ARM Cortex-A系列编程指南之ARMv8 A -- 第四章 ARMv8寄存器
1、通用寄存器
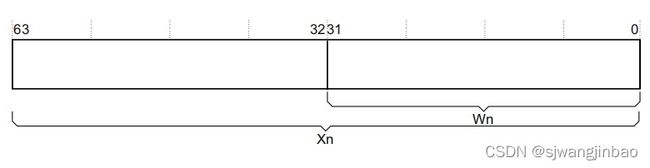
AArch64运行环境提供了31个64bit的通用寄存器:X0~X31,同时他们也都有32bit的形式:W0~W31,他们对应映射到64bit寄存器的低32位。
读取W寄存器,将会只读X的低32位;
写W寄存器,将会将X的高32位写为0。也就是说设置W0为0xFFFFFFFF,结果设置X0为0x00000000FFFFFFFF。
2、AArch64特殊寄存器
除了31个核心寄存器外,还有一些特殊寄存器。
在AArch64运行状态,异常返回的状态,保存在每个异常等级的ELR和SPSR寄存器 (EL0不用异常返回,所以这个异常等级没有ELR和SPSR寄存器)。
2.1 XZR/WZR寄存器(零寄存器)
读的时候返回0,写的时候忽略写的值。
2.2 SP寄存器(堆栈指针)
每个异常等级都有自己的SP寄存器(SP_EL0, SP_EL1, SP_EL2, SP_EL3)。但是,除了EL0以外,其它异常等级都有两个选择,或者用自己等级的SP_ELn,或者用EL0等级的SP_EL0;EL0就只能用SP_EL0了。
| 异常等级 | 选项 |
| EL0 | EL0t |
| EL1 | EL1t, EL1h |
| EL2 | EL2t, EL2h |
| EL3 | EL3t, EL3h |
t表明选择了SP_EL0寄存器,h表明选择了SP_ELn寄存器。
2.3 PC寄存器(程序计数)
ARMv7有个R15寄存器,就是PC(程序计数)寄存器,是可以作为通用寄存器使用的。
但是ARMv8这里不一样了,不能被当做有名字的寄存器来访问了。
2.4 ELR(异常连接)寄存器
保存异常返回的地址。
2.5 SPSR寄存器(保存的进程状态寄存器)
当异常发生时,处理器的状态就被保存在SPSR寄存器里,和ARMv7中的CPSR类似。SPSR保存了处理异常前的PSTATE,当异常返回前需要将PSTATE设回来。
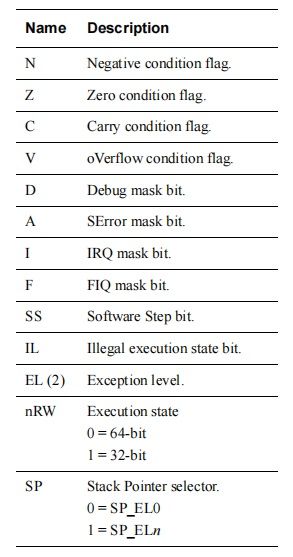
3、处理器状态(PSTATE)
AArch64没有像ARMv7的CPSR寄存器,需要通过PSATE,其各个字段定义如下:
其中N、Z、C、V可以在EL0访问,其他字段在EL0是未定义状态,需要在EL1或者更高级访问或执行。
在AArch64运行状态,通过执行ERET指令从异常返回,从而导致SPSR_ELn被拷贝到了PSTATE。
4、系统寄存器(System Registers)
在AArch64运行状态,使用MSR和MRS指令,通过系统寄存器(System Registers)来进行系统的配置。而在ARMv7上,使用协处理器CP15。之前的ARM版本都使用协处理器进行系统配置,但是AArch64不支持协处理器。
寄存器的名字,指出了其能被访问的最低的异常等级。比如:
TTBR0_EL1可以在EL1、EL2、EL3访问;
TTBR0_EL2可以在EL2、EL3访问。
访问这些寄存器的汇编指令(M代表move,R代表寄存器,S代表系统寄存器):
| 名字 | 寄存器 | 描述 | n的值 |
|
ACTLR_EL n
|
赋值控制寄存器 Auxiliary Control Register |
控制处理器特有的feature | 1,2,3 |
|
CCSIDR_EL n
|
当前缓存大小ID寄存器
Current Cache Size ID Register
|
提供当前选中的缓存信息 | 1 |
|
CLIDR_EL n
|
缓存等级ID寄存器
Cache Level ID Register
|
缓存的类型 | 1,2,3 |
|
CNTFRQ_EL n
|
计数时钟频率寄存器
Counter-timer Frequency Register
|
系统时钟的频率 | 0 |
|
CNTPCT_EL n
|
计数时钟的物理计数寄存器
Counter-timer Physical Count Register
|
64bit的时钟的物理计数 | 0 |
|
CNTKCTL_EL n
|
计数时钟的内核控制寄存器
Counter-timer Kernel Control Register
|
控制从虚拟计数器产生的事件。
Also controls access from EL0 to the physical counter,
virtual counter, EL1 physical timers, and the virtual timer.
|
1 |
|
CNTP_CVAL_EL n
|
Counter-timer Physical Timer Compare Value Register
|
Holds the compare value for the EL1 physical timer.
|
0 |
|
CPACR_EL n
|
Coprocessor Access Control Register
|
Controls access to Trace, floating-point, and NEON
functionality
|
1 |
|
CSSELR_EL n
|
Cache Size Selection Register
|
Selects the current Cache Size ID Register, CCSIDR_EL1, by
specifying the required cache level and the cache type, either
instruction or data cache.
|
1 |
|
CNTP_CTL_EL n
|
Counter-timer Physical Control Register
|
Control register for the EL1 physical timer.
|
0 |
|
CTR_EL n
|
Cache Type Register
|
Information about the architecture of the integrated caches.
|
0 |
|
DCZID_EL n
|
Data Cache Zero ID Register
|
Indicates the block size written with byte values of 0 by the Data
Cache Zero by Virtual Address (DCZVA) system instruction.
|
0 |
|
ELR_EL n
|
Exception Link Register
|
Holds the address of the instruction which caused the exception.
|
1,2,3 |
|
ESR_EL n
|
Exception Syndrome Register
|
Includes information about the reasons for the exception.
|
1,2,3 |
|
FAR_EL n
|
Fault Address Register
|
Holds the virtual faulting address.
|
1,2,3 |
|
FPCR
|
Floating-point Control Register
|
Controls floating-point extension behavior. The fields in this
register map to the equivalent fields in the AArch32 FPSCR.
|
- |
|
FPSR
|
Floating-point Status Register
|
Provides floating-point system status information. The fields in
this register map to the equivalent fields in the AArch32
FPSCR.
|
- |
|
HCR_EL n
|
Hypervisor Configuration Register
|
Controls virtualization settings and trapping of exceptions to
EL2.
|
2 |
|
MAIR_EL n
|
Memory Attribute Indirection Register
|
Provides the memory attribute encodings corresponding to the
possible values in a Long-descriptor format translation table
entry for stage 1 translations at EL n .
|
1,2,3 |
|
MIDR_EL n
|
Main ID Register
|
The type of processor the code is running on (part number and
revision).
|
1 |
|
MPIDR_EL n
|
Multiprocessor Affinity Register
|
The processor and cluster IDs, in multi-core or cluster systems.
|
1 |
|
SCR_EL n
|
Secure Configuration Register
|
Controls Secure state and trapping of exceptions to EL3.
|
3 |
|
SCTLR_EL n
|
System Control Register
|
Controls architectural features, for example the MMU, caches
and alignment checking.
|
0,1,2,3 |
|
SPSR_EL n
|
Saved Program Status Register
|
Holds the saved processor state when an exception is taken to
this mode or Exception level.
|
abt, fiq, irq,
und, 1,2, 3
|
|
TCR_EL n
|
Translation Control Register
|
Determines which of the Translation Table Base Registers
define the base address for a translation table walk required for
the stage 1 translation of a memory access from EL n . Also
controls the translation table format and holds cacheability and
shareability information.
|
1,2,3 |
|
TPIDR_EL n
|
User Read/Write Thread ID Register
|
Provides a location where software executing at EL n can store
thread identifying information, for OS management purposes.
|
0,1,2,3 |
|
TPIDRRO_EL n
|
User Read-Only Thread ID Register
|
Provides a location where software executing at EL1 or higher
can store thread identifying information. This informaton is
visible to software executing at EL0, for OS management
purposes.
|
0 |
|
TTBR0_EL n
|
Translation Table Base Register 0
|
Holds the base address of translation table 0, and information
about the memory it occupies. This is one of the translation
tables for the stage 1 translation of memory accesses at EL n .
|
1,2,3 |
|
TTBR1_EL n
|
Translation Table Base Register 1
|
Holds the base address of translation table 1, and information
about the memory it occupies. This is one of the translation
tables for the stage 1 translation of memory accesses at EL0 and
EL1.
|
1 |
|
VBAR_EL n
|
Vector Based Address Register
|
Holds the exception base address for any exception that is taken
to EL n .
|
1,2,3 |
|
VTCR_EL n
|
Virtualization Translation Control Register
|
Controls the translation table walks required for the stage 2
translation of memory accesses from Non-secure EL0 and EL1.
Also holds cacheability and shareability information for the
accesses.
|
2 |
|
VTTBR_EL n
|
Virtualization Translation Table Base Register
|
Holds the base address of the translation table for the stage 2
translation of memory accesses from Non-secure EL0 and EL1.
|
2 |
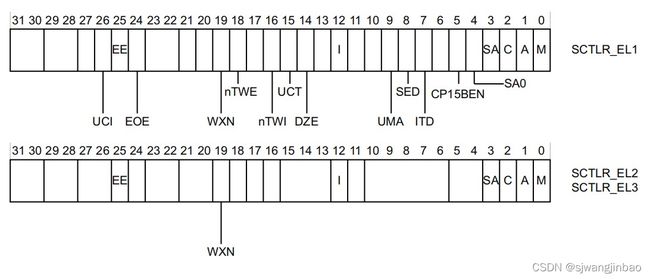
4.1 系统控制寄存器
SCTLR是控制标准内存、系统设备、并提供核心中实现的状态信息。
|
UCI
|
When set, enables EL0 access in AArch64 for DC CVAU , DC CIVAC , DC CVAC , and
IC IVAU instructions.
|
|
EE
|
Exception endianness.
0 Little endian.
1 Big endian.
|
|
EOE
|
Endianness of explicit data accesses at EL0. The possible values of this bit are:
0 Explicit data accesses at EL0 are little-endian.
1 Explicit data accesses at EL0 are big-endian.
|
|
WXN
|
Write permission implies XN (eXecute Never).
0 Regions with write permission are not forced to XN.
1 Regions with write permission are forced to XN.
|
|
nTWE
|
Not trap WFE. A value of 1 means that WFE instructions are executed as normal.
|
|
nTWI
|
Not trap WFI. A value of 1 means that WFI instructions are executed as normal.
|
|
UCT
|
When set, enables EL0 access in AArch64 to the CTR_EL0 register.
|
|
DZE
|
Access to DC ZVA instruction at EL0.
0 Execution prohibited.
1 Execution allowed.
|
|
I
|
Instruction cache enable. This is an enable bit for instruction caches at EL0 and
EL1. Instruction accesses to cacheable Normal memory are cached.
|
|
UMA
|
User Mask Access. Controls access to interrupt masks from EL0, when EL0 is
using AArch64.
|
|
SED
|
SETEND Disable. Disables SETEND instructions at EL0 using AArch32.
0 SETEND instructions are enabled.
1 The SETEND instruction is disabled.
|
|
ITD
|
IT Disable. The possible values of this bit are:
0 The IT instruction is available.
1 The IT instruction is treated as a 16-bit instruction. Only another 16-bit
instruction, or the first half of a 32-bit instruction, can follow. This
depends upon the implementation.
|
|
CP15BEN
|
CP15 barrier enable. If implemented, it is an enable bit for the AArch32 CP15
DMB, DSB, and ISB barrier operations.
|
|
SA0
|
Stack Alignment Check Enable for EL0.
|
|
SA
|
Stack Alignment Check Enable.
|
|
C
|
Data cache enable. This is an enable bit for data caches at EL0 and EL1. Data
accesses to cacheable Normal memory are cached.
|
|
A
|
Alignment check enable bit.
|
|
M
|
Enable the MMU.
|
对SCTLR的访问,举个例子:
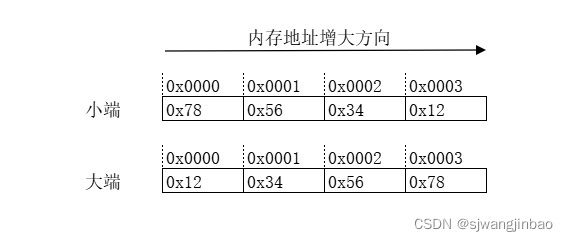
5、字节顺序(大小端)
字节顺序在EL0~EL3各个等级中是分开控制的:
EL1、EL2、EL3,控制字节序的寄存器是 SCTLR_ELn.EE。
EL0,控制字节序的寄存器是SCTLR_EL1.E0E。
在AArch64运行状态下,数据的读取可以是大端(BE),也可以是小端(LE)。但是指令的获取总是小端(LE)。
一个处理器是否大小端都支持,取决于处理器的实现。如果只支持小端,EE和E0E总是0;如果只支持大端,EE和E0E总是1。
在AArch32运行状态下,CPSR.E(等效于EL1~EL3的EE)已经被弃用了,SETEND也被弃用了。执行SETEND命令(设置SCTLR.SED)会导致未定义的异常。
6、改变运行状态(之前讲过,这次更深入些)
这次我们从寄存器的角度来看运行状态的改变。当从一个异常等级的AArch32状态,切换到一个异常等级的AArch64状态时(前面提到过,AArch32到AArch64,必须升级异常等级):
1)低异常等级AArch32可访问的寄存器,高32bit在切换到AArch64后是未知状态;
2)AArch32不能访问的寄存器,保持切换到AArch32之前的状态;
3)从EL2 AArch32,切换到EL3 AArch64,ELR_EL2的高32位是未知状态;
4)SP_EL0, SP_EL1, SP_EL2, ELR_EL1,在AArch32是不能被访问的,他们保持切换到AArch32之前的状态。
总结下来,应用程序可以是32位的,也可以是64位的,OS必须对两种状态以及他们的切换负责。
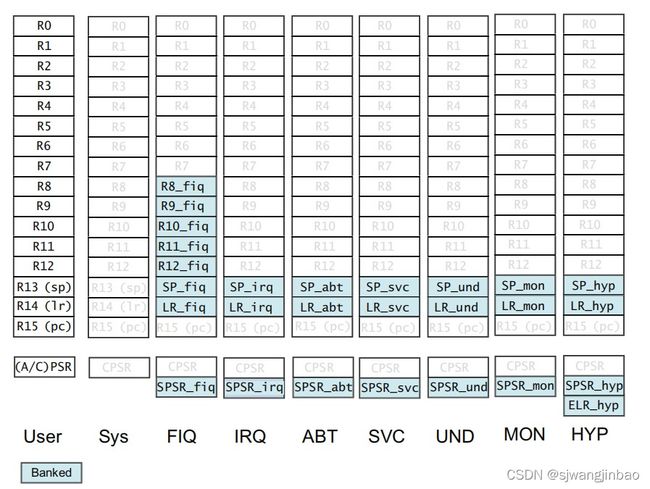
6.1 AArch32运行状态下的寄存器
ARMv8在32位状态下,和ARMv7保持一致,这说明
1)必须和ARMv7的特权等级保持一致
2)AARch32运行状态下,仅仅处理ARMv7的32位通用寄存器
所以,ARMv8架构和AArch32运行状态的寄存器必须有个一一对应。
在ARMv7,有如下寄存器:
1)16个32位的通用寄存器R0~R15。
R0~R14:通用的数据存储
R15:程序计数器(PC)
2)CPSR、SPSR
处理异常时,CPSR就会被拷贝到SPSR来保存异常发生前的CPSR状态。
这些寄存器有个banking的概念,也就是说同样一个寄存器,在不同特权等级下的内容是不同的,他们也是被存储在不同的区域,不同的特权等级访问某个寄存器(比如R0)其实是访问的不同的物理存储区域的内容。
引入banking的概念,是为了减少异常处理时候的延迟。
这些ARMv7的寄存器集,在ARMv8上的映射如下:
6.2 AArch32运行状态下的PSTATE
在AArch64运行状态下,传统的CPSR,会以PSTATE的形式获取;
在AArch32运行状态下,PSTATE会有一些额外的位:
| 名字 | 描述 |
| Q |
Cumulative saturation ( sticky ) flag.
|
|
GE (4)
|
Greater than or Equal flags.
|
|
IT (8)
|
If-Then execution bits.
|
| J | J bit |
| T | T32 bit |
| E |
Endianness bit.
|
| M |
Mode field.
|
7、NEON和浮点寄存器
ARMv8有32个128位的浮点数寄存器:V0~V32。
7.1 AArch64运行状态下的浮点寄存器
浮点寄存器V0~V32,根据精度不同,可以分为:
| 精度 | 大小(单位:bit) | 名字 |
| 半精度 | 16 | Hn |
| 单精度 | 32 | Sn |
| 双精度 | 64 | Dn |
比如浮点数的加法指令:
7.2 标量寄存器
| 大小(单位:bit) | 名称 | |
| Byte | 8 | Bn |
| Halfword | 16 | Hn |
| Word | 32 | Sn |
| Doubleword | 64 | Dn |
| Quadword | 128 | Qn |
这一章节之后还要回过头来再好好看看。
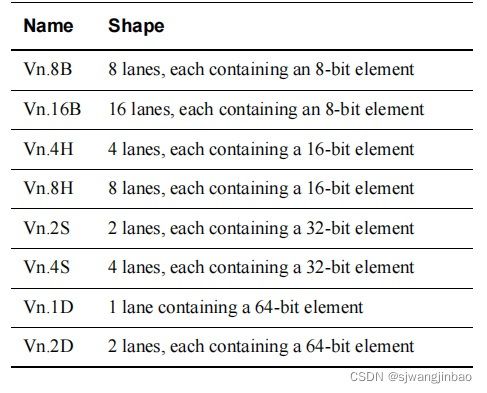
7.3 向量寄存器
向量可以是64位宽的一个元素的向量,也可以是128位宽的多个元素的向量。
7.4 在AArch32运行状态的NEON
AArch32运行状态的浮点寄存器,和SIMD寄存器,对应到AArch64运行状态是FP寄存器,和SIMD寄存器。
AArch64的V16~V31 FP,和NEON寄存器,在AArch32是不能访问的。在AArch32运行状态的异常等级中,这些寄存器保持之前在AArch64中的状态。
=========================================================================
注意:本文为本人原创,版权所属为个人所有,欢迎转载,但是转载请注明出处。
=========================================================================