API 文档搜索引擎
1. 认识搜索引擎:
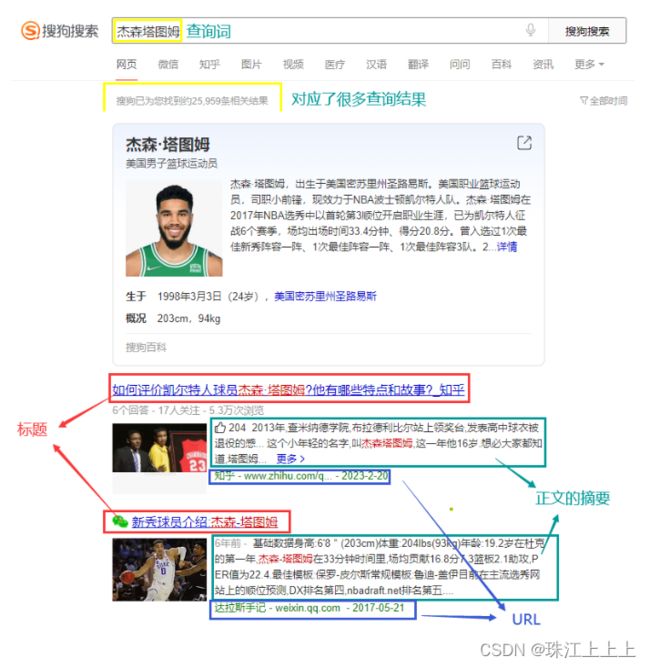
在搜狗搜索的搜索结果页中, 包含了若干条结果, 每一个结果包含了图标, 标题, 描述, 展示URL等
搜索引擎的本质:
输入一个查询词, 得到若干个搜索结果, 每个搜索结果包含了标题, 描述, 展示URL和点击URL
2. 搜索引擎思路:
2.1 搜索的核心思路:
当前我们有很多的网页(假设上亿个), 每个网页我们称为是一个文档
如何高效进行检索? 查找出有哪些网页是和查询词具有一定的相关性呢?
我们可以认为, 网页中包含了查询词(或者查询词的一部分), 就认为具有相关性.
那么我们就有了一个直观的解决思路
方案一 -- 暴力搜索
每次处理搜索请求的时候, 拿着查询词去所有的网页中搜索一遍, 检查每个网页是否包含查询词字符串.
这个方法是否可行?
显然, 这个方案的开销非常大. 并且随着文档数量的增多, 这样的开销会线性增长. 而搜索引擎往往对于效率的要求非常高.
方案二 -- 倒排索引
这是一种专门针对搜索引擎场景而设计的数据结构.
文档(doc): 被检索的html页面(经过预处理)
正排索引: "一个文档包含了哪些词". 描述一个文档的基本信息, 包括文档标题, 文档正文, 文档标题和正文的分词 /断句结果
倒排索引: "一个词被哪些文档引用了". 描述了一个词的基本信息, 包括这个词都被哪些文档引用, 这个词在该文档 中的重要程度, 以及这个词的出现位置等.
2.2 项目目标:
-
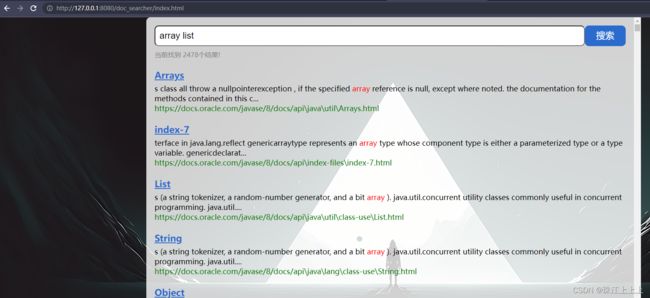
实现一个 Java API 文档的简单的搜索引擎.
-
最终效果
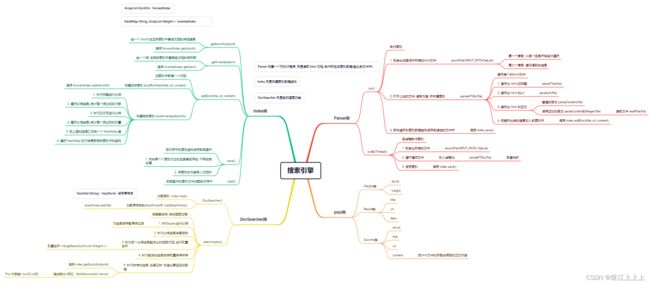
2.3 核心流程
-
索引模块: 扫描下载到的文档, 分析数据内容构建正排+倒排索引, 并保存到文件中.
-
搜索模块: 加载索引. 根据输入的查询词, 基于正排+倒排索引进行检索, 得到检索结果.
-
web模块: 编写一个简单的页面, 展示搜索结果. 点击其中的搜索结果能跳转到对应的 Java API 文档页面.
3. 实现搜索引擎:
3.. Weight, Result, DocInfo类
/**
* 这个类就是把 文档id 和 文档与词的相关性 权重 进行一个包裹
*/
@Data
public class Weight {
private int docId;
// 这个 weight 就表示 文档 和 词 之间的"相关性"
// 这个值越大, 就认为相关性越强
private int weight;
}
/**
* 这个类来表示一个搜索结果
*/
@Data
public class Result {
private String title;
private String url;
// 描述是正文的一段摘要
private String desc;
}
/**
* 表示一个文档对象(HTML对象)
* 根据这些内容后面才能制作索引, 完成搜索过程.
*/
@Data
public class DocInfo {
// docId 文档的唯一身份标识(不能重复)
private int docId;
// 该文档的标题. 简单粗暴的使用文件名来表示.
// Collection.html => Collection
private String title;
// 该文档对应的线上文档的 URL. 根据本地文件路径可以构造出线上文档的 URL
private String url;
// 该文档的正文. 把 html 文件中的 html 标签去掉, 留下的内容
private String content;
}3.1 分词:
分词是搜索中的一个核心操作. 尤其是中文分词, 比较复杂(当然, 咱们此处暂不涉及中文分词)
我们可以使用现成的分词库 ansj.
注意: 当 ansj 对英文分词时, 会自动把单词转为小写.
-
导入依赖:
org.ansj
ansj_seg
5.1.6
-
实例代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 准备一个比较长的话, 用来分词
String str = "小明毕业于清华大学";
// Term 就表示一个分词结果
List terms = ToAnalysis.parse(str).getTerms();
for (Term term : terms){
System.out.println(term.getName());
}
} 3.2 实现 Parser 类:
Parser 构建一个可执行程序, 负责读取 html 文档, 制作并生成索引数据(输出到文件中)
-
从制定的路径中枚举出所有的文件
-
读取每个文件, 从文件中解析出 HTML 的标题, 正文, URL
-
先指定一个加载文档的路径
private static final String INPUT_PATH =
"C:/Users/LEO/Desktop/jdk-8u361-docs-all/docs/api";-
创建一个 index 实例
private Index index = new Index();(1) run 方法
public void run(){
long beg = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("*** 索引制作开始! ***");
// 整个 searcher.Parser 类的入口
// 1. 根据上面指定的路径, 枚举出该路径中所有的文件(html), 这个过程需要把所有子目录中的文件都能获取到
ArrayList fileList = new ArrayList<>();
enumFile(INPUT_PATH,fileList);
/**
* 获取到 INPUT_PATH 下的所有文件
* System.out.println(fileList);
* System.out.println(fileList.size());
*/
// 2. 针对上面罗列出的文件的路径, 打开文件, 读取文件内容, 并进行解析, 并构建索引
for (File f : fileList){
// 通过这个方法来解析单个的html文件
System.out.println("开始解析: " + f.getAbsolutePath());
parseHTML(f);
}
// 3. 把在内存中构造好的索引数据结构, 保存到指定的文件中
index.save();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("**** 索引制作完成! " + (end - beg) + "ms ****");
} (2) enumFile() 枚举出该路径中所有的文件
// 第一个参数表示: 从哪个目录开始进行递归遍历
// 第二个参数表示: 递归得到的结果
// inputPath: C:/Users/LEO/Desktop/jdk-8u361-docs-all/docs/api
private void enumFile(String inputPath, ArrayList fileList) {
File rootPath = new File(inputPath);
// listFiles 能够获取到 rootPath 当前目录下所包含的文件/目录
// 使用 listFiles 只能看到一级目录, 看不到子目录里的内容
// 要想看到子目录中的内容, 还需要进行递归
File[] files = rootPath.listFiles();
for (File f : files){
// 根据当前 f 的类型, 来决定是否要递归
// 如果 f 是一个普通文件, 就把 f 加入到 fileList 结果中
// 如果 f 是一个目录, 就递归的调用 enumFile 方法, 进一步的获取子目录中的内容
if(f.isDirectory()){
enumFile(f.getAbsolutePath(), fileList);
} else {
// 排除非html文件
// endsWith是String类的方法
if(f.getAbsolutePath().endsWith(".html")){
fileList.add(f);
}
}
}
} (3) parseHTML() 通过这个方法来解析单个的html文件
private void parseHTML(File f) {
// 1. 解析出 HTML 的标题
String title = parseTitle(f);
// 2. 解析出 HTML 对应的 URL
String url = parseUrl(f);
// 3. 解析出 HTML 对应的正文(有了正文才有后续的描述)
// String content = parseContent(f);
String content = parseContentByRegex(f); // 使用正则的版本
// 4. 把解析出来的这些信息加入到索引当中
index.addDoc(title, url, content);
}(4) parseTitle() 解析出html文件的标题
private String parseTitle(File f) {
String name = f.getName();
return name.substring(0, name.length() - ".html".length());
}(5) parseUrl() 解析出html文件的URL
private String parseUrl(File f) {
// String part1 = "file:///C:/Users/LEO/Desktop/jdk-8u361-docs-all/docs/api/";
String part11 = "https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api";
String part2 = f.getAbsolutePath().substring(INPUT_PATH.length());
return part11 + part2;
}(6) parseContent() 解析出html文件的正文
// (边读边判断)
public String parseContent(File f) {
// 先按照一个字符一个字符的方式来读取, 以<和>来控制拷贝数据的开关
// BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f),1024 * 1024);
try {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(f);
// 加上一个是否要进行拷贝, 开关
boolean isCopy = true;
// 还得准备一个保存结果的 StringBuilder
StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder();
while(true){
// 注意, 此处的 read 返回值是一个 int , 不是 char
// 此处使用 int 作为返回值, 主要是为了表示一些非法情况
// 如果读到了文件末尾, 继续读, 就会返回 -1
int ret = fileReader.read();
if(ret == -1){
// 表示文件读完了
break;
}
// 如果这个结果不是 -1, 那么就是一个合法的字符
char c = (char) ret;
if(isCopy) {
// 开关打开的状态, 遇到普通字符就应该拷贝到 Stringbuilder 中
if(c == '<'){
// 关闭开关
isCopy = false;
continue;
}
if(c == '\n' || c == '\r'){
// 目的是为了去掉换行, 把换行符替换成空格
c = ' ';
}
// 其他字符, 直接进行拷贝即可, 把结果给拷贝到最终的 StringBuilder 中
content.append(c);
} else {
// 开关关闭的状态, 就暂时不拷贝, 直到遇到 >
if(c == '>'){
isCopy = true;
}
}
}
fileReader.close();
return content.toString();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "";
}(7) parseContentByRegex() 使用正则获取html的正文
基于正则表达式去除 script 标签的内容
// (先全部读取完, 然后替换) readFile 是 parseContentByRegex 需要的读取文件的方法
private String readFile(File f){
try(BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f))){
StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder();
while(true){
int ret = bufferedReader.read();
if(ret == -1){
break;
}
char c = (char) ret;
if(c == '\n' || c == '\r'){
c = ' ';
}
content.append(c);
}
return content.toString();
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "";
}
// 这个方法内部就基于正则表达式, 实现去标签, 以及去除 script
public String parseContentByRegex(File f){
// 1. 先把整个文件都读到 String 里面
String content = readFile(f);
// 2. 替换掉 script 标签
content = content.replaceAll("(.*?)", " ");
// 3. 替换掉普通的 html 标签
content = content.replaceAll("<.*?>", " ");
// 4. 使用正则表达式把多个空格, 合并成一个空格
content = content.replaceAll("\\s+", " ");
return content;
} (8) 通过这个main方法实现整个制作索引的过程
要先将api文档扫描完并保存到磁盘上, 然后再启动tomcat
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 通过main方法来实现整个制作索引的过程
Parser parser = new Parser();
// parser.run();
parser.runByThread();
}3.3 实现 Index 类:
Index 负责构建索引数据结构
-
存放索引的路径
private static final String INDEX_PATH = "C:/Users/LEO/Desktop/jdk-8u361-docs-all/";-
objectMapper对象
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();-
正排索引
// 使用数组下标表示: docId
private ArrayList forwardIndex = new ArrayList<>(); -
倒排索引
// 使用 哈希表 来表示倒排索引
// key 就是 词
// value 就是 一组和这个词关联的文章
private HashMap> invertedIndex = new HashMap<>(); -
锁对象
// 新创建俩个锁对象
private Object locker1 = new Object();
private Object locker2 = new Object();(1) getDocInfo() 根据 docId 查正排.
// 1. 给定一个 docId 在正排索引中, 查询文档的详细信息
public DocInfo getDocInfo(int docId) {
return forwardIndex.get(docId);
}(2) getInverted() 根据关键词查倒排.
// 2. 给定一个词, 在倒排索引中, 查哪些文档和这个词关联
// List 这里的返回值是Integer是否可以? 不行!
// 词和文档之间是存在一定的"相关性"的
public List getInverted(String term) {
return invertedIndex.get(term);
} (3) addDoc() 往索引中新增一个文档.
// 3. 往索引中新增一个文档
public void addDoc(String title, String url, String content) {
// 新增文档操作, 需要同时给正排索引和倒排索引新增信息
// 构建正排索引
DocInfo docInfo = buildForWard(title, url, content);
// 构建倒排索引
buildInverted(docInfo);
}(4) buildForWard() 构建正排索引
// 3.2 构建正排索引
private DocInfo buildForWard(String title, String url, String content) {
DocInfo docInfo = new DocInfo();
docInfo.setTitle(title);
docInfo.setUrl(url);
docInfo.setContent(content);
synchronized (locker1) {
docInfo.setDocId(forwardIndex.size());
forwardIndex.add(docInfo);
}
return docInfo;
}(5) buildInverted() 构建倒排索引
// 3.1 构建倒排索引
private void buildInverted(DocInfo docInfo) {
class WordCnt {
// 表示这个词在标题中出现的次数
public int titleCount;
// 表示这个词在正文中出现的次数
public int contentCount;
}
// 这个数据结构用来统计词频
HashMap wordCntHashMap = new HashMap<>();
// 1. 针对文档[标题]进行分词
List terms = ToAnalysis.parse(docInfo.getTitle()).getTerms();
// 2. 遍历分词结果, 统计每个词出现的次数
for (Term term : terms) {
// 先判定一下 term 是否存在
String word = term.getName(); // 获取到分词结果具体的词的信息
WordCnt wordCnt = wordCntHashMap.get(word);
if (wordCnt == null) {
// 如果不存在, 就创建一个新的键值对, 插入进去, titleCount 设为 1
WordCnt newWordCnt = new WordCnt();
newWordCnt.titleCount = 1;
newWordCnt.contentCount = 0;
wordCntHashMap.put(word, newWordCnt);
} else {
// 如果存在, 就找到之前的值, 然后把对应的 titleCount + 1
wordCnt.titleCount += 1;
}
}
// 3. 针对[正文]页进行分词
terms = ToAnalysis.parse(docInfo.getContent()).getTerms();
// 4. 遍历分词结果, 统计每个词出现的次数
for (Term term : terms) {
String word = term.getName(); // 获取词
WordCnt wordCnt = wordCntHashMap.get(word);
if (wordCnt == null) {
WordCnt newWordCnt = new WordCnt();
newWordCnt.titleCount = 0;
newWordCnt.contentCount = 1;
wordCntHashMap.put(word, newWordCnt);
} else {
wordCnt.contentCount += 1;
}
}
// 5. 把上面的结果汇总到一个 HashMap 里面
// 最终文档的权重, 就设定为 [标题中出现的次数 * 10 + 正文中出现的次数]
// 6. 遍历刚才这个 HashMap 依次来更新倒排索引中的结构
for (Map.Entry entry : wordCntHashMap.entrySet()) {
// 先根据这里的词, 去倒排索引中查一查
// 倒排拉链
synchronized (locker2) {
List invertedList = invertedIndex.get(entry.getKey());
if (invertedList == null) {
// 如果为空, 就插入一个新的键值对
ArrayList newInvertedList = new ArrayList<>();
// 把新的文档(当前 searcher.DocInfo), 构造成 searcher.Weight 对象, 插入进来
Weight weight = new Weight();
weight.setDocId(docInfo.getDocId());
// 权重计算公式: 标题中出现的次数 * 10 + 正文中出现的次数
weight.setWeight(entry.getValue().titleCount * 10 +
entry.getValue().contentCount);
newInvertedList.add(weight);
invertedIndex.put(entry.getKey(), newInvertedList);
} else {
// 如果非空, 就把当前这个文档, 构造出一个 searcher.Weight 对象, 插入到倒排拉链的后面
Weight weight = new Weight();
weight.setDocId(docInfo.getDocId());
// 权重计算公式: 标题中出现的次数 * 10 + 正文中出现的次数
weight.setWeight(entry.getValue().titleCount * 10 +
entry.getValue().contentCount);
invertedList.add(weight);
}
}
}
} (6) save() 往磁盘中写索引数据
// 4. 把内存中的索引结构保存到磁盘中
public void save() {
// 使用俩个文件, 分别保存正排和倒排
long beg = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----- 保存索引开始! -----");
// 1. 先判定一个索引对应的目录是否存在, 不存在就创建
File indexPathFile = new File(INDEX_PATH);
if(! indexPathFile.exists()){
indexPathFile.mkdirs();
}
File forwardIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH + "forward.txt");
File invertedIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH + "inverted.txt");
try {
objectMapper.writeValue(forwardIndexFile, forwardIndex);
objectMapper.writeValue(invertedIndexFile, invertedIndex);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----- 保存索引完成! 消耗时间: " + (end - beg) + " ms -----");
}(7) load() 从磁盘加载索引数据
// 5. 把磁盘中的索引数据加载到内存中
public void load() {
long beg = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----- 加载索引开始! -----");
// 1. 先设置一下加载索引的路径
File forwardIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH + "forward.txt");
File invertedIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH + "inverted.txt");
try {
forwardIndex = objectMapper.readValue(forwardIndexFile, new TypeReference>() {});
invertedIndex = objectMapper.readValue(invertedIndexFile, new TypeReference>>() {});
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----- 加载索引完成! 消耗时间: " + (end - beg) + " ms -----");
} 3.4 实现 DocSearcher 类:
这个类负责实现搜索功能.
-
停用词文件的路径
private static final String STOP_WORD_PATH =
"C:/Users/LEO/Desktop/jdk-8u361-docs-all/stop_word.txt";-
保存停用词
private HashSet stopWords = new HashSet<>(); -
创建一个index实例
// 此处要加上索引对象的实例
// 同时要完成索引加载的工作
private Index index = new Index();(1) DocSearcher() 构造方法
public DocSearcher() {
index.load();
loadStopWords();
}(2) searcher() 方法
// 根据查询词, 完成搜索过程
public List search(String query) {
// 1. [分词] 针对 query 这个查询词进行分词
List oldTerms = ToAnalysis.parse(query).getTerms();
List terms = new ArrayList<>();
// 针对分词结果, 使用暂停词表进行过滤
for (Term term : oldTerms){
if(stopWords.contains(term.getName())){
continue;
}
terms.add(term);
}
// 2. [触发] 针对分词结果来查倒排
// List allTermResult = new ArrayList<>();
// 搜索一个词的文档有 List 个
// 搜索n个分词结果的文档有 List> 个
List> termResult = new ArrayList<>();
for (Term term : terms) {
String word = term.getName();
// 虽然倒排索引中, 有很多的词, 但是这里的词一定都是之前的文档中存在的
List invertedList = index.getInverted(word);
if (invertedList == null) {
// 说明这个词在所有文档中都不存在
continue;
}
termResult.add(invertedList);
}
// 3. [合并] 针对多个分词结果触发出的相同文档, 进行权重合并
List allTermResult = mergeResult(termResult);
// 4. [排序] 针对触发的结果按照权重降序排序
allTermResult.sort(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Weight o1, Weight o2) {
// 如果是升序排序: return o1.getWeight() - o2.getWeight()
// 如果是降序排序: return o2.getWeight() - o1.getWeight()
return o2.getWeight() - o1.getWeight();
}
});
// 5. [包装结果] 针对排序的结果, 去查正排, 构造出要返回的数据
List results = new ArrayList<>();
for (Weight weight : allTermResult) {
DocInfo docInfo = index.getDocInfo(weight.getDocId());
Result result = new Result();
result.setTitle(docInfo.getTitle());
result.setUrl(docInfo.getUrl());
result.setDesc(GenDes(docInfo.getContent(), terms));
results.add(result);
}
return results;
} (3) mergeResult() 权重合并
问题:
当搜索的查询词包含多个单词的时候, 可能同一个文档中, 会同时包含这多个分词结果.
像这样的文档应该要提高权重.
例如 查询词为 "array list"
某文档中同时存在 array 和 list, 这个时候这个文档的实际权重, 就要把 array 的权重和 list 的权重相加.
// 通过这个内部类, 来描述一个元素在二维数组中的位置
// Pos 类负责表示一个 Weight 的具体位置.
static class Pos{
public int row; // 行
private int col; // 列
public Pos(int row, int col) {
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
}
}
private List mergeResult(List> source) {
// 1. 先把每行的结果按照 id 升序排序
for (List row : source) {
row.sort(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Weight o1, Weight o2) {
return o1.getDocId() - o2.getDocId();
}
});
}
// 2. 借助优先队列, 进行归并
ArrayList target = new ArrayList<>();
// 2.1 创建优先队列, 指定比较规则
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Pos o1, Pos o2) {
return source.get(o1.row).get(o1.col).getDocId() - source.get(o2.row).get(o2.col).getDocId();
}
});
// 2.2 初始化队列, 放入每行的第一列元素
for (int row = 0; row < source.size(); row++) {
queue.offer(new Pos(row, 0));
}
// 2.3 循环从队列中取元素
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Pos curPos = queue.poll();
Weight curWeight = source.get(curPos.row).get(curPos.col);
if (target.size() != 0) {
Weight lastWeight = target.get(target.size() - 1);
if (curWeight.getDocId() == lastWeight.getDocId()) {
// 合并 weight 的权重
lastWeight.setWeight(lastWeight.getWeight() + curWeight.getWeight());
} else {
// 不合并, 直接插入
target.add(curWeight);
}
} else {
// 不合并, 直接插入
target.add(curWeight);
}
Pos newPos = new Pos(curPos.row, curPos.col + 1);
if (newPos.col >= source.get(newPos.row).size()) {
// 当前行已经到达末尾了
continue;
}
queue.offer(newPos);
}
return target;
} (4) GenDes() 制作描述部分 + 标红
private String GenDes(String content, List terms) {
// 用分词结果中的第一个在描述能找到的词, 作为位置的中心
// 先遍历分词结果, 看看哪个结果是在 content 中存在
int firstPos = -1;
for (Term term : terms) {
// 别忘了, 分词库直接针对词进行转小写
// 正因为如此, 就必须把正文也先转成小写, 然后再查询
String word = term.getName();
// 此处需要的是"全字匹配", 让word能够独立成词, 才要查出来, 而不是只作为词的一部分
content = content.toLowerCase().replaceAll("\\b" + word + "\\b", " " + word + " "); // ... arraylist).
firstPos = content.toLowerCase().indexOf(" " + word + " ");
if (firstPos >= 0) {
// 找到了位置
break;
}
}
if (firstPos == -1) {
// 所有的分词结果都不在正文中存在
// 极端情况, 标题有, 正文没有
if(content.length() > 160){
return content.substring(0, 160) + "...";
}
return content;
}
// 从 firstPos 作为基准位置, 往前找60个字符, 作为描述的起始位置
String desc = "";
int descBeg = firstPos < 60 ? 0 : firstPos - 60; // 描述的起始位置
if (descBeg + 160 > content.length()) {
desc = content.substring(descBeg); // 截取从descBeg位置开始到末尾结束
} else {
desc = content.substring(descBeg, descBeg + 160) + "...";
}
// [标红逻辑]
// 在此处加上一个替换操作, 把描述中的和分词结果相同的部分, 给加上一层 标签, 就可以通过 replace 的方式来实现
for (Term term : terms){
String word = term.getName();
// 注意. 此处要进行全字匹配, 也就是当查询词为 List 的时候, 不能把 ArrayList 中的 List 给单独标红
desc = desc.replaceAll("(?i) " + word + " ", " " + word + " ");
}
return desc;
} (5) loadStopWords() 加载停用词到stopWords中
// 加载停用词到stopWords中
public void loadStopWords(){
try(BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(STOP_WORD_PATH))){
while(true){
String line = bufferedReader.readLine();
if(line == null){
// 读取文件完毕
break;
}
stopWords.add(line);
}
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}3.5 实现 Web 模块:
(1) doGet() 方法
@WebServlet("/searcher")
public class DocSearcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
// 此处的 docSearcher 是全局唯一的, 因此需要 static 修饰
private static DocSearcher docSearcher = new DocSearcher();
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 1. 先解析请求, 拿到用户提交的查询词
String query = req.getParameter("query");
if (query == null || query.equals("")){
String msg = "您的参数非法! 没有获取到 query 的值!";
System.out.println(msg);
resp.sendError(404, msg);
return;
}
// 2. 打印记录一下 query 的值
System.out.println("query= " + query);
// 3. 调用搜索模块, 进行搜索
List results = docSearcher.search(query);
// 4. 把当前的搜索结果进行打包
resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf-8");
objectMapper.writeValue(resp.getWriter(), results);
}
}