记录一次Mongodb-mongotemplate的聚合查询
目录
-
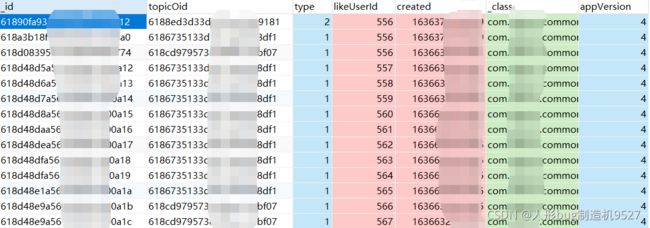
- 首先表结构如下
-
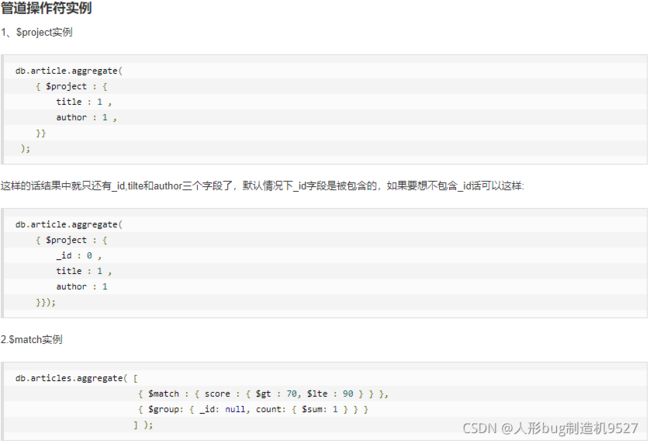
- 先是原生
- MongoTemplate
- 下面附上一些原生聚合查询的处理器以及使用实例;
-
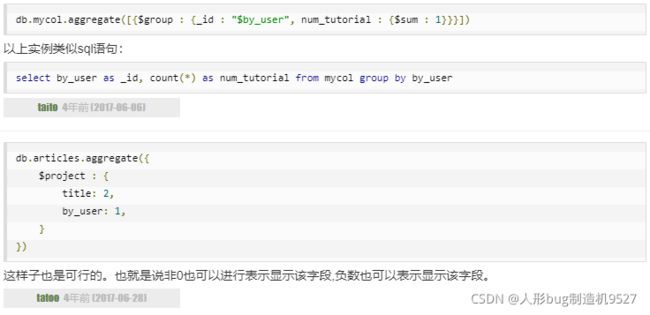
- 一些大佬的讨论
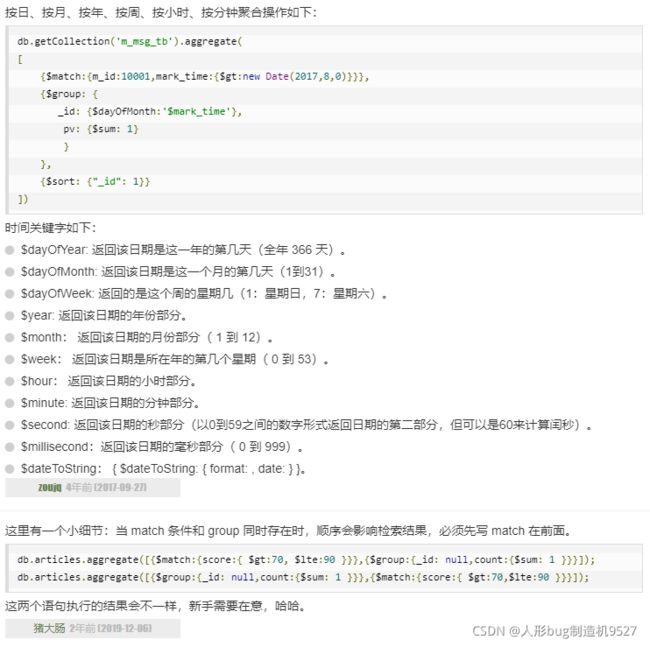
- 坑:
-
- count和group添加时机导致的错误
- 附上一些其他的MongoTemplate使用示例
-
- 表结构
- Main
- 统计某段时间内访问API的最新时间
- 按天统计
- 去重统计所有字段的总数
- 统计符合条件的所有数据量
- 所有数据按userId分组,也就是去重,看看有多少个userid
首先表结构如下
这里就是需要我们按照topicOid分组并统计次数按照次数倒序排
这里需要使用管道聚合查询,顾名思义就像一个管道一样,上一个处理完的数据传递给下一个;
这里有两种写法,一种是使用原生的语句字符串调用,一种是使用封装好的Mongotemplate进行查询;
先是原生
db.表名.aggregate
db.ad_topic_like.aggregate(
[
{$match:{type:{$eq:1},appVersion:{$eq:4}}},
{$group:{_id:"$topicOid",countNum:{$sum:1}}}, // 这里的1是统计结果*1
{$sort:{"countNum":-1}},
{$skip:0},
{$limit:10}
]
)
可以看到,就像管道一样,aggregate()里面是一个数组,处理的时候按照索引顺序逐个处理,里面的每一个{}就是一项处理流程,所以千万注意处理器的顺序;
java中的调用方法稍后补上
MongoTemplate
/**
* 分页查询所有idea信息,按点赞数排序
*
* @param page
* @param size
* @param appVersion 查询的模式,当前版本,投票中
* @return
*/
@Override
public List<UserIdea> userIdeaFindPage(Integer page, Integer size, Integer appVersion) {
// 先在topicLike中查所有类型为1的,点赞数排行的分页数据(这里只查idea的点赞排行)
// 创建筛选条件
Criteria criteria = new Criteria();
criteria.andOperator(
Criteria.where("type").is(TopicLikeTypeEnum.IDEA_LIKE.getType()),
Criteria.where("appVersion").is(appVersion)
);
// 创建排序条件[注意这里由于处理器使用在分组后,刚好需要按照分组统计后AS的别名进行排序,所以这里的排序字段一定要和AS对应]
Sort sort0 = new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC, "likeCount");
// 拼装查询条件
Aggregation aggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation(
// 添加筛选流程
Aggregation.match(criteria),
// 添加分组规则,这里使用count统计次数,赋予别名likeCount
Aggregation.group("topicOid").count().as("likeCount"),
// 添加排序规则
Aggregation.sort(sort0),
// 进行分页配置
Aggregation.skip(Long.valueOf((page - 1) * size)),
Aggregation.limit(size)
);
// 执行管道查询,,,注意这里参数中的第二个为collectionName,也就是集合名称,对应mongodb中的表名(管道,集合名称,接收结果的结果集)
AggregationResults<TopicLikeSortCount> ideaCount = mongoTemplate.aggregate(aggregation, "ad_topic_like", TopicLikeSortCount.class);
// 这里和上一条的泛型字段一定要包含id和我们使用的AS likeCount否则无法封装
List<TopicLikeSortCount> list = ideaCount.getMappedResults();
System.out.println(list);
return list;
}
这里的管道处理器和原生有相似的地方,稍微推导一下就知道怎么使用了;
下面附上一些原生聚合查询的处理器以及使用实例;
一些大佬的讨论
坑:
count和group添加时机导致的错误
Aggregation aggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation(
Aggregation.match(criteria),
Aggregation.group("userId"),
Aggregation.count().as("count")
);
Aggregation aggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation(
Aggregation.match(criteria),
Aggregation.group("userId").count().as("count");
);
第一个是把数据处理完了,数据整体,也就是分好组的数据交给下面,让他进行计数;
第二个是把数据按照userId分组并统计他们各自出现的次数,赋值给count;
理解:
第一个:分组完了。得到一个完整的分组后数据,然后执行count统计次数;
第二个:分组的同时,对每个分组的条数进行统计计数;
附上一些其他的MongoTemplate使用示例
表结构
{
"datetime" : "20200101000000",
"missid" : [
"54748",
"54859",
"54946"
],.....
}
Main
/*
* project:列出所有本次查询的字段,包括查询条件的字段和需要搜索的字段;
* match:搜索条件criteria
* unwind:某一个字段是集合,将该字段分解成数组
* group:分组的字段,以及聚合相关查询
* sum:求和(同sql查询) group("type").sum("size").as("total")
* count:数量(同sql查询) group("missid").count().as("count")
* as:别名(同sql查询)
* addToSet:将符合的字段值添加到一个集合或数组中
* sort:排序
* skip&limit:分页查询
*/
public String getLostStationSumByTimeRange(String timeRange) {
String[] times = timeRange.split(",");
Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("datetime").gte(times[0]).lte(times[1]);
Aggregation aggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation(match(criteria), project("missid"),
Aggregation.unwind("missid"), group("missid").count().as("count"),
project("count").and("missid").previousOperation(), Aggregation.sort(Sort.Direction.DESC, "count"));
AggregationResults<SubjectCount> ar = mongoTemplate.aggregate(aggregation, "XXLog",
SubjectCount.class);
List<SubjectCount> lists = ar.getMappedResults();
for(SubjectCount sub : lists) {
Station s = mongoTemplate.findOne(new Query(Criteria.where("stationid").is(Integer.parseInt(sub.getMissid()))), Station.class,"station");
if(s!=null) {
sub.setName(s.getName());
sub.setArea(s.getArea());
sub.setCity(s.getCity());
}
}
return new Gson().toJson(lists);
}
查询结果
[
{
"missid": "54659",
"count": 25,
"name": "xx",
"city": "xx",
"area": "xx"
},
{
"missid": "54862",
"count": 25,
"name": "xx",
"city": "xx",
"area": "xx"
}....]
统计某段时间内访问API的最新时间
public Object getAPINameByTimeRange(String timeRange) {
String[] times = timeRange.split(",");
Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("accesstime").gte(times[0]).lte(times[1]);
Aggregation aggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation(match(criteria),
sort(Sort.Direction.DESC, "accesstime"), //倒序
group("apiname").first("accesstime").as("accesstime"), //按api名字分组,取第一个时间
project("apiname", "accesstime").and("apiname").previousOperation());
AggregationResults<APIMonitor> ar = mongoTemplate.aggregate(aggregation, "monitor", APIMonitor.class);
List<APIMonitor> list = ar.getMappedResults();
}
按天统计
MongoDB3.4
public Object getAPIByDay(String timeRange) {
String[] times = timeRange.split(",");
Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("accesstime").gte(times[0]).lte(times[1]);
Aggregation aggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation(match(criteria),
project("day").andExpression("substr(accesstime,0,8)").as("time"), //转换格式
group("day", "time").count().as("total"),
sort(Sort.Direction.DESC, "time"));
AggregationResults<APIMonitor> ar = mongoTemplate.aggregate(aggregation, "Monitor", APIMonitor.class);
List<APIMonitor> list = ar.getMappedResults();
}
或者MongoDB3.6及以上
Aggregation aggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation(
Aggregation.project(""inDate")
.andExpression("{$dateToString:{format:'%Y年%m月%d日',date:'$inDate',timezone: 'Asia/Shanghai'}}").as("dateToString")
);
查询结果
[{
"total": 1933,
"time": "20200526"
},
{
"total": 27550,
"time": "20200525"
}]
后续用例来自
https://blog.csdn.net/jiangshuanshuan/article/details/106360423
去重统计所有字段的总数
结构
db.coll.aggregate(
{$group: {_id: "$key1.key_to_distinct"}},
{$group: {_id: 1, count: {$sum: 1}}}
)
Aggregation count = Aggregation.newAggregation(
Aggregation.group("userId"),
Aggregation.count().as("totalCount")
);
mongoTemplate.aggregate(count, MessagePO.class, Map.class);
统计符合条件的所有数据量
Aggregation aggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation(
Aggregation.match(criteria),
// 统计符合条件的所有数据量
//Aggregation.group("userId"),
Aggregation.count().as("count")
);
所有数据按userId分组,也就是去重,看看有多少个userid
Aggregation aggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation(
Aggregation.match(criteria),
// 所有数据按userId分组,也就是去重,看看有多少个userid
Aggregation.group("userId"),
Aggregation.count().as("count")
);