MySQL用户管理
目录
前言
1.用户
1.1.用户类型
1.2.用户信息
1.3.创建用户
1.4.删除用户
1.5.修改用户密码
2.数据库权限
2.1给用户授权
2.2回收权限
总结
前言
哈喽,各位小伙伴大家好!今天我们要介绍的是在MySQL是如何进行用户管理的。MySQL本质是一款网络服务,在使用之前是需要进行登录的,登录身份的不同对MySQL可执行操作的权限不一样,登录身份我们可以大致分为root用户和其它用户,下面我们就一起来看看在MySQL中如何管理用户以及不同用户的权限是什么样的。
1.用户
1.1.用户类型
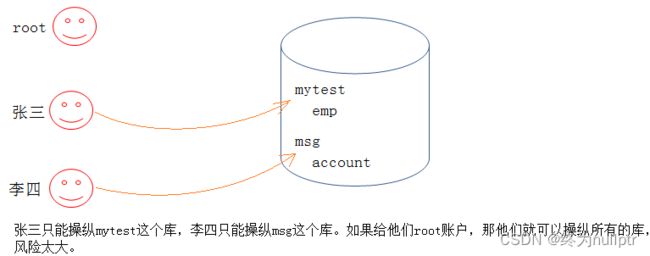
在MySQL中用户类型可以大致分为root用户和普通用户,关于root用户和普通用户的区别如图所示:
1.2.用户信息
MySQL中的用户,都存储在系统数据库mysql的user表中
mysql> use mysql;
Database changed
mysql> select host,user,authentication_string from user;
+-----------+---------------+-------------------------------------------+
| host | user | authentication_string |
+-----------+---------------+-------------------------------------------+
| localhost | root | *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B |
| localhost | mysql.session | *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE |
| localhost | mysql.sys | *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE |
+-----------+---------------+-------------------------------------------+字段解释:
host: 表示这个用户可以从哪个主机登陆,如果是localhost,表示只能从本机登陆
user: 用户名
authentication_string: 用户密码通过password函数加密后的
1.3.创建用户
语法:
create user '用户名'@'登陆主机/ip' identified by '密码';案例:
mysql> create user 'myl'@'localhost' identified by '12345678';mysql> select user,host,authentication_string from user;
+---------------+-----------+-------------------------------------------+
| user | host | authentication_string |
+---------------+-----------+-------------------------------------------+
| root | % | *A2F7C9D334175DE9AF4DB4F5473E0BD0F5FA9E75 |
| mysql.session | localhost | *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE |
| mysql.sys | localhost | *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE |
| myl | localhost | *84AAC12F54AB666ECFC2A83C676908C8BBC381B1 | --新增用户
+---------------+-----------+-------------------------------------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)1.4.删除用户
语法:
drop user '用户名'@'主机名'1.5.修改用户密码
语法:
set password=password('新的密码');root用户修改指定用户的密码
set password for '用户名'@'主机名'=password('新的密码');以上就是在MySQL中对用户的管理,实现对用户信息的增删查改
2.数据库权限
MySQL数据库提供的权限列表:
2.1给用户授权
刚创建的用户没有任何权限。需要给用户授权。
语法:
grant 权限列表 on 库.对象名 to '用户名'@'登陆位置' [identified by '密码']说明:
权限列表,多个权限用逗号分开
grant select on ...
grant select, delete, create on ....
grant all [privileges] on ... -- 表示赋予该用户在该对象上的所有权限*.* : 代表本系统中的所有数据库的所有对象(表,视图,存储过程等)
库.* : 表示某个数据库中的所有数据对象(表,视图,存储过程等)
identified by可选。 如果用户存在,赋予权限的同时修改密码,如果该用户不存在,就是创建用户
案例:
--使用root账号
--终端A
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| 57test |
| bit_index |
| ccdata_pro |
| innodb_test |
| musicserver |
| myisam_test |
| mysql |
| order_sys |
| performance_schema |
| scott |
| sys |
| test |
| vod_system |
+--------------------+
14 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> use test;
Database changed
mysql> show tables;
+----------------+
| Tables_in_test |
+----------------+
| account |
| student |
| user |
+----------------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
--给用户myl赋予test数据库下所有文件的select权限
mysql> grant select on test.* to 'whb'@'localhost';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
--使用myl账号
--终端B
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
+--------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
--暂停等root用户给myl赋完权之后,在查看
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| test | --赋完权之后,就能看到新的表
+--------------------+
2 rows in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> use test;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> show tables;
+----------------+
| Tables_in_test |
+----------------+
| account |
| student |
| user |
+----------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from account;
+----+--------+---------+
| id | name | blance |
+----+--------+---------+
| 2 | 李四 | 321.00 |
| 3 | 王五 | 5432.00 |
| 4 | 赵六 | 543.90 |
| 5 | 赵六 | 543.90 |
+----+--------+---------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
--没有删除权限
mysql> delete from account;
ERROR 1142 (42000): DELETE command denied to user 'myl'@'localhost' for table
'account'
备注:特定用户现有查看权限
mysql> show grants for 'myl'@'%';
+-----------------------------------------------+
| Grants for myl@% |
+-----------------------------------------------+
| GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO 'myl'@'%' |
| GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON `test`.* TO 'myl'@'%' |
+-----------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show grants for 'root'@'%';
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| Grants for root@% |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' WITH GRANT OPTION |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)注意:如果发现赋权限后,没有生效,执行如下指令:
flush privileges;
2.2回收权限
语法:
revoke 权限列表 on 库.对象名 from '用户名'@'登陆位置';示例:
-- 回收myl对test数据库的所有权限
--root身份,终端A
mysql> revoke all on test.* from 'myl'@'localhost';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
--myl身份,终端B
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| test |
+--------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
+--------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)总结
以上就是关于MySQL中对用户的管理和不同用户对应的数据库权限,希望能够对大家有所帮助,谢谢大家!