Mysql 常用统计语句
Mysql 常用统计语句
| SQL分类 首先,简要介绍基础语句: 1、创建数据库 CREATE DATABASE test; 2、删除数据库 Drop database test; 3、备份sql server — 创建 备份数据的 device USE master EXEC sp_addumpdevice ’disk’, ’testBack’, ’c:\mssql7backup\MyNwind_1.dat’ — 开始 备份 BACKUP DATABASE pubs TO testBack 4、创建新表 create table tabname (col1 type1 [not null] [primary key],col2 type2 [not null],…) 根据已有的表创建新表: A:create table tab_new like tab_old (使用旧表创建新表) B:create table tab_new as select col1,col2… from tab_old definition only 5、删除新表:drop table tabname 6、增加一个列:Alter table tabname add column col type 注:列增加后将不能删除。DB2中列加上后数据类型也不能改变,唯一能改变的是增加varchar类型的长度。 7、 添加主键:Alter table tabname add primary key (col) 英[ˈpraɪ məri] 删除主键:Alter table tabname drop primary key (col) 8、 创建索引:create [unique] index idxname on tabname (col….) 删除索引:drop index idxname 注:索引是不可更改的,想更改必须删除重新建。 9、 创建视图:create view viewname as select statement 删除视图:drop view viewname 10、几个简单的基本的sql语句 选择:select * from table1 where 范围 插入:insert into table1 (field1,field2) values (value1,value2) 删除:delete from table1 where 范围 更新:update table1 set field1=value1 where 范围 查找:select * from table1 where field1 like ’%value1%’ —like的语法很精妙,查资料! 排序:select * from table1 order by field1,field2 [desc] 总数:select count * as totalcount from table1 求和:select sum(field1) as sumvalue from table1 平均:select avg(field1) as avgvalue from table1 最大:select max(field1) as maxvalue from table1 最小:select min(field1) as minvalue from table1 11、几个高级查询-运算词 A: UNION 运算符 UNION 运算符通过组合其他两个结果表(例如 TABLE1 和 TABLE2)并消去表中任何重复行而派生出一个结果表。 当 ALL 随 UNION 一起使用时(即 UNION ALL),不消除重复行。 两种情况下,派生表的每一行不是来自 TABLE1 就是来自 TABLE2。 B: EXCEPT 运算符 EXCEPT 运算符通过包括所有在 TABLE1 中但不在 TABLE2 中的行并消除所有重复行而派生出一个结果表。当 ALL 随 EXCEPT 一起使用时 (EXCEPT ALL),不消除重复行。 C: INTERSECT 运算符 INTERSECT 运算符通过只包括 TABLE1 和 TABLE2 中都有的行并消除所有重复行而派生出一个结果表。当 ALL 随 INTERSECT 一起使用时 (INTERSECT ALL),不消除重复行。 注:使用运算词的几个查询结果行必须是一致的。 12、使用外连接 A、left outer join: 左外连接(左连接):结果集几包括连接表的匹配行,也包括左连接表的所有行。 SQL: select a.a, a.b, a.c, b.c, b.d, b.f from a LEFT OUT JOIN b ON a.a = b.c B:right outer join: 右外连接(右连接):结果集既包括连接表的匹配连接行,也包括右连接表的所有行。 C:full outer join: 全外连接:不仅包括符号连接表的匹配行,还包括两个连接表中的所有记录。 其次,大家来看一些不错的sql语句 1、复制表(只复制结构,源表名:a 新表名:b) 法一:select * into b from a where 1<>1 法二:select top 0 * into b from a 2、拷贝表(拷贝数据,源表名:a 目标表名:b) insert into b(a, b, c) select d,e,f from b; 3、跨数据库之间表的拷贝 insert into b(a, b, c) select d,e,f from b in ‘具体数据库’ where 条件 例子:…from b in ’"&Server.MapPath(".")&"\data.mdb" &"’ where… 4、子查询(表名1:a 表名2:b) select a,b,c from a where a IN (select d from b ) 或者: select a,b,c from a where a IN (1,2,3) 5、显示文章、提交人和最后回复时间 select a.title,a.username,b.adddate from table a,(select max(adddate) adddate from table where table.title=a.title) b 6、外连接查询(表名1:a 表名2:b) select a.a, a.b, a.c, b.c, b.d, b.f from a LEFT OUT JOIN b ON a.a = b.c 7、在线视图查询(表名1:a ) select * from (SELECT a,b,c FROM a) T where t.a > 1; 8、between的用法,between限制查询数据范围时包括了边界值,not between不包括 select * from table1 where time between time1 and time2 select a,b,c, from table1 where a not between 数值1 and 数值2 9、in 的使用方法 select * from table1 where a [not] in (‘值1’,’值2’,’值4’,’值6’) 10、两张关联表,删除主表中已经在副表中没有的信息 delete from table1 where not exists ( select * from table2 where table1.field1=table2.field1 ) 11、四表联查问题: select * from a left inner join b on a.a=b.b right inner join c on a.a=c.c inner join d on a.a=d.d where … 12、日程安排提前五分钟提醒 select * from 日程安排 where datediff(’minute’,f开始时间,getdate())>5 13、一条sql 语句搞定数据库分页 select top 10 b.* from (select top 20 主键字段,排序字段 from 表名 order by 排序字段 desc) a,表名 b where b.主键字段 = a.主键字段 order by a.排序字段 14、前10条记录 select top 10 * form table1 where 范围 15、选择在每一组b值相同的数据中对应的a最大的记录的所有信息 (类似这样的用法可以用于论坛每月排行榜,每月热销产品分析,按科目成绩排名,等等.) select a,b,c from tablename ta where a=(select max(a) from tablename tb where tb.b=ta.b) 16、包括所有在 TableA 中但不在 TableB和TableC 中的行并消除所有重复行而派生出一个结果表 (select a from tableA ) except (select a from tableB) except (select a from tableC) 17、随机取出10条数据 select top 10 * from tablename order by newid() 18、随机选择记录 select newid() 19、删除重复记录 Delete from tablename where id not in (select max(id) from tablename group by col1,col2,…) 20、列出数据库里所有的表名 select name from sysobjects where type=’U’ 21、列出表里的所有的 select name from syscolumns where id=object_id(’TableName’) |
| Mysql 常用统计语句
select * from 表名 where to_days(时间字段名) = to_days(now());
SELECT * FROM 表名 WHERE TO_DAYS( NOW( ) ) - TO_DAYS( 时间字段名) <= 1 3、7天 SELECT * FROM 表名 where DATE_SUB(CURDATE(), INTERVAL 7 DAY) <= date(时间字段名) 4、近30天 SELECT * FROM 表名 where DATE_SUB(CURDATE(), INTERVAL 30 DAY) <= date(时间字段名) 5、本月 SELECT * FROM 表名 WHERE DATE_FORMAT( 时间字段名, '%Y%m' ) = DATE_FORMAT( CURDATE( ) , '%Y%m' ) 6、上一月 SELECT * FROM 表名 WHERE PERIOD_DIFF( date_format( now( ) , '%Y%m' ) , date_format( 时间字段名, '%Y%m' ) ) =1 7、查询本季度数据 select * from `ht_invoice_information` where QUARTER(create_date)=QUARTER(now()); 8、查询上季度数据 select * from `ht_invoice_information` where QUARTER(create_date)=QUARTER(DATE_SUB(now(),interval 1 QUARTER)); 9、查询本年数据 select * from `ht_invoice_information` where YEAR(create_date)=YEAR(NOW()); 10、查询上年数据 select * from `ht_invoice_information` where year(create_date)=year(date_sub(now(),interval 1 year)); |
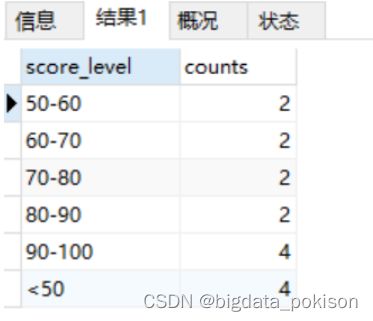
| 其他 一、使用SQL语句进行区间分组统计查询 (区间分组统计查询需要使用到 elt,interval) 案例1:根据学生的分数段统计各个分数段的学生总数 统计各个分数段的学生人数 比如:统计 <50, 50-60, 60-70, 70-80, 80-90, 90-100 的分数区间内的人数 利用interval划出6个区间,在利用elt函数将6个区间分别返回一个列名,SQL如下: select elt( interval(score,0,50,60,70,80,90), ‘<50’,‘50-60’,‘60-70’,‘70-80’,‘80-90’,‘90-100’ ) as score_level ,count(*) as counts from class group by elt( interval(score,0,50,60,70,80,90), ‘<50’,‘50-60’,‘60-70’,‘70-80’,‘80-90’,‘90-100’ ); |
参考链接:
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/promsing/article/details/112793260
原文链接:SQL常用语句(面试必备)_Sherry_wang168的博客-CSDN博客_面试常用sql语句
刷题:
牛客网 - 找工作神器|笔试题库|面试经验|实习招聘内推,求职就业一站解决_牛客网
题库 - 力扣 (LeetCode) 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台