MyBatis的动态SQL语句
文章目录
- 前言
-
- LocalDate
- 数据库代码
- po 包
- if+where 标签 查
- trim 标签 增
- set 标签 改
- foreach 标签 删
前言
提示:这里可以添加本文要记录的大概内容:
查询条件是动态的
MyBatis的动态SQL语句是指在运行时根据不同条件选择不同的SQL语句执行。
这些条件可以是参数值、条件语句、动态标签等。
动态SQL语句的编写可以有效地减少重复代码
LocalDate
在 Java 8 中,LocalDate 是 java.time 包中的一个类,表示一个日期(年、月、日)。为了创建一个 LocalDate 对象,需要使用 LocalDate.of() 方法,该方法接受三个参数:年、月、日。
例如:
LocalDate date = LocalDate.of(2022, 9, 1);
这将创建一个 LocalDate 对象,表示 2022 年 9 月 1 日。
在你的代码中,为了将生日传递给 Cust 对象,你需要使用 LocalDate.of() 方法来创建一个 LocalDate 对象,并将其传递给 Cust 构造函数。例如:
Cust cust = new Cust(null, "吴三", "17446541321", LocalDate.of(2008, 5, 12), 10.0);
这将创建一个 Cust 对象,并将生日设置为 2008 年 5 月 12 日。
所以,你需要注意的是,LocalDate 是一个类,而 LocalDate.of() 是用于创建 LocalDate 对象的方法。
具体使用:
LocalDate 类提供了一个静态方法 of(int year, int month, int dayOfMonth),该方法允许创建一个指定年份、月份和日期的 LocalDate 对象。
以下是使用 LocalDate.of() 方法创建 LocalDate 对象的步骤:
- 导入 java.time.LocalDate 类:
import java.time.LocalDate;
- 使用 of() 方法创建 LocalDate 对象:
LocalDate date = LocalDate.of(year, month, dayOfMonth);
其中 year、month 和 dayOfMonth 分别代表年份、月份和日期,是整数类型的值:
LocalDate date = LocalDate.of(2022, 10, 1);
创建了一个 LocalDate 对象,表示 2022 年 10 月 1 日。
-
处理 LocalDate 对象:
一旦创建了一个 LocalDate 对象,可以使用它来执行各种操作,例如:
- 获取日期的年份、月份和日期:
int year = date.getYear();
int month = date.getMonthValue();
int day = date.getDayOfMonth();
- 获取星期几:
DayOfWeek dayOfWeek = date.getDayOfWeek();
- 进行日期计算:
LocalDate plusDays = date.plusDays(7); // 返回一周后的日期
LocalDate minusMonths = date.minusMonths(2); // 返回两个月前的日期
- 比较日期:
LocalDate otherDate = LocalDate.of(2022, 10, 2);
boolean isBefore = date.isBefore(otherDate); // 返回 true
boolean isAfter = date.isAfter(otherDate); // 返回 false
boolean isEqual = date.isEqual(otherDate); // 返回 false
这些就是使用 LocalDate.of() 方法创建和处理 LocalDate 对象的步骤。
数据库代码
这里以客户表为例
CREATE TABLE cust (
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment, # id
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, # 姓名
phone VARCHAR(20), # 电话
birthday DATE, # 出生日期
balance DOUBLE # 余额
);
INSERT INTO cust (id, name, phone, birthday, balance) VALUES (1, '张三', '13611111111', '1990-01-01', 1000.00);
INSERT INTO cust (id, name, phone, birthday, balance) VALUES (2, '李四', '13722222222', '1995-02-02', 2000.00);
INSERT INTO cust (id, name, phone, birthday, balance) VALUES (3, '王五', '13833333333', '1985-03-03', 3000.00);
po 包
新建项目后完善 pom.xml 文件、mybatis 的配置文件、log4j 的日志文件
在 main/java 文件中新建包 mapper 和 po
po 包代码:这里面有个Date类型,要注意!
public class Cust {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String phone;
private Date birthday;
private double balance;
// 为了模糊查询某个时间段
private Date startTime;
private Date endTime;
// 自动生成 Getter、Setter、toString()、有参无参方法
}
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
if+where 标签 查
if+where语句可以根据条件动态构建where子句,以过滤查询结果。
在 mapper 包内新建接口文件和与之同名的映射文件
映射文件中的namespace必须是接口的限定名
先写接口文件:
在模糊查询功能中,输入 id 按照 id 查询,输入名字按照名字查询,输入手机号按照手机号查询,所以返回值是多个,查询多个用List
public interface CustMapper {
List<Cust> queryCusts(Cust cust);
}
复制方法名回到映射文件粘贴到 id
下面模糊查询某个时间段的映射文件代码:
<mapper namespace="com.mybatis.mapper.CustMapper">
<!-- 动态的where条件 -->
<select id="queryCusts" parameterType="Cust" resultType="Cust">
select * from cust
<where>
<if test="startTime != null">
and birthday >=#{startTime}
</if>
<if test="endTime != null">
and birthday <=#{endTime}
</if>
</where>
</select>
</mapper>
以上代码中,映射文件中的 select 语句使用了动态的 where 条件,其中的 if 标签用于判断 startTime 和 endTime 是否为 null,若不为 null,则生成相应的SQL语句。
若输入了 startTime,则添加一个条件为 birthday>=startTime 的 where 子句;
若输入了 endTime,则添加一个条件为 birthday<=endTime 的 where 子句。
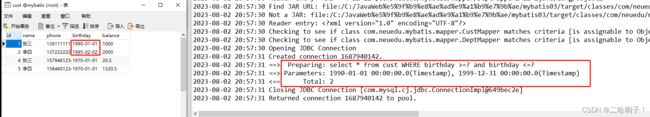
测试代码(模糊查询某个时间段):
@Test
public void where() throws Exception {
CustMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CustMapper.class);
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date startTime = sdf.parse("1990-01-01");
Date endTime = sdf.parse("1999-12-31");
Cust cust = new Cust();
cust.setStartTime(startTime);
cust.setEndTime(endTime);
mapper.queryCusts(cust);
}
在测试代码中,将 startTime 和 endTime 分别解析成日期格式,并通过set方法设置到Cust 对象中,作为参数传递给 queryCusts 方法进行查询。
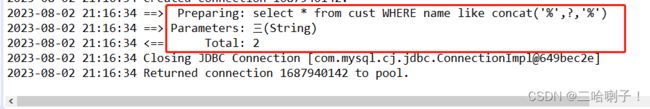
如果是模糊查询 id、姓名、手机号:
映射文件代码:
<mapper namespace="com.mybatis.mapper.CustMapper">
<!-- 动态的where条件 -->
<select id="queryCusts" parameterType="Cust" resultType="Cust">
select * from cust
<where>
<if test="id != null">
and id = #{id}
</if>
<!-- 类型是String,也不能等于空 -->
<if test="name != null and name != '' ">
and name like concat('%',#{name},'%')
</if>
<if test="phone != null and phone != '' ">
and phone like concat('%',#{phone},'%')
</if>
</where>
</select>
</mapper>
测试代码(模糊查询 id、姓名、手机号):
@Test
public void where() {
CustMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CustMapper.class);
Cust cust = new Cust(null, "三", null,null,1000.0);
mapper.queryCusts(cust);
}
在测试代码中创建了一个Cust 对象,只设置了 name 属性值为"三",然后调用queryCusts 方法进行查询。因为 id 和 phone 属性值为null,所以查询条件中只会有name 相关的查询语句。此时,查询结果会返回所有名字包含"三"的记录。
需要注意的是,测试代码中设置的name值必须是一个非空字符串才会被加入到查询条件中。如果 name 属性值为 null 或空字符串,那么查询条件中不会包含对 name 的筛选。
trim 标签 增
Trim语句:可以包装一组语句,去除多余的空格或逗号;
mapper接口的代码:
void insertCust(Cust cust);
在映射文件增加对应的语句:
增加客户信息
<insert id="insertCust" parameterType="Cust" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into cust
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
id, name,
<if test="phone != null and phone != '' ">
phone,
</if>
<if test="birthday != null">
birthday,
</if>
<if test="balance != null">
balance,
</if>
</trim>
<trim prefix="values(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
#{id}, #{name},
<if test="phone != null and phone != '' ">
#{phone},
</if>
<if test="birthday != null">
#{birthday},
</if>
<if test="balance != null">
#{balance},
</if>
</trim>
</insert>
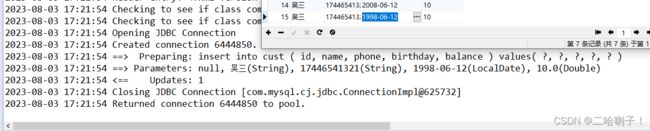
接下来是测试:【注意: LocalDate】当然前面的类型也要改
@Test
public void trim() {
CustMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CustMapper.class);
Cust cust = new Cust(null, "吴三", "17446541321", LocalDate.of(1998, 6, 12), 10.0);
mapper.insertCust(cust);
}
set 标签 改
set语句:可用于构建UPDATE语句的SET子句;
mapper接口的代码:
void updateCust(Cust cust);
在对应的映射文件中:
根据 id 更改名字 和 电话号码
<update id="updateCust" parameterType="Cust">
update cust
<set>
<if test="name != null and name != '' ">
name = #{name},
</if>
<if test="phone != null and phone != '' ">
phone = #{phone},
</if>
</set>
where id = #{id}
</update>
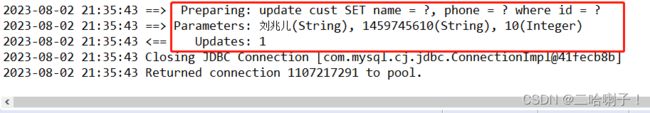
测试类代码:
@Test
public void set() {
CustMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CustMapper.class);
Cust cust = new Cust(10, "刘兆儿", "1459745610",null,1000.0);
mapper.updateCust(cust);
}
foreach 标签 删
Foreach语句:用于遍历集合或数组,可以重复执行SQL语句;
可能要删多个数据,可以用数组(array)或 集合(list)
mapper接口的代码:
void deleteCusts(int[] ids);
在对应的映射文件中:
<delete id="deleteCusts" parameterType="int">
delete from cust where id in
<foreach collection="array" item="no" open="(" close=")" separator=",">
#{no}
</foreach>
</delete>
测试类代码:
@Test
public void foreach() {
CustMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CustMapper.class);
// id
int [] nos = {1,2,3,4,5};
mapper.deleteCusts(nos);
}