数据结构与算法基础-学习-26-图之MST(最小代价生成树)之Kluskal(克鲁斯卡尔)算法
最小生成树的概念、源码实现和Prim(普利姆)算法的概念和源码实现请参考之前的博客:《数据结构与算法基础-学习-25-图之MST(最小代价生成树)之Prim(普利姆)算法》
一、算法思路
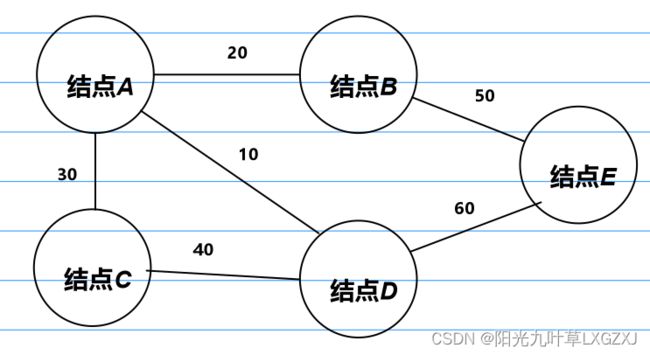
Kluskal算法相较于Prim算法选择的是边,我们还是以之前的图来举例。
我们可以看到有6条边,需要先对这些边进行升序排列,这个排序算法我选择的是插入排序,之前听老师讲的,还有其他更好更快的排序方式,好像叫桶排序,等以后会了,再和大家分享。排序结果如下:
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf WeightSortList
Data : [(0, 3, 10, 0xbf7c20),(0, 1, 20, 0xbf7c00),(0, 2, 30, 0xbf7c80),(2, 3, 40, 0xbf7c60),(1, 4, 50, 0xbf7ca0),(3, 4, 60, 0xbf7c40)]
NodeCnt : 6(0, 3, 10, 0xbf7c20)分别表示:起始节点索引,结束节点索引,权值,下一个节点的指针(我是用链表实现的),由于是无向网是12条边,还需要去重。
Kluskal算法的难点在于如何判断是否形成环,为此我们需要维护一个祖先数组,里面记录了每个节点的祖先索引号。
我们先初始化这个数组,如下:
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf Parent Array
{ -1 ,-1 ,-1 ,-1 ,-1 }第一条边:(0, 3, 10, 0xbf7c20)也就是A->D传入:
先判断是否成环,0号位的值是-1,停止往下搜索。3号位的值是-1,停止往下搜索。0 != 3,所以没有成环。加入到MST中,修改祖先数组,3号位的祖先是0。
新的祖先数组如下:
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf Parent Array
{ -1 ,-1 ,-1 ,0 ,-1 }第二条边:(0, 1, 20, 0x8ffc00)也就是A->B传入:
先判断是否成环,0号位的值是-1,停止往下搜索。1号位的值是-1,停止往下搜索。0 != 1,所以没有成环。加入到MST中,修改祖先数组,1号位的祖先是0。
新的祖先数组如下:
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf Parent Array
{ -1 ,0 ,-1 ,0 ,-1 }第三条边:(0, 2, 30, 0x8ffc80)也就是A->C传入:
先判断是否成环,0号位的值是-1,停止往下搜索。2号位的值是-1,停止往下搜索。0 != 2,所以没有成环。加入到MST中,修改祖先数组,2号位的祖先是0。
新的祖先数组如下:
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf Parent Array
{ -1 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,-1 }第四条边:(2, 3, 40, 0x104fc60)也就是C->D传入:
先判断是否成环,2号位的值是0,0号位的值是-1,停止往下搜索。3号位的值是0,0号位的值是-1,停止往下搜索。0 = 0,所以成环。这条边不加入到MST中。不修改祖先数组。
第五条边:(1, 4, 50, 0x104fca0)也就是B->E传入:
先判断是否成环,1号位的值是0,0号位的值是-1,停止往下搜索。4号位的值是-1,停止往下搜索。0 != 4,所以没有成环。加入到MST中,修改祖先数组,2号位的祖先是0。
已经加入了四条边,五个点,只需要四条边便可以组成最小生成树,打印最终的MST。
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf MST
{ (0,3,10),(0,1,20),(0,2,30),(1,4,50)}二、结构体定义
typedef struct WeightSortType
{
VertexIndexType StartIndex;//起始顶点
VertexIndexType EndIndex; //结束顶点
WeightType Weight; //起始顶点到结束顶点边上的权值
struct WeightSortType* NextNodePtr;
}WeightSortType;
//尾指针循环链表
typedef struct WeightSortListType
{
WeightSortType* TailNodePtr;
WeightType NodeCnt;
}WeightSortListType;用于链表的插入排序。
三、函数定义
1、KluskalMST
Status KluskalMST(AGraph* AG, MstType* MST)
{
JudgeAllNullPointer(AG);
JudgeAllNullPointer(MST);
WeightSortListType* SortList = NULL;
//对数据进行升序排序
InitWeightSortList(&SortList);
KluskalWeightSort(AG, SortList);
PrintfWeightSortList(SortList);
//初始化祖先数组
VertexIndexType ParentArray[AG->VertexNum];
memset(ParentArray, PARENT_INIT_VALUE, sizeof(VertexIndexType) * AG->VertexNum);
//遍历升序数组
WeightSortType* TmpNodePtr = SortList->TailNodePtr->NextNodePtr;//指向尾指针循环链表的头节点。
while(TmpNodePtr != NULL)
{
PrintfParentArray(ParentArray, AG->VertexNum);
if(JudgeMstIsCycle(ParentArray, TmpNodePtr->StartIndex, TmpNodePtr->EndIndex) == FailFlag)//表示没有成环。
{
PushMST(MST, TmpNodePtr->StartIndex, TmpNodePtr->EndIndex, TmpNodePtr->Weight);
}
if(MST->ArrayMaxLen == MST->ArrayLen)//判断是否最小生成树达到N-1条边。
{
break;
}
TmpNodePtr = TmpNodePtr->NextNodePtr;
}
DestroyWeightSortList(&SortList);
Log("Kluskal Create MST OK\n",Info);
return SuccessFlag;
}Kluskal算法形成MST的过程。
克鲁斯卡尔算法适用于稀疏图,所有我们这边用邻接表实现。
邻接表的概念和源码实现请参考之前的博客《数据结构与算法基础-学习-23-图之邻接矩阵与邻接表》
2、InitWeightSortList
Status InitWeightSortList(WeightSortListType** WST)
{
JudgeAllNullPointer(WST);
*WST = (WeightSortListType*)MyMalloc(sizeof(WeightSortListType));
(*WST)->TailNodePtr = NULL;
(*WST)->NodeCnt = 0;
Log("Init WeightSortList OK\n",Debug);
return SuccessFlag;
}
初始化权值排序链表。
3、DestroyWeightSortList
Status DestroyWeightSortList(WeightSortListType** WST)
{
JudgeAllNullPointer(WST);
JudgeAllNullPointer(*WST);
WeightSortType* TmpNode = (*WST)->TailNodePtr;
WeightSortType* TmpNextNode = NULL;
WeightType i = 0;
for(i = 0;i < (*WST)->NodeCnt; i++)
{
TmpNextNode = TmpNode->NextNodePtr;
free(TmpNode);
TmpNode = TmpNextNode;
}
(*WST)->TailNodePtr = NULL;
(*WST)->NodeCnt = 0;
free(*WST);
*WST = NULL;
Log("Destroy WeightSortList OK\n",Debug);
return SuccessFlag;
}
销毁权值排序链表。
4、KluskalWeightSort
/*
* 参数
* AG : 传入参数,邻接表。
* SortList : 传出参数,是一个尾指针循环链表,存储升序排列的权值以及顶点索引,为什么用链表呢,
* 1、数组实现的话,在进行排序时需要移动其他数据,比较耗时。
* 2、数据最后是升序的,我们是顺序访问,而不是随机访问。
*
* 支持有向网,无向网。
*
* ===============
* 实现
* 1、将邻接表中有权值的数据进行有序写入。
* 2、选用插入排序的方法对数据进行升序排列。
* 3、去重相同边。
*/
Status KluskalWeightSort(AGraph* AG, WeightSortListType* SortList)
{
JudgeAllNullPointer(AG);
JudgeAllNullPointer(SortList);
WeightType i;
ArcNode* TmpNode = NULL;
WeightSortType* TmpListNode = NULL;// 尾指针循环链表临时节点指针,遍历节点或记录头指针。
WeightSortType* TmpPreListNode = NULL;// 尾指针循环链表临时节点指针,存放上一个节点指针。
for(i = 0; i < AG->VertexNum; i++)
{
TmpNode = AG->Vertices[i].FirstArcNodePtr;
while(TmpNode != NULL)
{
if(JudgeCommonElem(i,TmpNode->EndVertexIndex,TmpNode->Weight,SortList) == SuccessFlag)//判断是否有重复的边,去重。
{
TmpNode = TmpNode->NextNodePtr;
continue;
}
if(SortList->NodeCnt == 0)
{
SortList->TailNodePtr = NewWeightSortType(i, TmpNode->EndVertexIndex, TmpNode->Weight);
SortList->TailNodePtr->NextNodePtr = SortList->TailNodePtr;
}
else
{
if(TmpNode->Weight >= SortList->TailNodePtr->Weight)//数据升序排列,邻接表中的权值大于尾节点的权值,直接插入在尾部即可。
{
TmpListNode = SortList->TailNodePtr->NextNodePtr;//存储头节点指针。
SortList->TailNodePtr->NextNodePtr = NewWeightSortType(i, TmpNode->EndVertexIndex, TmpNode->Weight);
SortList->TailNodePtr = SortList->TailNodePtr->NextNodePtr;
SortList->TailNodePtr->NextNodePtr = TmpListNode;
}
else if(TmpNode->Weight <= SortList->TailNodePtr->NextNodePtr->Weight)//小于头节点,头插法插入。
{
TmpListNode = SortList->TailNodePtr->NextNodePtr;//头节点指针
SortList->TailNodePtr->NextNodePtr = NewWeightSortType(i, TmpNode->EndVertexIndex, TmpNode->Weight);
SortList->TailNodePtr->NextNodePtr->NextNodePtr = TmpListNode;
}
else//多个节点,且邻接表的权值小于链表节点的权值。
{
TmpPreListNode = SortList->TailNodePtr->NextNodePtr;
TmpListNode = SortList->TailNodePtr->NextNodePtr->NextNodePtr;
while(TmpNode->Weight > TmpListNode->Weight)
{
TmpPreListNode = TmpListNode;
TmpListNode = TmpListNode->NextNodePtr;
}
TmpPreListNode->NextNodePtr = NewWeightSortType(i, TmpNode->EndVertexIndex, TmpNode->Weight);
TmpPreListNode->NextNodePtr->NextNodePtr = TmpListNode;
}
}
SortList->NodeCnt++;
TmpNode = TmpNode->NextNodePtr;
}
}
Log("Kluskal WeightSort OK\n",Debug);
return SuccessFlag;
}5、JudgeCommonElem
//判断是否存在相同的边。
Status JudgeCommonElem(WeightType StartIndex, WeightType EndIndex, WeightType Weight, WeightSortListType* SortList)
{
WeightType i;
WeightSortType* TmpNode = SortList->TailNodePtr;
for(i = 0; i < SortList->NodeCnt; i++)
{
if(Weight == TmpNode->Weight)
{
if(TmpNode->StartIndex == EndIndex && TmpNode->EndIndex == StartIndex)
{
return SuccessFlag;
}
}
TmpNode = TmpNode->NextNodePtr;
}
return FailFlag;
}
6、NewWeightSortType
WeightSortType* NewWeightSortType(VertexIndexType StartIndex, VertexIndexType EndIndex, WeightType Weight)
{
WeightSortType* Result = (WeightSortType*)MyMalloc(sizeof(WeightSortType));
Result->StartIndex = StartIndex;
Result->EndIndex = EndIndex;
Result->Weight = Weight;
Result->NextNodePtr = NULL;
return Result;
}
链表中新生成一个节点。
7、JudgeMstIsCycle
//判断最小生成树是否是环。
Status JudgeMstIsCycle(VertexIndexType* ParentArray, VertexIndexType StartIndex, VertexIndexType EndIndex)
{
JudgeAllNullPointer(ParentArray);
//找到起始节点和结束节点的祖先。
VertexIndexType PreVertexIndex1 = StartIndex;
while(ParentArray[PreVertexIndex1] != PARENT_INIT_VALUE)
{
PreVertexIndex1 = ParentArray[PreVertexIndex1];
}
VertexIndexType PreVertexIndex2 = EndIndex;
while(ParentArray[PreVertexIndex2] != PARENT_INIT_VALUE)
{
PreVertexIndex2 = ParentArray[PreVertexIndex2];
}
//printf("%d, %d\n",StartIndex,EndIndex);
//printf("%d, %d\n",PreVertexIndex1,PreVertexIndex2);
//printf("==============\n");
//判断起始节点和结束节点的祖先是否相等。
if(PreVertexIndex1 == PreVertexIndex2)//相等表示形成环。
{
LogFormat(Debug,"MST Is Cycle, StartIndex : %d, EndIndex : %d\n",StartIndex,EndIndex);
return SuccessFlag;
}
else//不相等,将结束节点的祖先改为起始节点。
{
ParentArray[PreVertexIndex2] = PreVertexIndex1;
return FailFlag;
}
}四、Linux环境编译测试
[gbase@czg2 Graph]$ ./TestGraph
[2023-7]--[ Info ]--Create Net Data : OK
[2023-7]--[ Info ]--Create Undirection Net Use AMGraph : OK
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf AMGraph :
VertexArray : [A ,B ,C ,D ,E ]
ArcArray :
[32767 ,20 ,30 ,10 ,32767 ]
[20 ,32767 ,32767 ,32767 ,50 ]
[30 ,32767 ,32767 ,40 ,32767 ]
[10 ,32767 ,40 ,32767 ,60 ]
[32767 ,50 ,32767 ,60 ,32767 ]
CurVertexNum : 5
CurArcNum : 12
[2023-7]--[ Info ]--Create Undirection Net Use AGraph : OK
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf AGraph :
A : [(2, 30, 0x104f8b0),(1, 20, 0x104f870),(3, 10, (nil))]
B : [(4, 50, 0x104f8d0),(0, 20, (nil))]
C : [(3, 40, 0x104f910),(0, 30, (nil))]
D : [(4, 60, 0x104f950),(2, 40, 0x104f890),(0, 10, (nil))]
E : [(3, 60, 0x104f990),(1, 50, (nil))]
VertexNum : 5
ArcNum : 12
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Traverse Use AMGraph : [4 ,1 ,0 ,2 ,3 ]
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Traverse Use AGraph : [4 ,3 ,2 ,0 ,1 ]
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Init SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Leave SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Leave SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Leave SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Destroy SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Breadth First Search Use AMGraph OK
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Traverse Use AMGraph : [4 ,1 ,3 ,0 ,2 ]
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Init SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Leave SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Leave SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Enter SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Destroy SqQueue Normal
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Breadth First Search Use AGraph OK
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Traverse Use AGraph : [4 ,3 ,1 ,2 ,0 ]
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Init WeightSortList OK
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Kluskal WeightSort OK
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf WeightSortList
Data : [(0, 3, 10, 0x104fc20),(0, 1, 20, 0x104fc00),(0, 2, 30, 0x104fc80),(2, 3, 40, 0x104fc60),(1, 4, 50, 0x104fca0),(3, 4, 60, 0x104fc40)]
NodeCnt : 6
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf Parent Array
{ -1 ,-1 ,-1 ,-1 ,-1 }
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf Parent Array
{ -1 ,-1 ,-1 ,0 ,-1 }
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf Parent Array
{ -1 ,0 ,-1 ,0 ,-1 }
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf Parent Array
{ -1 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,-1 }
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--MST Is Cycle, StartIndex : 2, EndIndex : 3
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf Parent Array
{ -1 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,-1 }
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Destroy WeightSortList OK
[2023-7]--[ Info ]--Kluskal Create MST OK
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf MST
{ (0,3,10),(0,1,20),(0,2,30),(1,4,50)}
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf ShortestEdgeArray
{(0,0),(0,20),(0,30),(0,10),(0,32767)}
ArrayLen : 1
ArrayMaxLen : 5
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Init ShortestEdgeArray OK
LowestEdgeVertexIndex : 3
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf ShortestEdgeArray
{(0,0),(0,20),(0,30),(0,0),(3,60)}
ArrayLen : 2
ArrayMaxLen : 5
LowestEdgeVertexIndex : 1
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf ShortestEdgeArray
{(0,0),(0,0),(0,30),(0,0),(1,50)}
ArrayLen : 3
ArrayMaxLen : 5
LowestEdgeVertexIndex : 2
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf ShortestEdgeArray
{(0,0),(0,0),(0,0),(0,0),(1,50)}
ArrayLen : 4
ArrayMaxLen : 5
LowestEdgeVertexIndex : 4
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Destroy ShortestEdgeArray OK
[2023-7]--[ Info ]--Prim Create MST OK
[2023-7]--[ Debug ]--Printf MST
{ (0,3,10),(0,1,20),(0,2,30),(1,4,50)}
[2023-7]--[ Info ]--Destroy Net Data : OK
[2023-7]--[ Info ]--Destroy Undirection Net Use AMGraph: OK
[2023-7]--[ Info ]--Destroy Undirection Net Use AGraph : OK五、Prim算法和Kluskal算法对比
| 算法名 | Prim | Kluskal |
| 思路 | 选择点 | 选择边 |
| 时间复杂度 | O(N^2)(n为顶点数) | O(eloge)(e为边数) |
| 适用范围 | 稠密图 | 稀疏图 |