现一对一结果集封装
@Many:实现一对多结果集封装
1.2 MyBatis的增删改查
我们完成简单的student表的增删改查的操作
-
步骤一:创建mapper接口
public interface StudentMapper { //查询全部 @Select("SELECT * FROM student") public abstract List<Student> selectAll(); //新增操作 @Insert("INSERT INTO student VALUES (#{id},#{name},#{age})") public abstract Integer insert(Student stu); //修改操作 @Update("UPDATE student SET name=#{name},age=#{age} WHERE id=#{id}") public abstract Integer update(Student stu); //删除操作 @Delete("DELETE FROM student WHERE id=#{id}") public abstract Integer delete(Integer id); } -
步骤二:测试类
public class Test01 { @Test public void selectAll() throws Exception{ //1.加载核心配置文件 InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml"); //2.获取SqlSession工厂对象 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is); //3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); //4.获取StudentMapper接口的实现类对象 StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); //5.调用实现类对象中的方法,接收结果 List<Student> list = mapper.selectAll(); //6.处理结果 for (Student student : list) { System.out.println(student); } //7.释放资源 sqlSession.close(); is.close(); } @Test public void insert() throws Exception{ //1.加载核心配置文件 InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml"); //2.获取SqlSession工厂对象 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is); //3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); //4.获取StudentMapper接口的实现类对象 StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); //5.调用实现类对象中的方法,接收结果 Student stu = new Student(4,"赵六",26); Integer result = mapper.insert(stu); //6.处理结果 System.out.println(result); //7.释放资源 sqlSession.close(); is.close(); } @Test public void update() throws Exception{ //1.加载核心配置文件 InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml"); //2.获取SqlSession工厂对象 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is); //3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); //4.获取StudentMapper接口的实现类对象 StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); //5.调用实现类对象中的方法,接收结果 Student stu = new Student(4,"赵六",36); Integer result = mapper.update(stu); //6.处理结果 System.out.println(result); //7.释放资源 sqlSession.close(); is.close(); } @Test public void delete() throws Exception{ //1.加载核心配置文件 InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml"); //2.获取SqlSession工厂对象 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is); //3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); //4.获取StudentMapper接口的实现类对象 StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); //5.调用实现类对象中的方法,接收结果 Integer result = mapper.delete(4); //6.处理结果 System.out.println(result); //7.释放资源 sqlSession.close(); is.close(); } } -
注意:
修改MyBatis的核心配置文件,我们使用了注解替代的映射文件,所以我们只需要加载使用了注解的Mapper接口即可
<mappers>
<mapper class="com.itheima.mapper.UserMapper">mapper>
mappers>
或者指定扫描包含映射关系的接口所在的包也可以
<mappers>
<package name="com.itheima.mapper">package>
mappers>
1.3 注解开发总结
注解可以简化开发操作,省略映射配置文件的编写。
-
常用注解
@Select(“查询的 SQL 语句”):执行查询操作注解
@Insert(“查询的 SQL 语句”):执行新增操作注解
@Update(“查询的 SQL 语句”):执行修改操作注解
@Delete(“查询的 SQL 语句”):执行删除操作注解
-
配置映射关系
<mappers> <package name="接口所在包"/> mappers>
二.MyBatis注解开发的多表操作
2.1 MyBatis的注解实现复杂映射开发
实现复杂关系映射之前我们可以在映射文件中通过配置来实现,使用注解开发后,我们可以使用@Results注解,@Result注解,@One注解,@Many注解组合完成复杂关系的配置
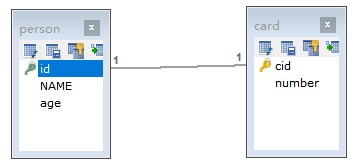
2.2 一对一查询
2.2.1 一对一查询的模型
一对一查询的需求:查询一个用户信息,与此同时查询出该用户对应的身份证信息
2.2.2 一对一查询的语句
对应的sql语句:
SELECT * FROM card;
SELECT * FROM person WHERE id=#{id};
2.2.3 创建PersonMapper接口
public interface PersonMapper {
//根据id查询
@Select("SELECT * FROM person WHERE id=#{id}")
public abstract Person selectById(Integer id);
}
2.2.4 使用注解配置Mapper
public interface CardMapper {
//查询全部
@Select("SELECT * FROM card")
@Results({
@Result(column = "id",property = "id"),
@Result(column = "number",property = "number"),
@Result(
property = "p", // 被包含对象的变量名
javaType = Person.class, // 被包含对象的实际数据类型
column = "pid", // 根据查询出的card表中的pid字段来查询person表
/*
one、@One 一对一固定写法
select属性:指定调用哪个接口中的哪个方法
*/
one = @One(select = "com.itheima.one_to_one.PersonMapper.selectById")
)
})
public abstract List<Card> selectAll();
}
2.2.5 测试类
public class Test01 {
@Test
public void selectAll() throws Exception{
//1.加载核心配置文件
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");
//2.获取SqlSession工厂对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
//3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
//4.获取CardMapper接口的实现类对象
CardMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CardMapper.class);
//5.调用实现类对象中的方法,接收结果
List<Card> list = mapper.selectAll();
//6.处理结果
for (Card card : list) {
System.out.println(card);
}
//7.释放资源
sqlSession.close();
is.close();
}
}
2.2.6 一对一配置总结
@Results:封装映射关系的父注解。
Result[] value():定义了 Result 数组
@Result:封装映射关系的子注解。
column 属性:查询出的表中字段名称
property 属性:实体对象中的属性名称
javaType 属性:被包含对象的数据类型
one 属性:一对一查询固定属性
@One:一对一查询的注解。
select 属性:指定调用某个接口中的方法
2.3 一对多查询
2.3.1 一对多查询的模型
一对多查询的需求:查询一个课程,与此同时查询出该该课程对应的学生信息
2.3.2 一对多查询的语句
对应的sql语句:
SELECT * FROM classes
SELECT * FROM student WHERE cid=#{cid}
2.3.3 创建StudentMapper接口
public interface StudentMapper {
//根据cid查询student表
@Select("SELECT * FROM student WHERE cid=#{cid}")
public abstract List<Student> selectByCid(Integer cid);
}
2.3.4 使用注解配置Mapper
public interface ClassesMapper {
//查询全部
@Select("SELECT * FROM classes")
@Results({
@Result(column = "id",property = "id"),
@Result(column = "name",property = "name"),
@Result(
property = "students", // 被包含对象的变量名
javaType = List.class, // 被包含对象的实际数据类型
column = "id", // 根据查询出的classes表的id字段来查询student表
/*
many、@Many 一对多查询的固定写法
select属性:指定调用哪个接口中的哪个查询方法
*/
many = @Many(select = "com.itheima.one_to_many.StudentMapper.selectByCid")
)
})
public abstract List<Classes> selectAll();
}
2.3.5 测试类
public class Test01 {
@Test
public void selectAll() throws Exception{
//1.加载核心配置文件
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");
//2.获取SqlSession工厂对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
//3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
//4.获取ClassesMapper接口的实现类对象
ClassesMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(ClassesMapper.class);
//5.调用实现类对象中的方法,接收结果
List<Classes> list = mapper.selectAll();
//6.处理结果
for (Classes cls : list) {
System.out.println(cls.getId() + "," + cls.getName());
List<Student> students = cls.getStudents();
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println("\t" + student);
}
}
//7.释放资源
sqlSession.close();
is.close();
}
}
2.3.6 一对多配置总结
@Results:封装映射关系的父注解。
Result[] value():定义了 Result 数组
@Result:封装映射关系的子注解。
column 属性:查询出的表中字段名称
property 属性:实体对象中的属性名称
javaType 属性:被包含对象的数据类型
many 属性:一对多查询固定属性
@Many:一对多查询的注解。
select 属性:指定调用某个接口中的方法
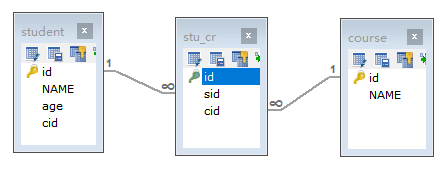
2.4 多对多查询
2.4.1 多对多查询的模型
多对多查询的需求:查询学生以及所对应的课程信息
2.4.2 多对多查询的语句
对应的sql语句:
SELECT DISTINCT s.id,s.name,s.age FROM student s,stu_cr sc WHERE sc.sid=s.id
SELECT c.id,c.name FROM stu_cr sc,course c WHERE sc.cid=c.id AND sc.sid=#{id}
2.4.3 添加CourseMapper 接口方法
public interface CourseMapper {
//根据学生id查询所选课程
@Select("SELECT c.id,c.name FROM stu_cr sc,course c WHERE sc.cid=c.id AND sc.sid=#{id}")
public abstract List<Course> selectBySid(Integer id);
}
2.4.4 使用注解配置Mapper
public interface StudentMapper {
//查询全部
@Select("SELECT DISTINCT s.id,s.name,s.age FROM student s,stu_cr sc WHERE sc.sid=s.id")
@Results({
@Result(column = "id",property = "id"),
@Result(column = "name",property = "name"),
@Result(column = "age",property = "age"),
@Result(
property = "courses", // 被包含对象的变量名
javaType = List.class, // 被包含对象的实际数据类型
column = "id", // 根据查询出student表的id来作为关联条件,去查询中间表和课程表
/*
many、@Many 一对多查询的固定写法
select属性:指定调用哪个接口中的哪个查询方法
*/
many = @Many(select = "com.itheima.many_to_many.CourseMapper.selectBySid")
)
})
public abstract List<Student> selectAll();
}
2.4.5 测试类
public class Test01 {
@Test
public void selectAll() throws Exception{
//1.加载核心配置文件
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");
//2.获取SqlSession工厂对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
//3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
//4.获取StudentMapper接口的实现类对象
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
//5.调用实现类对象中的方法,接收结果
List<Student> list = mapper.selectAll();
//6.处理结果
for (Student student : list) {
System.out.println(student.getId() + "," + student.getName() + "," + student.getAge());
List<Course> courses = student.getCourses();
for (Course cours : courses) {
System.out.println("\t" + cours);
}
}
//7.释放资源
sqlSession.close();
is.close();
}
}
2.4.6 多对多配置总结
@Results:封装映射关系的父注解。
Result[] value():定义了 Result 数组
@Result:封装映射关系的子注解。
column 属性:查询出的表中字段名称
property 属性:实体对象中的属性名称
javaType 属性:被包含对象的数据类型
many 属性:一对多查询固定属性
@Many:一对多查询的注解。
select 属性:指定调用某个接口中的方法
三.构建sql
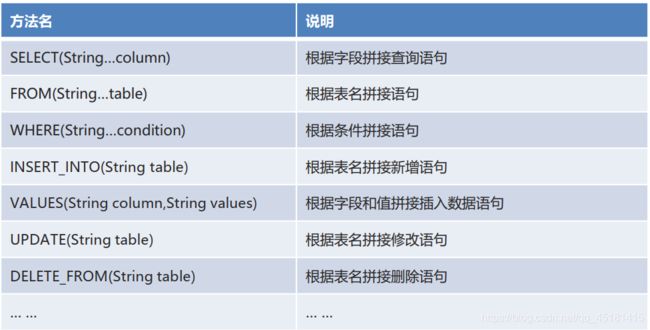
3.1 SQL 构建对象介绍
- 我们之前通过注解开发时,相关 SQL 语句都是自己直接拼写的。一些关键字写起来比较麻烦、而且容易出错。
- MyBatis 给我们提供了 org.apache.ibatis.jdbc.SQL 功能类,专门用于构建 SQL 语句
3.2 查询功能的实现
-
定义功能类并提供获取查询的 SQL 语句的方法。
-
@SelectProvider:生成查询用的 SQL 语句注解。
type 属性:生成 SQL 语句功能类对象
method 属性:指定调用方法
3.3 新增功能的实现
-
定义功能类并提供获取新增的 SQL 语句的方法。
-
@InsertProvider:生成新增用的 SQL 语句注解。
type 属性:生成 SQL 语句功能类对象
method 属性:指定调用方法
3.4 修改功能的实现
-
定义功能类并提供获取修改的 SQL 语句的方法。
-
@UpdateProvider:生成修改用的 SQL 语句注解。
type 属性:生成 SQL 语句功能类对象
method 属性:指定调用方法
3.5 删除功能的实现
-
定义功能类并提供获取删除的 SQL 语句的方法。
-
@DeleteProvider:生成删除用的 SQL 语句注解。
type 属性:生成 SQL 语句功能类对象
method 属性:指定调用方法
四.综合案例
4.1 系统介绍
我们之前在做学生管理系统时,使用的是原始JDBC操作数据库的,操作非常麻烦,现在我们使用MyBatis操作数据库,简化Dao的开发。
4.2 环境搭建(略)
4.3 代码改造
-
步骤一:新增MyBatis配置文件
<configuration> <properties resource="config.properties"/> <settings> <setting name="logImpl" value="log4j"/> settings> <environments default="mysql"> <environment id="mysql"> <transactionManager type="JDBC">transactionManager> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${driver}" /> <property name="url" value="${url}" /> <property name="username" value="${username}" /> <property name="password" value="${password}" /> dataSource> environment> environments> <mappers> <package name="com.itheima"/> mappers> configuration> -
步骤二: 修改StudentDao