对数组进行排序:Arrays.sort()
大家好,我是三叔,很高兴这期又和大家见面了,一个奋斗在互联网的打工人。
笔者在上期给大家介绍了如何使用String的toCharArray()方法,这期给各位读者朋友介绍一下Java中的Arrays.sort()方法。
在Java中,Arrays类是一个非常有用的工具类,它提供了各种对数组进行操作的方法。其中之一是sort()方法,用于对数组进行排序。Arrays.sort()方法可以对任何数组进行排序,包括基本类型和对象类型数组。本文将介绍如何使用Arrays.sort()方法对数组进行排序。
如何使用Arrays.sort()
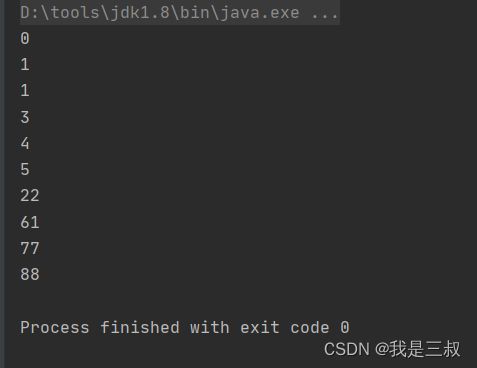
不废话,上代码:
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 88, 22, 61, 0, 77};
Arrays.sort(arr);
for (int i : arr) {
// 打印看一看
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
sort()源码解析
Arrays.sort()方法还有其他参数可以使用,例如可以指定排序的范围和排序的方式。下面是Arrays.sort()方法的详细参数:
下面展示了不同类型的数组对象,也可以指定数组下标来进行排序
public static void sort(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex);
public static void sort(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex);
public static void sort(float[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex);
public static void sort(double[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex);
public static void sort(Object[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex);
public static <T> void sort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, Comparator<? super T> c);
public static void sort(char[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex);
public static void sort(byte[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex);
public static void sort(short[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex);
例如:对数组下标2对应的到下标为6的结束排序,也就是对4、1、5、88进行排序,包含起始下标(fromIndex),不包含结束下标(endIndex这个索引值)
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 88, 22, 61, 0, 77};
Arrays.sort(arr, 2, 6);
for (int i : arr) {
// 打印看一看
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
结果如下: