ansible控制主机和受控主机之间免密及提权案例
目录
案例描述
环境准备
案例一--免密远程控制主机
效果展示:
解决方案
1.添加主机
2.通过ssh-key生成密钥对
3.生成ssh-copy-id
4.验证
案例二-----免密普通用户提权
效果展示
解决方案
1.使用普通用户,与案例一 一样,进行发送密钥对和id
keygen
copy-id
测试
2.在node1用户下的/etc/sudoers/中
查看:
相关知识:
1.gpasswd
2.ssh-copy-id
3.ssh-keygen
案例描述
一、描述:控制主机和受控主机通过root用户以免密验证远程控制受控主机实施对应任务
二、描述: 控制主机和受控主机通过普通用户以免密验证远程控制主机实施特权控制操作
环境准备
我这里一共三台主机,一个控制端,两个受控端
案例一--免密远程控制主机
描述:控制主机和受控主机通过root用户以免密验证远程控制受控主机实施对应任务
为了确保在ansible执行中,各个主机不会受到这些限制,我们可以提供密钥保存到各个主机上,以实现免密登陆效果。
效果展示:
设置之前效果:
[root@control ~]# ssh root@node1
The authenticity of host 'node1 (192.168.197.153)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:p1vEMDKw2flRy/TI2CE3STJ451XMUm+Sg7/ztyJMaF4.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
Warning: Permanently added 'node1,192.168.197.153' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
root@node1's password:
Activate the web console with: systemctl enable --now cockpit.socketThis system is not registered to Red Hat Insights. See https://cloud.redhat.com/
To register this system, run: insights-client --registerLast login: Wed Aug 2 02:55:02 2023 from 192.168.197.1
[root@node1 ~]#
设置之后效果:
[root@control ~]# ssh node1
Activate the web console with: systemctl enable --now cockpit.socketThis system is not registered to Red Hat Insights. See https://cloud.redhat.com/
To register this system, run: insights-client --registerLast login: Wed Aug 2 05:05:59 2023 from 192.168.197.152
解决方案
1.添加主机
在/etc/hosts下
192.168.197.153 node1 node1.example.com
192.168.197.154 node3 node1.example.com
2.通过ssh-key生成密钥对
ssh-keygen是一个用于生成SSH密钥对的命令行工具。SSH密钥对由公钥和私钥组成,用于通过SSH协议进行安全的身份验证。
[root@control ~]# ssh-keygen -t RSA
Generating public/private RSA key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:6338jg7huU2z/sTmRfgax98A1g/nvbHYyIu5woTOSmY root@control
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 3072]----+
| |
| |
| |
| . . |
| S . o + o|
| . + + o O.|
| Eo + +.o *.O|
| + + + =*B+**|
| .. . +BBOB+o|
+----[SHA256]-----+
3.生成ssh-copy-id
ssh-copy-id是一个方便的工具,用于将本地计算机上的公钥复制到远程服务器的授权密钥列表中,以实现无密码的SSH登录。
[root@control ~]# ssh-copy-id -i node1
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@node1's password:Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'node1'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
4.验证
[root@control ~]# ssh node1
Activate the web console with: systemctl enable --now cockpit.socketThis system is not registered to Red Hat Insights. See https://cloud.redhat.com/
To register this system, run: insights-client --registerLast login: Wed Aug 2 05:10:12 2023 from 192.168.197.152
[root@node1 ~]#
[root@control ~]# ssh node2
Activate the web console with: systemctl enable --now cockpit.socketThis system is not registered to Red Hat Insights. See https://cloud.redhat.com/
To register this system, run: insights-client --registerLast login: Wed Aug 2 05:10:12 2023 from 192.168.197.152
[root@node2 ~]#
也可以通过ansible的ping模块进行测试
首先在/etcansible/hosts下添加两个主机名称
测试
[root@control ~]# ansible node1,node2 -m ping -o
node1 | SUCCESS => {"ansible_facts": {"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"},"changed": false,"ping": "pong"}
node2 | SUCCESS => {"ansible_facts": {"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"},"changed": false,"ping": "pong"}
案例二-----免密普通用户提权
描述: 控制主机和受控主机通过普通用户以免密验证远程控制主机实施特权控制操作
效果展示
没提权之前,是执行不了某些权限的,如需要root权限去添加用户
[redhat@control ~]$ ssh node1 useradd user1
useradd: Permission denied.
useradd: cannot lock /etc/passwd; try again later.
提权之后:
[redhat@control ~]$ ssh node1 sudo useradd user1
[redhat@control ~]$
解决方案
1.使用普通用户,与案例一 一样,进行发送密钥对和id
keygen
[redhat@control ~]$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/home/redhat/.ssh/id_rsa):
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /home/redhat/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /home/redhat/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:2JMBtnjN6BCC7cUpqkeZqWgKvSm3DyIhcbd8LdUYiIw redhat@control
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 3072]----+
| o.+.oo.. |
|. E.*+.* + |
|.o.*+ + * . |
|.o*o = = o |
|=+ o = S |
|*oo . . . |
|*..o |
|+.+. |
| o.o. |
+----[SHA256]-----+
copy-id
[redhat@control ~]$ ssh-copy-id -i node1
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/home/redhat/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
redhat@node1's password:Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'node1'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
测试
[redhat@control ~]$ ssh node1 hostname
node1
测试添加用户
[redhat@control ~]$ ssh node1 useradd user1
useradd: Permission denied.--------》被拒绝,没有权限
useradd: cannot lock /etc/passwd; try again later.
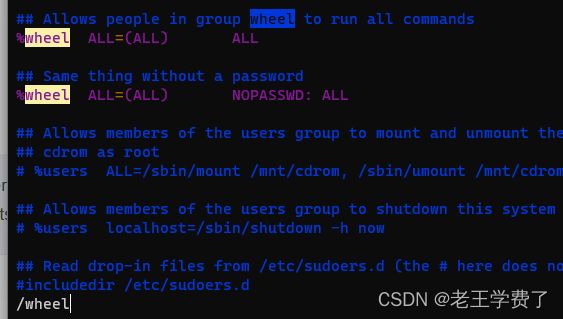
2.在node1用户下的/etc/sudoers/中
修改:
查看修改是否成功
[root@node1 ~]# cat /etc/sudoers | grep wheel
## Allows people in group wheel to run all commands
%wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL
%wheel ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL
然后给权限
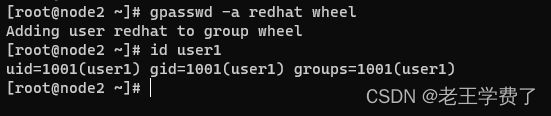
gpasswd 就是将redhat用户添加到whell组中,必须要执行这个,不然是会出错的,redhat用户不能正常使用提权
[root@node1 ~]# gpasswd -a redhat wheel
Adding user redhat to group wheel
[redhat@control ~]$ ssh node1 sudo useradd user1
useradd: warning: the home directory already exists.
Not copying any file from skel directory into it.
Creating mailbox file: File exists有警告,但是可用,可能我添加出错了node2可正常使用
node2机子一样的设置,只需要给%wheel添加一个NOPASSWD,这个%代表组的意思,就是添加在组里面,这个组都可以访问,不需要密码
[redhat@control ~]$ ssh node2 sudo useradd user1
[redhat@control ~]$
查看:
有用户
相关知识:
1.gpasswd
gpasswd -a redhat wheel是一个命令,用于将用户"redhat"添加到"wheel"用户组。"wheel"用户组通常用于授予系统管理员或特权用户执行敏感操作的权限。通过将用户添加到"wheel"组,可以实现对系统的控制和管理。
请注意,执行此命令需要具有root或sudo特权用户身份。您需要在终端或命令提示符下执行该命令,并提供适当的凭据。
2.ssh-copy-id
ssh-copy-id是一个方便的工具,用于将本地计算机上的公钥复制到远程服务器的授权密钥列表中,以实现无密码的SSH登录。要使用
ssh-copy-id命令,按照以下步骤进行操作:
- 打开终端或命令提示符。
- 输入以下命令,并将
username替换为您在远程服务器上的用户名,以及hostname替换为远程服务器的主机名或IP地址:Copy Code
ssh-copy-id username@hostname您也可以使用-p选项指定非默认的SSH端口号。例如,如果SSH服务器侦听在2222端口上,则可以使用以下命令:Copy Code
ssh-copy-id -p 2222 username@hostname- 按回车键后,它会提示您输入远程服务器的密码(一次性)。
- 如果密码验证成功,
ssh-copy-id会自动将本地计算机上的公钥追加到远程服务器上的~/.ssh/authorized_keys文件中。- 完成后,您可以尝试使用
ssh username@hostname命令登录到远程服务器,此时不再需要输入密码。请注意,使用
ssh-copy-id之前,确保本地计算机已经生成了SSH密钥对,并且具有可用的公钥。如果没有生成密钥对,请先使用ssh-keygen命令生成密钥对。
3.ssh-keygen
ssh-keygen是一个用于生成SSH密钥对的命令行工具。SSH密钥对由公钥和私钥组成,用于通过SSH协议进行安全的身份验证。要使用
ssh-keygen生成SSH密钥对,请按照以下步骤操作:
- 打开终端或命令提示符。
- 输入以下命令:
Copy Code
ssh-keygen- 按回车键以接受默认选项,或根据需要输入自定义选项。
- 默认情况下,
ssh-keygen将在用户主目录下的.ssh文件夹中生成密钥对。- 您可以选择为密钥对指定名称和位置,或为其设置密码(提供额外的安全性)。
- 在生成密钥对时,可能会提示您输入密码短语(passphrase)。密码短语是对私钥加密的额外保护层,可以为空。
- 如果设置了密码短语,则在使用私钥进行身份验证时,还需要提供该密码短语。
- 当生成密钥对完成后,将在指定的位置生成两个文件:
- 公钥文件:通常以
.pub结尾,包含您的公钥,用于在远程服务器上进行身份验证。- 私钥文件:没有特定的文件扩展名,是私人的密钥,必须妥善保管,不要泄露给他人。
请记住,私钥是非常敏感的信息,不应该与他人分享或暴露在不安全的环境中。公钥可以自由地在需要进行身份验证的服务器上进行使用和配置。