从实体按键看 Android 车载的自定义事件机制
作者:TechMerger
在汽车数字化、智能化变革的进程中,越来越多的车机设计或部分、或全部地舍弃了实体按键,进而把车主操作的入口转移到了车机 UI 以及语音助手。
但统一、高效的零层级 UI 颇为困难,语音的准确率、覆盖率亦不够完善,那么在当下的阶段适当地保留部分实体按键是比较明智的选择。
开发者都了解 Android 平台可以监听按键、屏幕触控、耳机插拔等硬件的事件来源,来获取用户输入,进而封装成 KeyEvent、MotionEvent 等各种事件类型,并发送到 System 或 App 来进一步处理。
其原理都是利用 InputManagerService 系统服务读取 EventHub 所对应的事件类型,依照对应的 Mapper 转换、Dispatcher 分发以及 Channel 传送等步骤来完成的。
而本次探讨的 Android 变体即 Automotive OS(简称 AAOS)作用在车载场景下,其需要更多、丰富的事件需求,比如来自方控、中控等。
可其和 Android 标准的 Event 来源不同,方控等设备并不处于同一个系统当中,属于系统以外的 ECU 单元。那么如何高效、快捷地添加对这些系统以外的按键支持和处理,显得非常必要。
这就要谈到 AAOS 里特有的车载事件定制 CustomInputService。
自定义按键的实战
AAOS 默认支持的自定义事件 Code 位于文件 hardware/interfaces/automotive/vehicle/2.0/types.hal 中,App 可以利用这些预设的事件 Code 进行监听和自定义处理逻辑。
当然,Car OEM 厂商可以使用任意有符号的 32 位数值来扩展支持自定义输入 HW_CUSTOM_INPUT 的 CustomInputType 枚举范围,以支持更多的按键 Code,确保处理的范围符合实际的车辆按键需求。
// hardware/interfaces/automotive/vehicle/2.0/types.hal
/**
* Input code values for HW_CUSTOM_INPUT.
*/
enum CustomInputType : int32_t {
CUSTOM_EVENT_F1 = 1001,
CUSTOM_EVENT_F2 = 1002,
CUSTOM_EVENT_F3 = 1003,
CUSTOM_EVENT_F4 = 1004,
CUSTOM_EVENT_F5 = 1005,
CUSTOM_EVENT_F6 = 1006,
CUSTOM_EVENT_F7 = 1007,
CUSTOM_EVENT_F8 = 1008,
CUSTOM_EVENT_F9 = 1009,
CUSTOM_EVENT_F10 = 1010,
};
我们利用上述 Code 来自定义一个打开高频 app 的专用控件,比如:接电话、挂电话、音量、语音、微信按钮、地图按钮、音乐控制等等。
实战的具体步骤来说,首先得声明特定权限,才能监听 Car 的自定义输入:
android.car.permission.CAR_MONITOR_INPUT
当然,如果涉及到向 Android 系统注入回标准 KeyEvent,还需要申明对应的注入权限:
android.permission.INJECT_EVENTS
总体的 Manifest 定义如下:
...
- onBind() 时候调用 connectToCarService() 创建 Car 实例、获取
CarInputManager、CustomInputEventListener实例,并向 CarInputManager 提供的requestInputEventCapture()进行注册,并传递 INPUT_TYPE_CUSTOM_INPUT_EVENT 作为输入类型参数 - onDestroy() 里释放对于该事件的监听
- 复写
CarInputCaptureCallback的onCustomInputEvents()方法,作为各事件的处理入口和时机,回调理将提供事件所属的屏幕类型和事件类型,CustomInputEventListener承载了具体的处理逻辑
// SampleCustomInputService.java
public class SampleCustomInputService extends Service implements
CarInputManager.CarInputCaptureCallback {
private Car mCar;
private CarInputManager mCarInputManager;
private CustomInputEventListener mEventHandler;
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
if (intent != null) {
connectToCarService();
}
return null;
}
private void connectToCarService() {
if (mCar != null && mCar.isConnected()) {
return;
}
mCar = Car.createCar(this, /* handler= */ null, Car.CAR_WAIT_TIMEOUT_WAIT_FOREVER,
(car, ready) -> {
mCar = car;
if (ready) {
mCarInputManager =
(CarInputManager) mCar.getCarManager(Car.CAR_INPUT_SERVICE);
mCarInputManager.requestInputEventCapture(
CarOccupantZoneManager.DISPLAY_TYPE_MAIN,
new int[]{CarInputManager.INPUT_TYPE_CUSTOM_INPUT_EVENT},
CarInputManager.CAPTURE_REQ_FLAGS_ALLOW_DELAYED_GRANT,
/* callback= */ this);
mEventHandler = new CustomInputEventListener(getApplicationContext(),
(CarAudioManager) mCar.getCarManager(Car.AUDIO_SERVICE),
(CarOccupantZoneManager) mCar.getCarManager(
Car.CAR_OCCUPANT_ZONE_SERVICE),
this);
}
});
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
if (mCarInputManager != null) {
mCarInputManager.releaseInputEventCapture(CarOccupantZoneManager.DISPLAY_TYPE_MAIN);
}
if (mCar != null) {
mCar.disconnect();
mCar = null;
}
}
@Override
public void onCustomInputEvents(int targetDisplayType,
@NonNull List events) {
for (CustomInputEvent event : events) {
mEventHandler.handle(targetDisplayType, event);
}
}
...
}
CustomInputEventListener 的核心逻辑在于 handle():
-
首先调用 isValidTargetDisplayType() 验证屏幕类型,决定是否处理
-
通过 getInputCode() 从
CustomInputEvent中提取 KEY CODE -
按照预设的 Event 类型进行对应的处理,比如:
- LAUNCH_MAPS_ACTION 的话,封装启动 Map App 的方法 launchMap(),注意需要根据起初的 DisplayType 获取目标屏幕的 ID:targetDisplayId 并传入
- INJECT_VOICE_ASSIST_ACTION_DOWN 的话,表明是启动语音助手按键的按下事件,注入 语音助手的标准 KeyEvent 即 KEYCODE_VOICE_ASSIST 的 DOWN 事件
- INJECT_VOICE_ASSIST_ACTION_UP 则是注入 KEYCODE_VOICE_ASSIST 的 UP 事件
- 等
// CustomInputEventListener.java
public final class CustomInputEventListener {
private final SampleCustomInputService mService;
...
public @interface EventAction {
/** Launches Map action. */
int LAUNCH_MAPS_ACTION = 1001;
...
/** Injects KEYCODE_VOICE_ASSIST (action down) key event */
int INJECT_VOICE_ASSIST_ACTION_DOWN = 1009;
/** Injects KEYCODE_VOICE_ASSIST (action up) key event */
int INJECT_VOICE_ASSIST_ACTION_UP = 1010;
}
public CustomInputEventListener( ... ) {
mContext = context;
...
}
public void handle(int targetDisplayType, CustomInputEvent event) {
if (!isValidTargetDisplayType(targetDisplayType)) {
return;
}
int targetDisplayId = getDisplayIdForDisplayType(targetDisplayType);
@EventAction int action = event.getInputCode();
switch (action) {
case EventAction.LAUNCH_MAPS_ACTION:
launchMap(targetDisplayId);
break;
...
case EventAction.INJECT_VOICE_ASSIST_ACTION_DOWN:
injectKeyEvent(targetDisplayType,
newKeyEvent(KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN, KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOICE_ASSIST));
break;
case EventAction.INJECT_VOICE_ASSIST_ACTION_UP:
injectKeyEvent(targetDisplayType,
newKeyEvent(KeyEvent.ACTION_UP, KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOICE_ASSIST));
break;
default: Log.e(TAG, "Ignoring event [" + action + "]");
}
}
private int getDisplayIdForDisplayType(int targetDisplayType) {
int displayId = mCarOccupantZoneManager.getDisplayIdForDriver(targetDisplayType);
return displayId;
}
private static boolean isValidTargetDisplayType(int displayType) {
if (displayType == CarOccupantZoneManager.DISPLAY_TYPE_MAIN) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
private void launchMap(int targetDisplayId) {
ActivityOptions options = ActivityOptions.makeBasic();
options.setLaunchDisplayId(targetDisplayId);
Intent mapsIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
mapsIntent.setClassName(mContext.getString(R.string.maps_app_package),
mContext.getString(R.string.maps_activity_class));
mapsIntent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP);
mService.startActivity(mapsIntent, options.toBundle());
}
...
private KeyEvent newKeyEvent(int action, int keyCode) {
long currentTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
return new KeyEvent(/* downTime= */ currentTime, /* eventTime= */ currentTime,
action, keyCode, /* repeat= */ 0);
}
private void injectKeyEvent(int targetDisplayType, KeyEvent event) {
mService.injectKeyEvent(event, targetDisplayType);
}
}
KeyEvent 的注入还需要回到自定义 CustomInputService 中,之后是调用 CarInputManager 将 Event 进一步注入。
将在下个章节阐述 CarInputManager 的进一步处理。
// SampleCustomInputService.java
public class SampleCustomInputService extends Service implements
CarInputManager.CarInputCaptureCallback {
...
public void injectKeyEvent(KeyEvent event, int targetDisplayType) {
if (mCarInputManager == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Service was properly initialized, reference to CarInputManager is null");
}
mCarInputManager.injectKeyEvent(event, targetDisplayType);
}
}
需要该 Service 生效的话,需要使用如下命令启动 Service,按照逻辑向系统注册事件监听。
adb shell am start-foreground-service com.android.car.custominput.sample/.SampleCustomInputService
接下来按压硬件的按键,或者像下面一样模拟按键的输入,比如下面模拟 1001 启动 Map 的按键按下:
adb shell cmd car_service inject-custom-input -d 0 f1
其他几个和上述逻辑相应的事件模拟命令:
adb shell cmd car_service inject-custom-input f2 // accept incoming calls
adb shell cmd car_service inject-custom-input f3 // reject incoming calls
adb shell cmd car_service inject-custom-input f4 // To increase media volume
adb shell cmd car_service inject-custom-input f5 // To decrease media volume
adb shell cmd car_service inject-custom-input f6 // To increase alarm volume
adb shell cmd car_service inject-custom-input f7 // To decrease alarm volume
adb shell cmd car_service inject-custom-input f8 // To simulate pressing BACK HOME button
系统的默认处理
以上述的 KEYCODE_VOICE_ASSIST 为例,看一下 CarInputManager 的进一步处理如何。
对应的在 CarInputService 中:
- 首先,injectKeyEvent() 将先检查注入方的相关权限:
INJECT_EVENTS - 接着,调用 onKeyEvent() 执行事件的后续处理
// packages/services/Car/service/src/com/android/car/CarInputService.java
public class CarInputService ... {
...
@Override
public void injectKeyEvent(KeyEvent event, @DisplayTypeEnum int targetDisplayType) {
// Permission check
if (PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED != mContext.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(
android.Manifest.permission.INJECT_EVENTS)) {
throw new SecurityException("Injecting KeyEvent requires INJECT_EVENTS permission");
}
long token = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
// Redirect event to onKeyEvent
onKeyEvent(event, targetDisplayType);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(token);
}
}
}
注入的事件类型为 KEYCODE_VOICE_ASSIST 的话,交给 handleVoiceAssistKey() 处理。
-
当 action 尚为 DOWN 时机,交给
VoiceKeyTimer的keyDown()开始计时 -
当 action 为 UP 时机:通过 Timer 的
keyUp()获取是否达到长按(长按时长默认是 400ms,可以在 SettingsProvider 中改写)条件,并调用dispatchProjectionKeyEvent()发送相应的事件:- 短按处理 KEY_EVENT_VOICE_SEARCH_SHORT_PRESS_KEY_UP
- 反之,发送 KEY_EVENT_VOICE_SEARCH_LONG_PRESS_KEY_UP
- 如果 dispatchProjectionKeyEvent() 没没有拦截处理,执行默认逻辑:
launchDefaultVoiceAssistantHandler()
// packages/services/Car/service/src/com/android/car/CarInputService.java
public class CarInputService ... {
...
@Override
public void onKeyEvent(KeyEvent event, @DisplayTypeEnum int targetDisplayType) {
switch (event.getKeyCode()) {
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOICE_ASSIST:
handleVoiceAssistKey(event);
return;
...
default:
break;
}
...
}
private void handleVoiceAssistKey(KeyEvent event) {
int action = event.getAction();
if (action == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN && event.getRepeatCount() == 0) {
mVoiceKeyTimer.keyDown();
dispatchProjectionKeyEvent(CarProjectionManager.KEY_EVENT_VOICE_SEARCH_KEY_DOWN);
} else if (action == KeyEvent.ACTION_UP) {
if (mVoiceKeyTimer.keyUp()) {
dispatchProjectionKeyEvent(
CarProjectionManager.KEY_EVENT_VOICE_SEARCH_LONG_PRESS_KEY_UP);
return;
}
if (dispatchProjectionKeyEvent(
CarProjectionManager.KEY_EVENT_VOICE_SEARCH_SHORT_PRESS_KEY_UP)) {
return;
}
launchDefaultVoiceAssistantHandler();
}
}
private void launchDefaultVoiceAssistantHandler() {
if (!AssistUtilsHelper.showPushToTalkSessionForActiveService(mContext, mShowCallback)) {
Slogf.w(TAG, "Unable to retrieve assist component for current user");
}
}
}
CarProjectionManager 是允许 App 向系统注册/注销某些事件处理的机制。
CarProjectionManager allows applications implementing projection to register/unregister itself with projection manager, listen for voice notification.
dispatchProjectionKeyEvent() 则将上述的短按、长按事件发送给 App 通过 CarProjectionManager 向其注册的 ProjectionKeyEventHandler 处理。
// packages/services/Car/service/src/com/android/car/CarInputService.java
public class CarInputService ... {
...
private boolean dispatchProjectionKeyEvent(@CarProjectionManager.KeyEventNum int event) {
CarProjectionManager.ProjectionKeyEventHandler projectionKeyEventHandler;
synchronized (mLock) {
projectionKeyEventHandler = mProjectionKeyEventHandler;
if (projectionKeyEventHandler == null || !mProjectionKeyEventsSubscribed.get(event)) {
return false;
}
}
projectionKeyEventHandler.onKeyEvent(event);
return true;
}
}
// packages/services/Car/service/src/com/android/car/CarProjectionService.java
class CarProjectionService ... {
@Override
public void onKeyEvent(@CarProjectionManager.KeyEventNum int keyEvent) {
Slogf.d(TAG, "Dispatching key event: " + keyEvent);
synchronized (mLock) {
for (BinderInterfaceContainer.BinderInterface
eventHandlerInterface : mKeyEventHandlers.getInterfaces()) {
ProjectionKeyEventHandler eventHandler =
(ProjectionKeyEventHandler) eventHandlerInterface;
if (eventHandler.canHandleEvent(keyEvent)) {
try {
// oneway
eventHandler.binderInterface.onKeyEvent(keyEvent);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slogf.e(TAG, "Cannot dispatch event to client", e);
}
}
}
}
}
...
}
假使没有 App 注册或者消费了 VOICE_SEARCH 的短按/长按事件,则调用默认的 launchDefaultVoiceAssistantHandler() 通过 Assist 相关的帮助类 AssistUtilsHelper 继续。
public final class AssistUtilsHelper {
...
public static boolean showPushToTalkSessionForActiveService( ... ) {
AssistUtils assistUtils = getAssistUtils(context);
...
Bundle args = new Bundle();
args.putBoolean(EXTRA_CAR_PUSH_TO_TALK, true);
IVoiceInteractionSessionShowCallback callbackWrapper =
new InternalVoiceInteractionSessionShowCallback(callback);
return assistUtils.showSessionForActiveService(args, SHOW_SOURCE_PUSH_TO_TALK,
callbackWrapper, /* activityToken= */ null);
}
...
}
默认的语音助手的启动是通过 Android 标准的 VoiceInteraction 链路完成,所以后续的处理是通过 showSessionForActiveService() 交由专门管理 VoiceInteraction 的 VoiceInteractionManagerService 系统服务来完成。
public class AssistUtils {
...
public boolean showSessionForActiveService(Bundle args, int sourceFlags,
IVoiceInteractionSessionShowCallback showCallback, IBinder activityToken) {
try {
if (mVoiceInteractionManagerService != null) {
return mVoiceInteractionManagerService.showSessionForActiveService(args,
sourceFlags, showCallback, activityToken);
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to call showSessionForActiveService", e);
}
return false;
}
...
}
具体的是找到默认的数字助手 DigitalAssitant app 的 VoiceInteractionService 进行绑定和启动对应的 Session。
public class VoiceInteractionManagerService extends SystemService {
class VoiceInteractionManagerServiceStub extends IVoiceInteractionManagerService.Stub {
public boolean showSessionForActiveService( ... ) {
...
final long caller = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
...
return mImpl.showSessionLocked(args,
sourceFlags
| VoiceInteractionSession.SHOW_WITH_ASSIST
| VoiceInteractionSession.SHOW_WITH_SCREENSHOT,
showCallback, activityToken);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(caller);
}
}
}
...
}
...
}
对 VoiceInteraction 细节感兴趣的可以参考其他文章:
自定义按键的来源
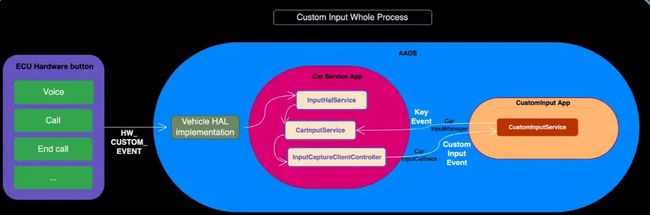
按键的信号输入来自于 ECU,其与 AAOS 的 Hal 按照定义监听 HW_CUSTOM_INPUT 输入事件的 property 变化,来自于上述提及的 types.hal 中定义的支持自定义输入事件 Code 发送到 Car Service 层。
Car Service App 的 VehicleHal 将在 onPropertyEvent() 中接收到 HAL service 的 property 发生变化。接着,订阅了 HW_CUSTOM_INPUT property 变化的 InputHalService 的 onHalEvents() 将被调用。
之后交由 CarInputService 处理,因其在 init() 时将自己作为 InputListener 的实现传递给了 InputHalService 持有。
处理自定义输入的 App 在调用 requestInputEventCapture() 时的 Callback 将被管理在 InputCaptureClientController 中的 SparseArray 里。
自然的 CarInputService 的 onCustomInputEvent() 需要将事件交给 InputCaptureClientController 来进一步分发。
public class CarInputService ... {
...
@Override
public void onCustomInputEvent(CustomInputEvent event) {
if (!mCaptureController.onCustomInputEvent(event)) {
return;
}
}
}
InputCaptureClientController 将从 SparseArray 中获取对应的 Callback 并回调 onCustomInputEvents()。
public class InputCaptureClientController {
...
public boolean onCustomInputEvent(CustomInputEvent event) {
int displayType = event.getTargetDisplayType();
if (!SUPPORTED_DISPLAY_TYPES.contains(displayType)) {
return false;
}
ICarInputCallback callback;
synchronized (mLock) {
callback = getClientForInputTypeLocked(displayType,
CarInputManager.INPUT_TYPE_CUSTOM_INPUT_EVENT);
if (callback == null) {
return false;
}
}
dispatchCustomInputEvent(displayType, event, callback);
return true;
}
private void dispatchCustomInputEvent(@DisplayTypeEnum int targetDisplayType,
CustomInputEvent event,
ICarInputCallback callback) {
CarServiceUtils.runOnCommon(() -> {
mCustomInputEventDispatchScratchList.clear();
mCustomInputEventDispatchScratchList.add(event);
try {
callback.onCustomInputEvents(targetDisplayType,
mCustomInputEventDispatchScratchList);
} ...
});
}
}
此后便抵达了 上个实战章节实现的 SampleCustomInputService 中的 onCustomInputEvents()。
模拟调试
在漫长的 HMI 实验台架、实车准备就绪之前,往往需要开发者提前验证链路的可行性,这时候就如何模拟这些自定义事件的注入就显得非常需要。
我们知道自定义实体按键的输入并不属于 EventHub 范畴,那么传统的 getevent、dumpsys input 也就无法监听到该事件的输入,自然也就无法使用 adb 的 input 和 sendevent 命令来反向注入,正如实战章节提到的那样,我们可以使用 Car 专用的 adb 命令来达到目的。
adb shell cmd car_service inject-custom-input
# or
adb shell cmd car_service inject-key
前者模拟的是自定义事件的注入,后者则是针对 Android 标准事件。
当然如果需要区分按键的短按和长按事件,需要像上面的事例一样提供针对 DOWN 和 UP 的两种 Code,那么模拟的时候也要模拟按键之间的时长。
adb shell cmd car_service inject-custom-input ; sleep 0.2; adb shell cmd car_service inject-custom-input
另外要留意,虽然都归属于 Android platform,但有些标准 KeyEvent 的模拟可以被 AAOS 所处理,而有些却不支持呢?
比如使用如下的命令模拟发出音量 mute Keycode,系统能完成静音,但使用同样命令模式的音量的 +/-,系统则无反应。
adb shell input keyevent
adb shell sendevent [device] [type] [code] [value]
这是因为部分 AAOS 的 OEM 实现里可能删除了部分标准 KeyEvent 的处理,而改部分的标准 Event 处理挪到了 Car Input 中统一处理了,所以需要使用上述的 car_service 对应的 inject-custom-input 才行。
结语
让我们再从整体上看下自定义按键事件的分发和处理过程:
如果自定义的按键数量不多,可以使用 AAOS 预置的 F1~F10。反之,可以采用任意有符号的 32 位数值来扩展自定义输入的范围。
当不用区分某种事件的短按、长按逻辑,使用一种 Code 映射即可,由 CustomInputService 直接执行。比如监控方控上的“通话”和“结束通话”实体按键:
- 当没有来电时,按下方向盘上的“通话”按钮会发送 DIAL intent 并显示拨号器的拨号键盘页面
- 当有来电时,按下方向盘上的“通话”按钮会使 TelecomManager 接听来电
- 当有来电时,按下方向盘上的“结束通话”按钮会使 TelecomManager 挂断电话
而当需要区分长、短按的时候,需要配置两种 Code 和 DOWN 及 UP 进行对应,由 CustomInputService 或 转发送给 CarInputService 按照 DOWN 和 UP 的时间间隔决定触发短按还是长按逻辑。
从遥远的未来来讲,实体按键的交互方式肯定会消亡,取而代之的是手势、语音、眼睛等更直接、丰富的方式。
但正如前言讲的,在现阶段适当地保留高频的实体按键,和车机的数字化、智能化之间并不冲突,车机的智能化不等于粗暴地抛弃实体按键等传统设计。
而且需要当心的一点是:如果车机交互做得不够好,还执意取消了实体键,那真是本末倒置了。
至于Android 车载相关的学习文档,目前网上很难找到比较完整的,在这里我推荐给大家一份《Android 车载学习手册》+《Android Framework学习手册》,学完以后想去面试车企可以参考这份《Android 车载面试习题》,最后祝大家都有一份稳定的工作。
Android 车载学习手册
- 第一章——Android Auto概述
- 第二章——开发汽车媒体应用
- 第三章——构建 Android Auto即时通信应用
- 第四章——构建车载导航和地图的注点应用
- 第五章——构建 Android Automotive OS 视频应用
《Android Framework学习手册》:https://qr18.cn/AQpN4J
- 开机Init 进程
- 开机启动 Zygote 进程
- 开机启动 SystemServer 进程
- Binder 驱动
- AMS 的启动过程
- PMS 的启动过程
- Launcher 的启动过程
- Android 四大组件
- Android 系统服务 - Input 事件的分发过程
- Android 底层渲染 - 屏幕刷新机制源码分析
- Android 源码分析实战