算法通关村第一关——链表青铜挑战笔记
1. 单链表
1. 单链表的建造
链表有两个属性,一个就是当前的值val,还有一个就是记录当前节点的下一个节点位置,由此可以写出建造链表的相关代码
public class ListNode {
int value;
ListNode next;
public ListNode(int value, ListNode next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public ListNode() {
}
public ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public ListNode(ListNode next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
2. 链表遍历
链表没有相关属性来记录当前的链表长度,所以只能经过遍历获取链表长度
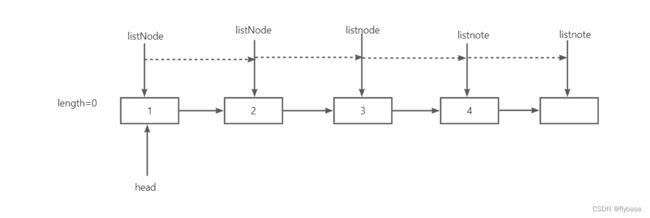
public static int getListNodeLength(ListNode head) {
int length = 0;
ListNode listNode = head;
while (listNode != null) {
length++;
listNode = listNode.next;
}
return length;
}
链表展示
public static void showNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode listNode = head;
while (listNode != null) {
System.out.print(listNode.value + "=>");
listNode = listNode.next;
}
System.out.println("null");
}
3. 插入元素
3.1 头插法

头插法相对简单
新节点的下一个元素指向当前的头节点,然后头节点移动到新的节点处
public static ListNode insertIntoNode(ListNode head, ListNode newNode) {
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
return head;
}
3.2 尾插法
在最后一个元素处后面插入元素,即最后一个元素的next指向插入元素,插入元素的下一个指向null

public static ListNode insertIntoTail(ListNode head, ListNode newNode) {
ListNode listNode = head;
while (listNode.next != null) {
listNode = listNode.next;
}
listNode.next = newNode;
newNode.next = null;
return head;
}
3.3 指定位置插入
需要找到插入元素的位置的前一个元素,先将新建节点的next指向当前位置的下一个节点的位置,然后将当前节点的next指向新建节点
这两个顺序不能颠倒,如果颠倒了,当前节点就无法找到当前节点的下一个元素的位置,这时候连接已经断了,成为了两个链表

public static ListNode insertIntoPosition(ListNode head, ListNode newNode, int position) {
ListNode listNode = head;
int length = 0;
while (length < position - 1) {
listNode = listNode.next;
length++;
}
newNode.next = listNode.next;
listNode.next = newNode;
return head;
}
综合使用
以上3个方法较为独立,都是没有考虑到一些特殊情况,比如链表为空,插入元素的位置查过当前链表的界限,下面将会综合以上考虑完成较为完整的插入代码
public static ListNode insertIntoListNode(ListNode head, ListNode newNode, int position) {
// 当前链表为空,插入元素则为第一个节点
if (head == null) {
return newNode;
}
// 是否超过界限
ListNode listNode = head;
int listNodeLength = getListNodeLength(head);
if (position < 1 || position > listNodeLength + 1) {
System.out.println("元素越界");
return head;
}
// 头节点
if (position == 1) {
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
return head;
}
// 指定位置
int count = 0;
ListNode node = head;
while (count < position - 1) {
node = node.next;
count++;
}
newNode.next = node.next;
node.next = newNode;
return head;
}
4 删除元素
4.1 头删
public static ListNode deleteHead(ListNode head) {
ListNode listNode = head;
listNode = listNode.next;
head = listNode;
return head;
}
4.2 尾删
主要需要找到尾部元素的前一个元素,将他的下一个节点指向null即可

public static ListNode deleteTail(ListNode head) {
ListNode listNode = head;
while (listNode.next.next != null) {
listNode = listNode.next;
}
listNode.next = null;
return head;
}
4.3 指定位置删除
需要找到删除元素的前一个元素,先保留删除元素和前一个元素之间的联系,不能断开,否则无法找到后面的其他节点
public static ListNode deleteByPosition(ListNode head, int position) {
ListNode listNode = head;
int count = 0;
while (count < position - 1) {
count++;
listNode = listNode.next;
}
ListNode deleteNode = listNode.next;
listNode.next = deleteNode.next;
return head;
}
综合删除
public static ListNode deletePosition(ListNode head, int position) {
ListNode listNode = head;
// 链表为空
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// 判断界限
int listNodeLength = getListNodeLength(head);
// 这里不需要判断listNodeLength+1,因为下面已经记录了删除元素的前一个节点,和删除节点的下一个节点存不存在没有关系
if (position > listNodeLength || position < 1) {
System.out.println("超过界限");
return head;
}
if (position == 1) {
listNode = listNode.next;
head = listNode;
return head;
}
ListNode preNode = head;
int count = 0;
while (count < position - 1) {
preNode = preNode.next;
count++;
}
ListNode deleteNode = preNode.next;
preNode.next = deleteNode.next;
return head;
}
2. 双向链表
1. 双向链表的建立
单链表只能获取自己的后一个节点的元素,而双向链表里面有两个指针,可以获取前后节点

public class DoubleListNode {
int value;
DoubleListNode preNode;
DoubleListNode nextNode;
public DoubleListNode(int value, DoubleListNode preNode, DoubleListNode nextNode) {
this.value = value;
this.preNode = preNode;
this.nextNode = nextNode;
}
public DoubleListNode() {
}
public DoubleListNode(DoubleListNode preNode) {
this.preNode = preNode;
}
public DoubleListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public DoubleListNode(DoubleListNode preNode, DoubleListNode nextNode) {
this.preNode = preNode;
this.nextNode = nextNode;
}
/**
* 展示数据
*/
public void displayNode() {
System.out.print("{" + value + "}");
}
}
数据准备
DoubleListNode doubleListNode1 = new DoubleListNode(1);
DoubleListNode doubleListNode2 = new DoubleListNode(2);
DoubleListNode doubleListNode3 = new DoubleListNode(3);
DoubleListNode doubleListNode4 = new DoubleListNode(5);
doubleListNode1.nextNode = doubleListNode2;
doubleListNode2.preNode = doubleListNode1;
doubleListNode2.nextNode = doubleListNode3;
doubleListNode3.preNode = doubleListNode2;
doubleListNode3.nextNode = doubleListNode4;
doubleListNode4.preNode = doubleListNode3;
2. 遍历
2.1 头部遍历
public static void displayDoubleNodeFromHead(DoubleListNode head) {
DoubleListNode current = head;
while (current != null) {
// 展示
current.displayNode();
current = current.nextNode;
}
System.out.println("");
}
2.2 尾部遍历
public static void displayDoubleNodeFromTail(DoubleListNode tail) {
DoubleListNode current = tail;
while (current != null) {
current.displayNode();
current = current.preNode;
}
}
这里面的tail记住选最后一个节点
3 插入数据
3.1 头部插入

只需要将新建节点的next指向原来的head,将原来的head的pre指向新建节点,head改变即可。
public static DoubleListNode insetIntoNodeHead(DoubleListNode head, DoubleListNode newNode) {
if (head == null) {
return newNode;
}
newNode.nextNode = head;
head.preNode = newNode;
head = newNode;
return head;
}
3.2 尾部插入

只需要将tail节点的next指向新建节点,新建节点的pre指向tail节点,tail改变
public static DoubleListNode insetIntoNodeTail(DoubleListNode tail, DoubleListNode newNode) {
if (tail == null) {
return newNode;
}
tail.nextNode = newNode;
newNode.preNode = tail;
tail = newNode;
return tail;
}
3.3 指定位置插入
这个就有点麻烦,需要改动四个指针,还需要考虑第一个和最后一个节点的位置。
public static DoubleListNode insetIntoNodeByPosition(DoubleListNode head, DoubleListNode newNode, int position) {
// 空节点
if (head == null) {
return newNode;
}
DoubleListNode current = head;
// 头节点
if (position == 1) {
newNode.nextNode = head;
head.preNode = newNode;
return newNode;
}
// 计算处添加节点的前一个节点
int count = 0;
while (count < position - 2 && current.nextNode != null) {
current = current.nextNode;
count++;
}
DoubleListNode nextNode = current.nextNode;
if (nextNode != null) {
nextNode.preNode = newNode;
newNode.nextNode = nextNode;
}
current.nextNode = newNode;
newNode.preNode = current;
return head;
}
注意这里需要将新的链表传递给展示的方法才能展示新的链表
DoubleListNode doubleListNode = insetIntoNodeByPosition(doubleListNode1, new DoubleListNode(4), 4);
displayDoubleNodeFromHead(doubleListNode);
4. 删除元素
4.1 删除头节点
public static DoubleListNode deleteNode(DoubleListNode head, int position) {
// 头节点不存在
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
DoubleListNode current = head;
// 删除头节点
if (position == 1) {
DoubleListNode nextNode = current.nextNode;
nextNode.preNode = null;
head = nextNode;
return head;
}
// 找到指定位置的节点
int count = 1;
while (count < position && current != null) {
current = current.nextNode;
count++;
}
if (current != null) {
DoubleListNode prevNode = current.preNode;
DoubleListNode nextNode = current.nextNode;
if (prevNode != null) {
prevNode.nextNode = nextNode;
}
if (nextNode != null) {
nextNode.preNode = prevNode;
} else {
// 当前节点是最后一个节点
prevNode.nextNode = null;
}
}
return head;
}
总结
双向链表的插入和删除相对较为繁琐,但是步骤很简单,自己多画一些图就能理解。
源码
https://github.com/flybase1/AlgorithmPrtojects
总结
里面部分代码还是可能有些问题,希望大家能够指出其中的错误,共同进步。



