一种简单的图形旋转算法
图形旋转好玩又有实用性, 这里介绍一种简单的图形旋转算法.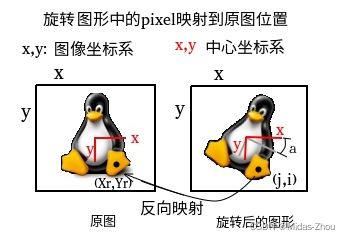
具体步骤如下:
1. 首先将原图和旋转图的坐标原点都变换到图形的中心位置处.
2. 历遍旋转图形中的每一个pixel, 将pixel的坐标(j,i)反向旋转映射到原图, 得到原图对应的坐标值(Xr,Yr).
3. 考虑到旋转图的尺寸可能大于原图,这时需要检测(Xr,Yr)是否在原图范围内,如果不是,则忽略下面步骤.
4. (Xr,Yr)通常并不是正好对应到原图中一个整点的像素, 而是会夹在四个像素中(如图), 对四个像素的位置进行插值计算(也即所谓的双线性插值), 可以得到对应位置的RGBA值.
5. 由于内存中的图形数据是以左上角为坐标原点逐行记录的, 我们需将(j,i)变换到此坐标系统下(步骤1的反向操作), 得到其对应的内存位置, 然后将RGBA数值存入此处.
6. 通过逐点计算,最终可以得到完整的旋转后的图形.
7. 待改进处: 这里由于对图形边缘点的采样不够密集,因此得到的旋转图形边缘会出现锯齿现象. 可以细化映射颗粒度,如以1/4像素为单位进行映射计算.
更普遍的情况是,我们需要对原图中的指定区域进行旋转操作, 即进行旋转抠图. 下面是这一算法的C语言实现:
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------
@eimg: 输入图像
@oimg: 输出图像(NULL忽略)
@height,width: 输出图像的尺寸
@px,py: 抠图相对原图的位置
@angle: 旋转角度
-------------------------------------------------------------------*/
EGI_IMGBUF* egi_imgbuf_rotBlockCopy2( EGI_IMGBUF *eimg, EGI_IMGBUF *oimg, int height, int width,
int px, int py, float angle)
{
int i,j;
float xr,yr;
int index_out;
EGI_IMGBUF *outimg=NULL;
float sina=sin(MATH_PI*angle/180);
float cosa=cos(MATH_PI*angle/180);
/* 1. Check input eimg */
if(eimg==NULL || eimg->imgbuf==NULL || eimg->height<=0 || eimg->width<=0 ) {
egi_dpstd("Input holding eimg is NULL or uninitiliazed!\n");
return NULL;
}
/* 2. Input oimg is NULL */
/* 注:这里将输出图像的长宽均设为奇数,这样中心点是个整点位置,便于计算. */
if(oimg==NULL) {
/* Make H/W an odd value, then it has a symmetrical center point. */
height |= 0x1;
width |= 0x1;
if(height<3)height=3;
if(width<3)width=3;
/* Create an imgbuf accordingly */
outimg=egi_imgbuf_create(height, width, 0, 0); /* H, W, alpah, color */
if(outimg==NULL) {
egi_dpstd("Fail to create outimg!\n");
return NULL;
}
/* Check ALPHA data */
if(eimg->alpha==NULL) {
free(outimg->alpha);
outimg->alpha=NULL;
}
}
/* Input oimg is NOT NULL */
else {
height=oimg->height;
width=oimg->width;
outimg=oimg;
}
/* 3. Clear outimg first. ALPHA to be 0, OR same as eimg. 如果是RGBA格式,可以在这里设置背景色. */
egi_imgbuf_resetColorAlpha(outimg, WEGI_COLOR_GRAY2, outimg->alpha==NULL ? -1:0 ); /* img, color, alpha */
/* 4. Map back point coordinates to eimg 以旋转图片中心为原点, 历遍旋转图形中的每一个像素点. 反向映射并插值计算得RGBA. */
int m=height>>1;
int n=width>>1;
for(i=-m; i<=m; i++) {
for(j=-n; j<=n; j++) {
/* 4.1 Map to original coordiante (xr,yr), Origin at center.
* 2D point rotation formula ( a positive: Right_hand Rule. ):
* x'=x*cos(a)-y*sin(a)
* y'=x*sin(a)+y*cos(a)
* Coord axis anti_clockwise, point colokwise rotate.
* points coordinates relative to up_right block coord.
* 旋转变换公式, 可以查数学手册.
*/
xr=cosa*j-sina*i;
yr=sina*j+cosa*i;
/* 4.2 Shift Origin to left_top, as of eimg->imgbuf 变换到原图坐标下 */
xr += px;
yr += py;
/* 4.3 Copy pixel alpha and color. Limit xr,yr, ignore if they are out of original imgbuf area. */
if( xr >= 0.0 && xr <= eimg->width-1 && yr >=0.0 && yr <= eimg->height-1) {
index_out=width*(i+m)+(j+n);
/* 4.3.1 的到相互邻的4个像数 */
int indx1 = eimg->width*floorf(yr)+floorf(xr);
int indx2 = eimg->width*floorf(yr)+ceilf(xr);
int indx3 = eimg->width*ceilf(yr)+floorf(xr);
int indx4 = eimg->width*ceilf(yr)+ceilf(xr);
EGI_16BIT_COLOR pcolor;
EGI_8BIT_ALPHA palpha;
float pft;
/* 4.3.2 Interpolate within 4 pixles 4点插值得到RGBA */
if(eimg->alpha!=NULL && outimg->alpha!=NULL) {
egi_16bitColor_interplt4p(eimg->imgbuf[indx1], eimg->imgbuf[indx2], /* color1, color2 */
eimg->imgbuf[indx3], eimg->imgbuf[indx4], /* color3, color4 */
eimg->alpha[indx1], eimg->alpha[indx2], /* alpha1, alpha2 */
eimg->alpha[indx3], eimg->alpha[indx4], /* alpha3, alpah4 */
modff(xr,&pft)*(1<<15), modff(yr, &pft)*(1<<15), /* f15_x, f15_y */
&pcolor, &palpha );
outimg->imgbuf[index_out]=pcolor;
outimg->alpha[index_out]=palpha;
}
else {
egi_16bitColor_interplt4p(eimg->imgbuf[indx1], eimg->imgbuf[indx2], /* color1, color2 */
eimg->imgbuf[indx3], eimg->imgbuf[indx4], /* color3, color4 */
0, 0, 0, 0, /* alpha1, alpha2, alpha3, alpha4 */
modff(xr,&pft)*(1<<15), modff(yr, &pft)*(1<<15), /* f15_x, f15_y */
&pcolor, NULL );
outimg->imgbuf[index_out]=pcolor;
}
}
}
}
return outimg;
}(更多代码见 https://github.com/widora/wegi)
效果:



