Chapter20 音乐
目录
音乐
琴键
哆来咪
振动与调式
利萨如曲线
和声与音调与和弦
音乐
在音乐理论中,一个八音度(octave)是一个频率范围相差二倍的区间。在大多数西洋乐器中,一个八音度被分为12个频率比相等的半音程(semitone)。因为12个半音程构成了二倍的八音度频率范围,所以一个半音程的频率倍数为
。 该数值在本节将会频繁出现,可以令
sigma = 2^(1/12)琴键
钢琴键盘有两个八度音,白键标为 CDEFGAB,加上下一个C键。如果白键和黑键都计算的话,每一个八度音有12个键。每个键的频率比相邻的键高或低半音程。每一个黑键可以理解成上一个白键的升音(sharp,记为#),或下一个白键的降音(flat,b)
function pianoex(a) % PIANOEX A simple music synthesizer. % pianoex, with no arguments, presents a gui with 25 piano keys, % 13 toggles to form chords, 3 toggles to choose intonation, and % an oscilloscope and staff to display the generated notes and chords. % % pianoex(n) plays the n-th note above middle C. % pianoex(-n) plays the n-th note below middle C. % pianoex([n1 n2 ... ]) plays the chord specified by a vector. % % pianoex(score) plays the cell array score constructed like % the one in vivaldi.m. % % for n = [0 2 4 5 7 9 11 12] % pianoex(n) % end % plays the C-major scale. % % Requires sound card and, optionally, the Signal Processing Toolbox. if isempty(get(gca,'userdata')) make_keyboard end if nargin > 0 T = 5/8; H = get(gca,'userdata'); tv = get(H.voice,'value'); voice = find([tv{:}]==1); set(H.togs(1),'value',1,'background','blue') for k = 1:size(a,1) if iscell(a) if size(a(k,:),2)==2 [y,fs] = synthesize(a{k,1},a{k,2}*T,voice); else [y,fs] = synthesize(a{k,1},T,voice); end v = a{k,1}; else if isscalar(a) H.root = a; ch = get(H.togs,'value'); a = a + find([ch{:}]) - 1; end [y,fs] = synthesize(a,T,voice); v = a; end sound(y,fs); for j = 1:25 set(H.keys(j),'background',get(H.keys(j),'userdata')) end set(H.keys(v(v<13)+13),'background','blue') j = round(get(H.scope,'xdata')*fs); set(H.scope,'ydata',y(j)) set(H.notes,'vis','off') set(H.sharps,'vis','off') delta = [0 0 1 1 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6]/2; for n = 1:length(v) y = 3.5*floor(v(n)/12)+delta(mod(v(n),12)+1); set(H.notes(n),'ydata',y,'vis','on') if any(mod(v(n),12) == [1 3 6 8 10]) set(H.sharps(n),'pos',[.25 y],'vis','on'); end end drawnow end set(gca,'userdata',H); end end % ------------------------------------ function [y,fs] = synthesize(chord,T,voice) % SYNTHESIZE Generate musical notes and cords. % synthesize(note,T,voice) Generates a note for T seconds with given tuning. % synthesize([note1, ..., noten],T,voice) Generates a chord of several notes. % Notes are integers specifying half tones above and below middle C. % voice = 1 for piano, 2 for just intonation, 3 for equal temperament. % Examples: % synthesize(0) generatees middle C (261.625 Hz) for 1/2 second. % synthesize(1) is C#. % synthesize(-1) is C-flat. % synthesize(12) is high C, one octave above middle C. % synthesize([0 4 7]) is the perfect fifth major triad C-E-G. % A scale with one second per note: % for k = [0 2 4 5 7 9 11 12] % synthesize(k,1) % end switch voice case 1 % equal temperament sigma = 2^(1/12); C4 = 440*sigma^(-9); fs = 44100; t = 0:1/fs:T; y = zeros(size(t)); for n = chord hz = C4 * sigma^n; y = y + sin(2*pi*hz*t); end y = y/length(chord); case 2 % just intonation sigma = 2^(1/12); C4 = 440*sigma^(-9); fs = 44100; t = 0:1/fs:T; r = [1 16/15 9/8 6/5 5/4 4/3 7/5 3/2 8/5 5/3 7/4 15/8]; r = [r/2 r 2*r 4]; y = zeros(size(t)); for n = chord hz = C4 * r(n+13); y = y + sin(2*pi*hz*t); end y = y/length(chord); case 3 % piano middle_c = get(gcf,'userdata'); fs = 44100; t = 0:1/fs:T; y = zeros(size(t)); for n = chord y = y + resamplex(middle_c,2^(n/12),length(y)); end end end % ------------------------------------ function y = resamplex(y,factor,L) % RESAMPLE % Requires Signal Processing Toolbox [p,q] = rat(factor,1.e-4); y = resample(y,q,p)'; L = floor(L); if L < length(y) y = y(1:L); else y(L) = 0; end r = 150:-1:0; y(L-r:L) = y(L-r:L).*r/150; end % ------------------------------------ function make_keyboard % MAKE_KEYBOARD Create a piano keyboard. clf white = [-12:2:-8 -7:2:-1 0:2:4 5:2:11 12]; black = setdiff(-11:11,white); dx = 1/16; H.keys = zeros(1,25); for k = [white black] if k == -12 % White bw = [1 1 1]; x = dx/2; y = .08; dy = .40; elseif k == -11 % Black bw = [0 0 0]; x = dx; y = .23; dy = .25; end callback = ['pianoex(' int2str(k) '), set(gcbo,''value'',0)']; H.keys(k+13) = uicontrol('units','normal','position',[x y dx dy], ... 'style','toggle','background',bw,'userdata',bw,'callback',callback); x = x + dx; if k == -9 || k == -2 || k == 3 x = x + dx; end end % Key Labels y = .02; dy = .05; s = 'C'; grayc = get(gcf,'color'); for x = dx/2:dx:1-dx uicontrol('units','normal','position',[x y dx dy],'background',grayc, ... 'style','text','string',s,'fontsize',14,'fontweight','bold') s = char(s+1); if s > 'G', s = 'A'; end end % Clefs axes('position',[.03 .65 .07 .3]) C = load('clefs.mat'); image(C.clefs_pic) colormap(gray) axis off % Staff axes('position',[.1 .65 .1 .3],'xticklabel','','yticklabel','', ... 'xlim',[0 1],'ylim',[-7 7]); box on for y = [-5:-1 1:5] line([0 1],[y y],'color','black') end line([.33 .67],[0 0],'color','black') % Notes H.notes = zeros(13,1); H.sharps = zeros(13,1); for n = 1:13 H.notes(n) = line(.5,0,'marker','.','markersize',24,'vis','off'); H.sharps(n) = text(.375,0,'#','fontsize',12,'color','blue','vis','off'); end % Chord toggles H.togs = zeros(1,13); callback = ['if get(gcbo,''value'')==0,' ... 'set(gcbo,''background'',[.94 .94 .94]),' ... 'else, set(gcbo,''background'',''blue''), end,' ... 'H=get(gca,''userdata''); pianoex(H.root)']; for k = 0:12 H.togs(k+1) = uicontrol('style','toggle','units','normal', ... 'pos',[.05+k*.05 .54 .04 .04],'value',k==0,'background',grayc, ... 'callback',callback); uicontrol('style','text','units','normal','string',num2str(k), ... 'fontsize',12,'fontweight','bold','pos',[.04+k*.05 .49 .05 .05], ... 'background',grayc) end set(H.togs(1),'value',1,'background','blue') % Tuning H.voice = zeros(1,3); voicestring = {'equal','just','piano'}; callback = ['H=get(gca,''userdata'');' ... 'set(H.voice,''background'',[.94 .94 .94],''value'',0),' ... 'set(gcbo,''background'',''blue'',''value'',1),' ... 'pianoex(H.root)']; % Do not show piano if Signal Processing Toolbox is not available. kmax = 2 + (exist('resample','file')==2); for k = 1:kmax H.voice(k) = uicontrol('style','toggle','units','normal', ... 'pos',[1.00-k*.08 .54 .04 .04],'value',0,'background',grayc, ... 'callback',callback); uicontrol('style','text','units','normal','string',voicestring{k}, ... 'fontsize',12,'fontweight','bold', ... 'pos',[.98-k*.08 .49 .08 .05],'background',grayc) end set(H.voice(1),'value',1,'background','blue'); % Scope tmin = .06; tmax = .12; s = tmin:4/44100:tmax; axes('position',[.30 .65 .65 .30],'xlim',[tmin tmax],'ylim',[-1 1]) H.scope = line(s,0*s); box on set(zoom,'motion','horizontal','direction','in','enable','on') % Piano sample S = load('piano_c.mat'); middle_c = double(S.piano_c)/2^15; H.root = 0; set(gca,'userdata',H) set(gcf,'userdata',middle_c) shg end
在微型键盘上用for循环演奏出两个八音度的25个琴键半音音阶。
for n= -12:12, pianoex(n), end哆来咪
对于![]() 来说,C大调音阶为
来说,C大调音阶为![]() 。
。
在微型键盘上演奏:
for n =[0 2 4 5 7 9 11 12], pianoex(n), end
计算出音符间半音程个数:
diff([0 2 5 7 9 11 12])
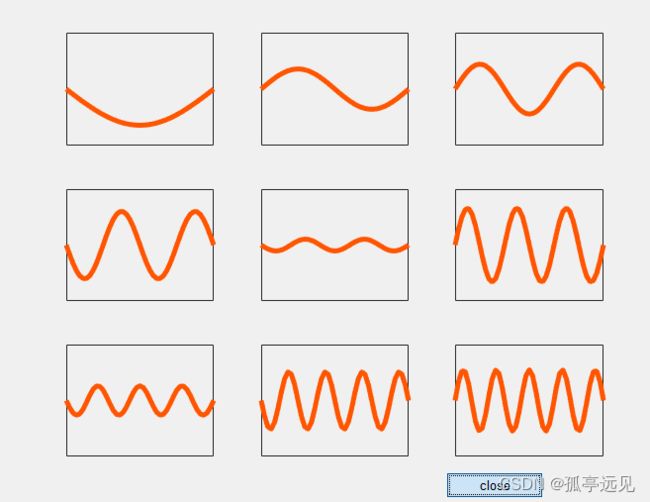
振动与调式
振动的模型可以称为由一些称为调式或特征函数的加权和来表示。不同的调式在不同的特征频率或特征值下振动。
依赖于时间的模态振动为:
![]()
function vibrating_string
% VIBRATING_STRING Wave equation in one dimension.
% Solutions of the one-dimensional wave equation are expressed
% as a time-varying weighted sums of the first nine modes.
% The one-dimensional domain is an interval of length pi, so the k-th
% frequency and mode are lambda(k) = k^2 and u(k) = sin(k*x).
m = 11; % Number of grid points
speed = 1;
bvals = [0; 0; 0; 0];
t = 0;
while bvals(4) == 0
% Initialize figure
shg
clf
set(gcf,'colormap',hot(64))
b = zeros(1,4);
for k = 1:4
b(k) = uicontrol('style','toggle','value',bvals(k), ...
'units','normal','position',[.08+.15*k .03 .14 .05]);
end
set(b(1),'string','modes/wave')
set(b(2),'string','slower')
set(b(3),'string','faster')
set(b(4),'string','stop')
if bvals(2)==1
speed = speed/sqrt(2);
set(b(2),'value',0);
end
if bvals(3)==1
speed = speed*sqrt(2);
set(b(3),'value',0);
end
bvals = cell2mat(get(b,'value'));
modes = bvals(1)==0;
x = (0:4*m)/(4*m)*pi;
orange = [1 1/3 0];
gray = get(gcf,'color');
if modes
% Modes
for k = 1:9
subplot(3,3,k)
h(k) = plot(x,zeros(size(x)));
axis([0 pi -3/2 3/2])
set(h(k),'color',orange,'linewidth',3)
set(gca,'color',gray','xtick',[],'ytick',[])
end
delta = 0.005*speed;
bvs = bvals;
while all(bvs == bvals)
t = t + delta;
for k = 1:9
u = sin(k*t)*sin(k*x);
set(h(k),'ydata',u)
end
drawnow
bvs = cell2mat(get(b,'value'));
end
else
% Wave
% The coefficients.
a = 1./(1:9);
h = plot(x,zeros(size(x)));
axis([0 pi -9/4 9/4])
set(h,'color',orange,'linewidth',3)
set(gca,'color',gray','xtick',[],'ytick',[])
delta = 0.005*speed;
bvs = bvals;
while all(bvs == bvals)
t = t + delta;
u = zeros(size(x));
for k = 1:9
u = u + a(k)*sin(k*t)*sin(k*x);
end
set(h,'ydata',u)
drawnow
bvs = cell2mat(get(b,'value'));
end
end
bvals = bvs;
end
set(b(1:3),'vis','off')
set(b(4),'string','close','callback','close(gcf)')
利萨如曲线
利萨如曲线给出了音乐和弦数学描述的一些内在内容。
二维利萨如曲线是由下面的参数方程绘制的:
![]()
三维利萨如曲线由以下参数方程绘制:
![]()
绘图命令可简化如下:
![]()
function lissajous(a,b)
% LISSAJOUS 2D and 3D Lissajous curves.
% x = sin(t), y = sin(a*t) or
% x = sin(t), y = sin(a*t), z = sin(b*t).
% Usage:
% lissajous(a,b)
% lissajous('a','b'), to retain symbolic representation.
% lissajous, to open gui with default values.
% Enter rational and irrational values of a and b in the edit boxes.
% Enter b = 0 for 2D curves.
% eg:
% a = 3/2 , b = 5/4
% a = 2^(7/12), b = 2^(4/12)
% a = 5/4 , b = 0
%
% See Wikipedia article: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lissajous_curve
% Default value of the parameters.
if nargin == 0
a = '3/2';
b = '5/4';
elseif nargin == 1
b = 0;
end
% Retain both character and numeric representation of the parameters.
if ischar(a)
sa = a;
a = str2num(a);
else
sa = rats(a);
end
if ischar(b)
sb = b;
b = str2num(b);
else
sb = rats(b);
end
% Initialize
loop = true;
t = 0;
dt = pi/1024;
initialize_graphics;
% Run the loop until the 'X' toggle is pushed.
while loop
t = t + dt;
x = sin(t);
y = sin(a*t);
z = sin(b*t);
plotdot(x,y,z)
end
close
% ------------------------------------------------
function initialize_graphics
clf
shg
set(gcf,'color','white')
initialize_plot
uicontrol('string','a = ','style','edit','units','normalized', ...
'position',[.25,.05,.05,.05],'background','white')
uicontrol('tag','a','style','edit','units','normalized', ...
'position',[.30,.05,.20,.05],'background','white', ...
'string',sa,'callback',@abcallback);
uicontrol('string','b = ','style','edit','units','normalized', ...
'position',[.55,.05,.05,.05],'background','white')
uicontrol('tag','b','style','edit','units','normalized', ...
'position',[.60,.05,.20,.05],'background','white', ...
'string',sb,'callback',@abcallback);
uicontrol('string','line','style','toggle','units','normalized', ...
'tag','mode','position',[.06,.48,.05,.05],'background','white', ...
'foreground','blue','callback',@modecallback);
uicontrol('string','X','style','toggle','units','normalized', ...
'position',[.95,.95,.04,.04],'background','white', ...
'callback',@xcallback);
end
% ------------------------------------------------
function initialize_plot
mode = get(findobj('tag','mode'),'value');
if isempty(mode) || mode==0
plot3(0,0,0,'.','erasemode','none')
else
plot3(0,0,0,'.','markersize',24,'color',[0 2/3 0])
end
axis([-1 1 -1 1 -1 1])
set(gca,'xtick',[],'ytick',[],'ztick',[])
axis square
box on
switch b
case 0
view(2)
title('sin(t), sin(a*t)')
case 1
view(3)
title('sin(t), sin(a*t), sin(b*t)')
end
t = 0;
end
% ------------------------------------------------
function plotdot(x,y,z)
% Move dot on plot.
set(get(gca,'child'),'xdata',x,'ydata',y,'zdata',z)
drawnow
end
% ------------------------------------------------
function abcallback(h,~)
% Callback for ab controls.
switch get(h,'tag')
case 'a', a = str2num(get(h,'string'));
case 'b', b = str2num(get(h,'string'));
end
initialize_plot
end
% ------------------------------------------------
function modecallback(h,~)
% Callback for mode control.
switch get(h,'value')
case 0, set(h,'string','line','foreground','blue')
dt = dt/4; % Slower
case 1, set(h,'string','dot','foreground',[0 2/3 0])
dt = 4*dt; % Faster
end
initialize_plot
end
% ------------------------------------------------
function xcallback(~,~)
% Callback for X control.
loop = false;
end
end % Lissajous
和声与音调与和弦
平均乐律和纯律。平均乐律由反复求![]() 的幂次定义,纯律是由一系列分数定义的。
的幂次定义,纯律是由一系列分数定义的。
%% Equal temperament and just intonation
[sigma.^(0:12)
1 16/15 9/8 6/5 5/4 4/3 7/5 3/2 8/5 5/3 7/4 15/8 2]' 和弦是两个或两个以上的音符同时发声的演奏方式。在pianoex程序界面上可以选中1到12的双态开关来产生和弦,标注为0的开关总处于选中的状态。
%% C major fifth chord, equal temperament and just temperament
[sigma.^[0 4 7]
1 5/4 3/2]'