K-近邻法分类(KNN)
一、K-近邻法分类(MATLAB)
% ====================K-近邻法(KNN)=================================
% X: 训练样本
% x: 待判样本
% K: 近邻数目
% flag1: 记录K个最近邻中属于第一类的个数
% flag2: 记录K个最近邻中属于第二类的个数
% ===================================================================
clear,close all;
N=150;
X = [randn(N,2)+2*ones(N,2);...
randn(N,2)-2*ones(N,2);];
% ====================================================================
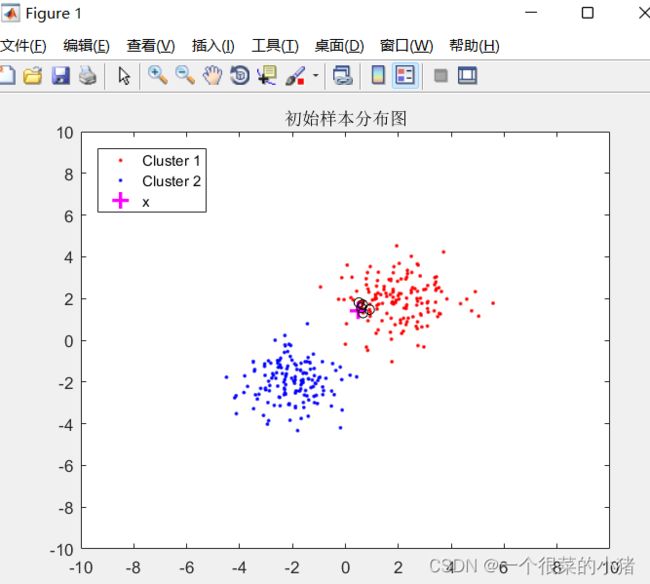
fig=figure;
plot(X(1:N,1),X(1:N,2),'r.')
hold on,plot(X(N+1:2*N,1),X(N+1:2*N,2),'b.')
title('初始样本分布图'),axis([-10,10,-10,10])
% ====================================================================
x=randn(1,2);%待判样本
hold on,plot(x(1),x(2),'m+','MarkerSize',10,'LineWidth',2)
for i=1:2*N
dist(i)=norm(x-X(i,:));
end
[Sdist,index]=sort(dist,'ascend');
K=5; %近邻数目
for i=1:K
hold on,plot(X(index(i),1),X(index(i),2),'ko');
end
legend('Cluster 1','Cluster 2','x','Location','NW')
flag1=0;flag2=0;
for i=1:K
if ceil(index(i)/N)==1
flag1=flag1+1;
elseif ceil(index(i)/N)==2
flag2=flag2+1;
end
end
disp(strcat('K近邻中包含',num2str(flag1),'个第一类样本'));
disp(strcat('K近邻中包含',num2str(flag2),'个第二类样本'));
if flag1>flag2
disp('判断待判样本属于第一类');
else
disp('判断待判样本属于第二类');
end
待判样本为随机
情况一:
K近邻中包含5个第一类样本
K近邻中包含0个第二类样本
判断待判样本属于第一类
情况二:
K近邻中包含1个第一类样本
K近邻中包含4个第二类样本
判断待判样本属于第二类
二、快速近邻法分类
该算法在聚类完成之后,进行树搜索,速度的确比一般的近邻方法快,但是由于聚类要消耗大量的时间,因此总速度不如一般的近邻方法。
% ==========================快速近邻算法===============================
% ================聚类过程所使用的主要变量==============================
% X: 随机产生的样本集
% l: 划分的子集数目
% L: 水平数目
% Xp: 节点p对应的样本子集
% Mp: 各类的均值
% Rp: 从Mp到Xi的最远距离
% =============树搜索过程所使用的重要变量=================================
% CurL: 当前水平
% p: 当前结点
% CurTable: 当前目录表中的子样本集
% CurPinT: 在当前目录表中的子样本结点
% RpCur: 当前目录表中结点p对应的Rp
% x: 待判样本
% =====================================================================
% 实验结果表明,该算法在聚类完成之后,进行树搜索,速度的确比一般的近邻方法快
% 当时由于聚类要消耗大量的时间,因此总速度不如一般的近邻方法
% =====================================================================
% Copyright Wang Chuanting.
% $Revision: 1.0 $ $Date: 2008/05/09 09:40:34 $
% ======================================================================
% ======================================================================
% ---首先进行聚类---
clear,close all;
% tic
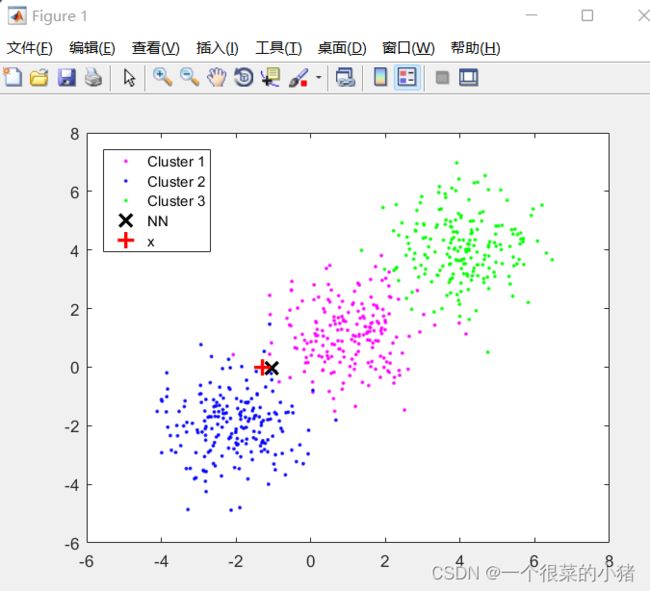
X = [randn(200,2)+ones(200,2);...
randn(200,2)-2*ones(200,2);...
randn(200,2)+4*ones(200,2);];
% ---每个水平均划分为l个子集---
[row,col]=size(X);
all_idx=0;L=3;l=3;
%计算总节点的数目
for i=1:L
all_idx=all_idx+l^i;
end
Xp=cell(all_idx,1);
Mp=zeros(all_idx,col);
Rp=zeros(all_idx,1);
p=1;
for i=1:L
if i==1
[IDX,C,sumd,D] = kmeans(X,l);
for j=1:l
Xp(p)={X((IDX==j),:)};
Mp(p,:)=C(j,:);
Rp(p)=max(D((IDX==j),j));
p=p+1;
end
else
endk=p-1;begink=endk-l^(i-1)+1;
for k=begink:endk
[IDX,C,sumd,D] = kmeans(Xp{k,1},l);
X1=Xp{k,1};
for j=1:l
Xp(p)={X1((IDX==j),:)};
Mp(p,:)=C(j,:);
Rp(p)=max(D((IDX==j),j));
p=p+1;
end
end
end
end
% ====================================================================
% ---进行树搜索---
tic
x=randn(1,2);%待判样本
B=inf;CurL=1;p=0;TT=1;
while TT==1 %步骤2
Xcurp=cell(1);
CurTable=cell(l,1);
CurPinT=zeros(l,1);
Dx=zeros(l,1);
RpCur=zeros(l,1);
%当前节点的直接后继放入目录表
for i=1:l
CurTable(i,1)=Xp(i+p*l,1);
CurPinT(i)=i+p*l;
Dx(i)=norm(x-Mp(i+p*l,:))^2;
RpCur(i)=Rp(i+p*l);
end
while 1 %步骤3
[rowT,colT]=size(CurTable);
for i=1:rowT
if Dx(i)>B+RpCur(i)+eps%从目录表中去掉当前节点p
CurTable(i,:)=[];
CurPinT(i)=[];
Dx(i)=[];
RpCur(i)=[];
break;
end
end
[CurRowT,CurColT]=size(CurTable);
if CurRowT==0
CurL=CurL-1;p=floor((p-1)/3);
if CurL==0
TT=0; break;
else
%转步骤3
end
elseif CurRowT>0
[Dxx,Dxind]=sort(Dx,'ascend');
p1=CurPinT(Dxind(1));
p=p1;
%从当前目录表去掉p1
for j=1:CurRowT
if CurPinT(j)==p1
Xcurp(1,1)=CurTable(j,1);
CurTable(j,:)=[];
CurPinT(j)=[];
CurD=Dx(j);%记录D(x,Mp)
Dx(j)=[];
RpCur(j)=[];
break;
end
end
if CurL==L
XcurpMat=cell2mat(Xcurp);
[CurpRow,CurpCol]=size(XcurpMat);
CurpMean=Mp(p,:);
for k=1:CurpRow
Dxi=norm((XcurpMat(k,:)-CurpMean))^2;
if CurD>Dxi+B+eps
else
Dxxi=norm((x-XcurpMat(k,:)))^2;
if Dxxi