算法(2)
二叉树
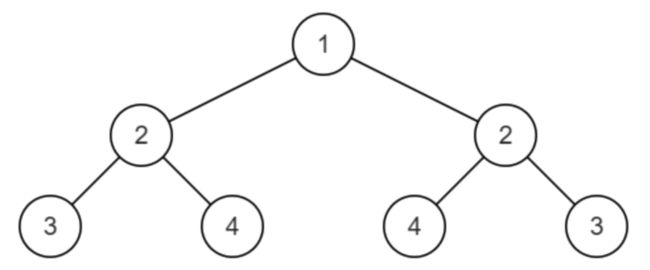
镜像二叉树
树轴对称
第一个节点的左子树与第二个节点的右子树同步递归对比,第一个节点的右子树与第二个节点的左子树同步递归比较。
二叉树序列化、反序列化
当然你也可以根据满二叉树结点位置的标号规律来序列化,还可以根据先序遍历和中序遍历的结果来序列化。不对序列化之后的字符串进行约束,所以欢迎各种奇思妙想。
思路 : 序列化树,递归前序遍历,反序列化同。序列化为字符串 1!#22! ,用!分割灭一个数值,#区分空节点。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
//序列的下标
public int index = 0;
//处理序列化的功能函数(递归)
private void SerializeFunction(TreeNode root, StringBuilder str) {
//如果节点为空,表示左子节点或右子节点为空,用#表示
if (root == null) {
str.append('#');
return;
}
//根节点
str.append(root.val).append('!');
//左子树
SerializeFunction(root.left, str);
//右子树
SerializeFunction(root.right, str);
}
public String Serialize(TreeNode root) {
//处理空树
if (root == null)
return "#";
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
SerializeFunction(root, res);
//把str转换成char
return res.toString();
}
//处理反序列化的功能函数(递归)
private TreeNode DeserializeFunction(String str) {
//到达叶节点时,构建完毕,返回继续构建父节点
//空节点
if (str.charAt(index) == '#') {
index++;
return null;
}
//数字转换
int val = 0;
//遇到分隔符或者结尾
while (str.charAt(index) != '!' && index != str.length()) {
val = val * 10 + ((str.charAt(index)) - '0');
index++;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(val);
//序列到底了,构建完成
if (index == str.length())
return root;
else
index++;
//反序列化与序列化一致,都是前序
root.left = DeserializeFunction(str);
root.right = DeserializeFunction(str);
return root;
}
public TreeNode Deserialize(String str) {
//空序列对应空树
if (str == "#")
return null;
TreeNode res = DeserializeFunction(str);
return res;
}
}
二叉搜索树第k节点
中序遍历返回遍历的第k个节点。
返回二叉搜索树 两个节点的最近公共祖先
思路1:返回当前节点到p和q的距离之和,能获得最小的距离就是根节点。递归,可以适用于(非有序的),题目中给定有序,那就只要判断当前节点是不是 root.val >=p&&q>=root.val 或者root.val <= p&& q>= root.val的那个节点即可。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, int p, int q) {
if (root == null) return -1;
if (root.val >= p && root.val <= q) {
return root.val;
} else if (root.val <= p && root.val >= q) {
return root.val;
} else {
if (root.val < p) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
} else {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
}
}
}
}
思路2:题目给定二叉搜索树,有序的,那就可以分别判断两个节点p、q在当前节点的左子树还是右子树。然后再遍历的过程中记录到达p或者q遍历过的元素路径,最后比较两个路径,最后一个相同的元素即是要求节点。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
//求得根节点到目标节点的路径
public ArrayList<Integer> getPath(TreeNode root, int target) {
ArrayList<Integer> path = new ArrayList<Integer>();
TreeNode node = root;
//节点值都不同,可以直接用值比较
while(node.val != target){
path.add(node.val);
//小的在左子树
if(target < node.val)
node = node.left;
//大的在右子树
else
node = node.right;
}
path.add(node.val);
return path;
}
public int lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, int p, int q) {
//求根节点到两个节点的路径
ArrayList<Integer> path_p = getPath(root, p);
ArrayList<Integer> path_q = getPath(root, q);
int res = 0;
//比较两个路径,找到第一个不同的点
for(int i = 0; i < path_p.size() && i < path_q.size(); i++){
int x = path_p.get(i);
int y = path_q.get(i);
//最后一个相同的节点就是最近公共祖先
if(x == y)
res = path_p.get(i);
else
break;
}
return res;
}
}
返回二叉树中 两个节点的最近公共祖先
二叉树,递归遍历每个节点,要求当前节点往左or右能够到达p,且往右or左能够到达q。否则往子树递归遍历。
public int lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, int o1, int o2) {
return helper(root, o1, o2).val;
}
public TreeNode helper(TreeNode root, int o1, int o2) {
if (root == null || root.val == o1 || root.val == o2)
return root;
TreeNode left = helper(root.left, o1, o2);
TreeNode right = helper(root.right, o1, o2);
//如果left为空,说明这两个节点在root结点的右子树上,我们只需要返回右子树查找的结果即可
if (left == null)
return right;
//同上
if (right == null)
return left;
//如果left和right都不为空,说明这两个节点一个在root的左子树上一个在root的右子树上,
//我们只需要返回cur结点即可。
return root;
}
返回二叉树和为t的路径
回溯
import java.util.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> FindPath(TreeNode root, int expectNumber) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null) return res;
ArrayList<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<> ();
_find(res, temp, expectNumber, root);
return res;
}
static void _find(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res, ArrayList<Integer> list,
int t, TreeNode root) {
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
if (root.val == t) {
list.add(root.val);
ArrayList<Integer> ls = new ArrayList<>(list);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
res.add(ls);
return ;
}
else return ;
}
if (root.left == null) {
list.add(root.val);
_find(res, list, t - root.val, root.right);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
return ;
}
if (root.right == null) {
list.add(root.val);
_find(res, list, t - root.val, root.left);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
return ;
}
list.add(root.val);
_find(res, list, t - root.val, root.left);
_find(res, list, t - root.val, root.right);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
}
}
平衡二叉树判断
递归的判断左右子树是否平衡,平衡继续判断当前节点的左子树和右子树的高度差是否满足小于2要求。满足返回true,否则返回false。
public class Solution {
public boolean IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
//判断左子树和右子树是否符合规则,且深度不能超过2
//先递归判断左子树 右子树 是否符合规则,否则判断当前节点的的左子树和右子树的高度差是否小于2
return IsBalanced_Solution(root.left) && IsBalanced_Solution(root.right) && Math.abs(deep(root.left) - deep(root.right)) < 2;
}
//判断二叉树深度
public int deep(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(deep(root.left), deep(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
链表
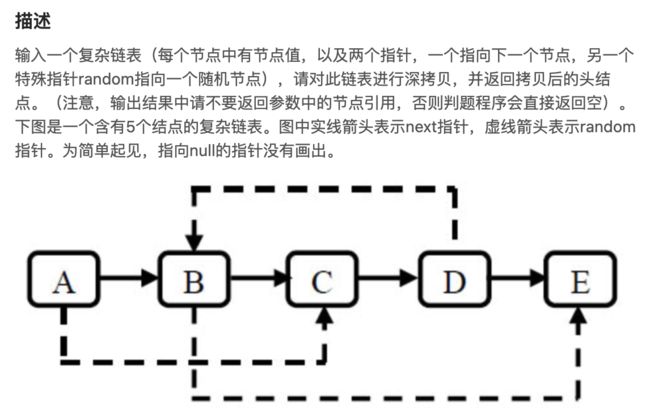
复杂链表深拷贝
import java.util.*;
/*
public class RandomListNode {
int label;
RandomListNode next = null;
RandomListNode random = null;
RandomListNode(int label) {
this.label = label;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null) return null;
RandomListNode node = pHead;
RandomListNode head = null;
RandomListNode temp = null;
HashMap<RandomListNode, RandomListNode> map = new HashMap<>();
while (node != null) {
if (head == null) {
RandomListNode rn = new RandomListNode(node.label);
head = rn;
temp = rn;
map.put(node, temp);
} else {
temp.next = new RandomListNode(node.label);
map.put(node, temp.next);
temp = temp.next;
}
node = node.next;
}
while (pHead != null) {
if (pHead.random != null)
map.get(pHead).random = map.get(pHead.random);
pHead = pHead .next;
}
return head;
}
}
递归回溯
n皇后
找到对角线数组与行、列号的关系。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param n int整型 the n
* @return int整型
*/
static int count = 0;
public int Nqueen (int n) {
// write code here
//记录行列 斜对角线是否摆放过
boolean r [] = new boolean [n];
boolean l [] = new boolean [n];
//正对角线 n-j-1+i
boolean tx[] = new boolean [2 * n - 1];
//斜对角线 i+j
boolean rx[] = new boolean [2 * n - 1];
//放第一个
// for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
dfs(r, l, rx, tx, 0);
// }
// System.out.println(count);
return count;
}
static void dfs(boolean r[], boolean l[], boolean rx[], boolean tx[],
int index) {
if (index == r.length) {
count++;
return ;
}
int n = r.length;
//试探第j列
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (!r[index] && !l[j] && !tx[n - j - 1 + index] && !rx[index + j]) {
r[index] = true;
l[j] = true;
tx[n - j - 1 + index] = true;
rx[index + j] = true;
dfs(r, l, rx, tx, index + 1);
r[index] = false;
l[j] = false;
tx[n - j - 1 + index] = false;
rx[index + j] = false;
}
}
}
}
矩阵最长路径问题
给定矩阵求最长递增序列长度。起点终点不限,智能上下左右。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-PYvX44xs-1690389890287)(https://s2.loli.net/2022/07/15/vkDchA2qdfSGeIK.png)]
递归
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
* 递增路径的最大长度
* @param matrix int整型二维数组 描述矩阵的每个数
* @return int整型
*/
public int solve (int[][] matrix) {
// write code here
//深度优先搜索
int dis = 0;
boolean maze[][] = new boolean [matrix.length][matrix[0].length];
int m = 0;
int r = matrix.length;
int l = matrix[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < l; j++) {
m = Math.max(_dfs(i, j, maze, matrix) + 1, m);
}
}
return m;
}
static int _dfs(int x, int y, boolean [][]maze, int matrix[][]) {
int r = maze.length;
int l = maze[0].length;
int max = 0;
maze[x][y] = true;
int v = matrix[x][y];
//右
if (y < l - 1 && !maze[x][y + 1] && matrix[x][y + 1] > v) {
max = Math.max(_dfs(x, y + 1, maze,matrix) + 1, max);
}
//下
if (x < r - 1 && !maze[x + 1][y] && matrix[x + 1][y] > v) {
max = Math.max(_dfs(x + 1, y, maze,matrix) + 1, max);
}
if (x > 0 && !maze[x - 1][y] && matrix[x - 1][y] > v) {
max = Math.max(_dfs(x - 1, y, maze,matrix) + 1, max);
}
if (y > 0 && !maze[x][y - 1] && matrix[x][y - 1] > v) {
max = Math.max(_dfs(x, y - 1, maze,matrix) + 1, max);
}
maze[x][y] = false;
return max;
}
}
dp优化,dp[x][y]表示从x,y开始所能拓展到的最长递增序列长度。当后面再次遍历到x,y节点可以直接返回。同时maze不需要,因为每一步都是也只能往高处走,不会往回走的情况。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
* 递增路径的最大长度
* @param matrix int整型二维数组 描述矩阵的每个数
* @return int整型
*/
public int solve (int[][] matrix) {
// write code here
//深度优先搜索
//矩阵不为空
if (matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0)
return 0;
// boolean maze[][] = new boolean [matrix.length][matrix[0].length];
int m = 0;
int r = matrix.length;
int l = matrix[0].length;
int dp [][] = new int[r][l];
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < l; j++) {
m = Math.max(_dfs(i, j, matrix, dp), m);
}
}
return m;
}
static int _dfs(int x, int y, int matrix[][], int dp[][]) {
//优化 减少递归
if (dp[x][y] != 0) return dp[x][y];
int r = matrix.length;
int l = matrix[0].length;
int max = 1;
int v = matrix[x][y];
//右
if (y < l - 1 && matrix[x][y + 1] > v) {
max = Math.max(_dfs(x, y + 1, matrix, dp) + 1, max);
}
//下
if (x < r - 1 && matrix[x + 1][y] > v) {
max = Math.max(_dfs(x + 1, y, matrix, dp) + 1, max);
}
if (x > 0 && matrix[x - 1][y] > v) {
max = Math.max(_dfs(x - 1, y, matrix, dp) + 1, max);
}
if (y > 0 && matrix[x][y - 1] > v) {
max = Math.max(_dfs(x, y - 1, matrix, dp) + 1, max);
}
//表示从dp[x][y] 拓展的最长递增子序列长度
dp[x][y] = max;
return max;
}
}
贪心
活动安排
给定各个活动的开始结束时间,要求最大活动数量。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
//创建一个集合存储数据
List<Node> xD = new ArrayList<Node>();
Node node;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
//数据类型的起始值
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
node = new Node(a, b);
//将活动对应的起始和结束时间加入集合
xD.add(node);
}
//对活动时间进行排序,按照末尾时间从小到大的标准
Collections.sort(xD, (o1, o2)-> {
return o1.end - o2.end;
});
int begin = 0, count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
//当当前的起始值大于上一个活动的结束值时,符合要求
if (xD.get(i).start >= begin) {
//更新begin的值
begin = xD.get(i).end;
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
//节点类
class Node {
//该数据类型包含一个起始值,一个结束值,一个标记,
int start;
int end;
public Node(int start, int end) {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
}