数据结构--动态顺序表
文章目录
- 线性表
- 动态顺序表
-
- 数组与顺序表
- 接口实现
-
- 初始化:
- 尾插:
- 尾删
- 头插
- 头删
- 指定位置插入
- 指定位置删除
- 查找
- 摧毁
- 完整代码
线性表
线性表是数据结构中最基本、最简单也是最常用的一种数据结构。线性表是指由n个具有相同数据类型的元素组成的有限序列。
线性表分为顺序表和链表两种实现方式。
-
顺序表:
顺序表是线性表的一种实现方式,它在计算机内存中以数组的形式保存数据元素。顺序表的特点是元素在内存中是连续存储的,通过索引可以直接访问元素,因此具有较快的随机访问速度。但是顺序表的长度是固定的,需要提前申请足够的内存空间,并且插入和删除元素时需要移动其他元素,效率较低。

-
链表:
链表是线性表的另一种实现方式,它通过指针将多个节点串联起来。每个节点包含元素和指向下一个节点的指针,所以链表的内存分布可以是离散的。链表的优点是可以动态地分配内存,插入和删除操作只需要修改指针,效率较高。但是链表的访问速度比较慢,需要遍历节点找到目标位置。
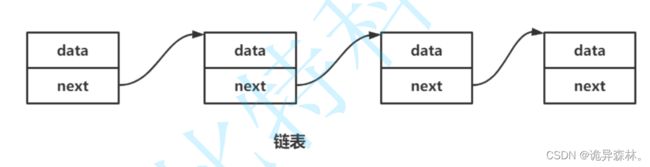
本章主要介绍的是顺序表。
动态顺序表
顺序表分为静态顺序表和动态顺序表;
静态顺序表是用定长数组来进行存储元素;
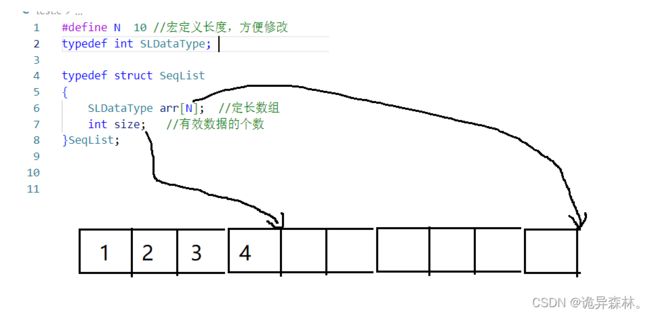
动态顺序表是利用动态存储开辟的数组:
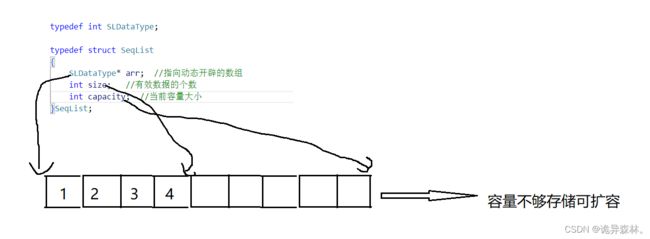
数组与顺序表
顺序表和数组在某种程度上可以说是相似的,因为顺序表的基本实现就是数组。顺序表是对数组的一种封装,它在数组的基础上提供了更加灵活的内存管理方式,使得插入、删除等操作更加高效。
接口实现
我们要将函数都包含在一个头文件中,然后用一个源文件来对函数的实现;
结构:
#pragma once
#include初始化:
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = (SLTypeData*)malloc(sizeof(SLTypeData) * 4);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
perror("malloc failed");
exit(-1);
}
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 4;
}
对数组先开辟4个空间,然后判断是否开辟成功,成功就对size和容量进行初始化赋值;
尾插:
void AddCapacity(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
SLTypeData* cmp = (SLTypeData*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(SLTypeData) * (ps->capacity + 3));
if (cmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc failed");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = cmp;
ps->capacity += 3;
}
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLTypeData x)
{
//满需要扩容
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
AddCapacity(ps);
}
//开始尾插
ps->a[ps->size] = x;
ps->size++;
}
在这里,由于还有头插和位置插入,所以就写一个函数来进行增加容量;每次容量增加3;尾插只需要在size下标进行赋值,最后再把size++即可;
我们写一个打印函数验证一下:
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
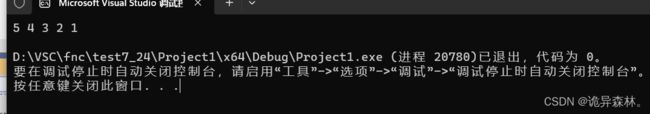
然后在主函数中加以验证:
#include"SeqList.h"
int main()
{
SL test;
SLInit(&test);
SLPushBack(&test, 1);
SLPushBack(&test, 2);
SLPushBack(&test, 3);
SLPushBack(&test, 4);
SLPushBack(&test, 5);
SLPrint(&test);
return 0;
}
尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps->size > 0);
ps->size--;
}
验证:
int main()
{
SL test;
SLInit(&test);
SLPushBack(&test, 1);
SLPushBack(&test, 2);
SLPushBack(&test, 3);
SLPushBack(&test, 4);
SLPushBack(&test, 5);
SLPrint(&test);
SLPopBack(&test);
SLPrint(&test);
return 0;
}
头插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLTypeData x)
{
assert(ps);
//满扩容
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
AddCapacity(ps);
}
//往后移
for (int i = ps->size; i > 0; i--)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i-1];
}
//头插
ps->a[0] = x;
ps->size++;
}
这里要插入需要对当前数组进行挪移,给第一个元素腾出空间存储;
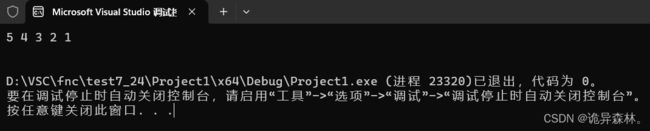
验证:
int main()
{
SL test;
SLInit(&test);
SLPushFront(&test, 1);
SLPushFront(&test, 2);
SLPushFront(&test, 3);
SLPushFront(&test, 4);
SLPushFront(&test, 5);
SLPrint(&test);
return 0;
}
头删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//判断
assert(ps->size > 0);
//左移
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
}
//size减1
ps->size--;
}
头一个元素删完之后,需要将后面元素向前移动;最后将size–;
验证:
int main()
{
SL test;
SLInit(&test);
SLPushFront(&test, 1);
SLPushFront(&test, 2);
SLPushFront(&test, 3);
SLPushFront(&test, 4);
SLPushFront(&test, 5);
SLPrint(&test);
SLPopFront(&test);
SLPrint(&test);
return 0;
}
指定位置插入
//起始位置为1,例如pos=1,那么就是在下标为0的位置插入
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLTypeData x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos > 0 && pos <= ps->size + 1); //指定pos范围
//满扩容
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
AddCapacity(ps);
}
//位置后移
for (int i = ps->size; i > pos - 1; i--)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i - 1];
}
//插入
ps->a[pos - 1] = x;
ps->size++;
}
验证:
int main()
{
SL test;
SLInit(&test);
SLPushFront(&test, 1);
SLPushFront(&test, 2);
SLPushFront(&test, 3);
SLPushFront(&test, 4);
SLPushFront(&test, 5);
SLPrint(&test);
SLInsert(&test, 3, 88);
SLPrint(&test);
return 0;
}
指定位置删除
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos > 0 && pos <= ps->size);//指定pos范围
//左移
for (int i = pos - 1; i < ps->size-1; i++)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
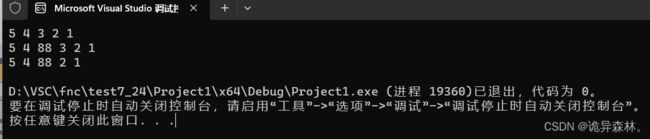
验证:
int main()
{
SL test;
SLInit(&test);
SLPushFront(&test, 1);
SLPushFront(&test, 2);
SLPushFront(&test, 3);
SLPushFront(&test, 4);
SLPushFront(&test, 5);
SLPrint(&test);
SLInsert(&test, 3, 88);
SLPrint(&test);
SLErase(&test, 4);
SLPrint(&test);
return 0;
}
查找
查找对应的元素,如果有多个元素一样,返回的是最左边的元素;
返回的初始位置为1,例如下标为0,那么返回位置为1;
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLTypeData x)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
{
return i+1;
}
}
return -1;
}
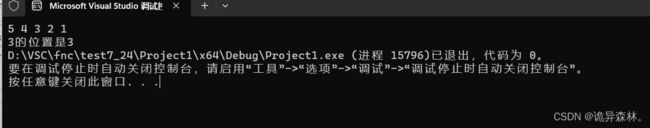
验证:
int main()
{
SL test;
SLInit(&test);
SLPushFront(&test, 1);
SLPushFront(&test, 2);
SLPushFront(&test, 3);
SLPushFront(&test, 4);
SLPushFront(&test, 5);
SLPrint(&test);
int pos = SLFind(&test, 3);
printf("3的位置是%d", pos);
return 0;
}
摧毁
void SLDestory(SL* ps)
{
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
验证:
int main()
{
SL test;
SLInit(&test);
SLPushFront(&test, 1);
SLPushFront(&test, 2);
SLPushFront(&test, 3);
SLPushFront(&test, 4);
SLPushFront(&test, 5);
SLPrint(&test);
SLDestory(&test);
SLPrint(&test);
return 0;
}
完整代码
SeqList.h
#pragma once
#includeSeqList.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "SeqList.h"
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = (SLTypeData*)malloc(sizeof(SLTypeData) * 4);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
perror("malloc failed");
exit(-1);
}
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 4;
}
void SLDestory(SL* ps)
{
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//满扩容
void AddCapacity(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
SLTypeData* cmp = (SLTypeData*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(SLTypeData) * (ps->capacity + 3));
if (cmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc failed");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = cmp;
ps->capacity += 3;
}
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLTypeData x)
{
//满需要扩容
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
AddCapacity(ps);
}
//开始尾插
ps->a[ps->size] = x;
ps->size++;
}
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps->size > 0);
ps->size--;
}
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLTypeData x)
{
assert(ps);
//满扩容
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
AddCapacity(ps);
}
//往后移
for (int i = ps->size; i > 0; i--)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i-1];
}
//头插
ps->a[0] = x;
ps->size++;
}
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//判断
assert(ps->size > 0);
//左移
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
}
//size减1
ps->size--;
}
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLTypeData x)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
{
return i+1;
}
}
return -1;
}
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLTypeData x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos > 0 && pos <= ps->size + 1);
//满扩容
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
AddCapacity(ps);
}
//位置后移
for (int i = ps->size; i > pos - 1; i--)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i - 1];
}
//插入
ps->a[pos - 1] = x;
ps->size++;
}
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos > 0 && pos <= ps->size);
assert(pos > 0);
//左移
for (int i = pos - 1; i < ps->size-1; i++)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"SeqList.h"
int main()
{
SL test;
SLInit(&test);
SLPushFront(&test, 1);
SLPushFront(&test, 2);
SLPushFront(&test, 3);
SLPushFront(&test, 4);
SLPushFront(&test, 5);
SLPrint(&test);
SLDestory(&test);
SLPrint(&test);
return 0;
}