VLE基于预训练文本和图像编码器的图像-文本多模态理解模型:支持视觉问答、图文匹配、图片分类、常识推理等
![]()
项目设计集合(人工智能方向):助力新人快速实战掌握技能、自主完成项目设计升级,提升自身的硬实力(不仅限NLP、知识图谱、计算机视觉等领域):汇总有意义的项目设计集合,助力新人快速实战掌握技能,助力用户更好利用 CSDN 平台,自主完成项目设计升级,提升自身的硬实力。
![]()
-
专栏订阅:项目大全提升自身的硬实力
-
[专栏详细介绍:项目设计集合(人工智能方向):助力新人快速实战掌握技能、自主完成项目设计升级,提升自身的硬实力(不仅限NLP、知识图谱、计算机视觉等领域)
VLE基于预训练文本和图像编码器的图像-文本多模态理解模型:支持视觉问答、图文匹配、图片分类、常识推理等
多模态预训练模型通过在多种模态的大规模数据上的预训练,可以综合利用来自不同模态的信息,执行各种跨模态任务。在本项目中,我们推出了VLE (Vision-Language Encoder),一种基于预训练文本和图像编码器的图像-文本多模态理解模型,可应用于如视觉问答、图像-文本检索等多模态判别任务。特别地,在对语言理解和推理能力有更强要求的视觉常识推理(VCR)任务中,VLE取得了公开模型中的最佳效果。
最近,大型语言模型(LLM)取得了巨大成功,并被用于翻译、问答、摘要等文本任务。虽然LLM是单模态模型,但它们的能力也可用于辅助多模态理解任务。借助LLM的zero-shot能力,我们设计了一种VQA+LLM方案,将大型语言模型集成到视觉问答任务中,实现了帮助视觉问答模型生成更准确和流畅的答案。
开源VLE相关资源以供学术研究参考。
在线演示地址:https://huggingface.co/spaces/hfl/VQA_VLE_LLM
中文LERT | 中英文PERT | 中文MacBERT | 中文MiniRBT | 中文ELECTRA | 中文XLNet | 中文BERT | 知识蒸馏工具TextBrewer | 模型裁剪工具TextPruner
查看更多哈工大讯飞联合实验室(HFL)发布的资源:https://github.com/iflytek/HFL-Anthology
1.模型结构
VLE模型采用双流结构,与METER模型结构类似,由两个单模态编码器(图像编码器和文本编码器)和一个跨模态融合模块构成。VLE与METER的结构上的差异在于:
- VLE使用DeBERTa-v3作为文本编码器,其性能优于METER中使用的RoBERTa-base。
- 在VLE-large中,跨模态融合模块的隐层维度增加至1024,以增加模型的容量。
- 在精调阶段,VLE引入了额外的token类型向量表示。
2.预训练
VLE使用图文对数据进行预训练。在预训练阶段,VLE采用了四个预训练任务:
- MLM (Masked Language Modeling):掩码预测任务。给定图文对,随机遮掩文本中的部分单词,训练模型还原遮掩的文本。
- ITM (Image-Text Matching):图文匹配预测任务。给定图文对,训练模型判断图像和文本是否匹配。
- MPC (Masked Patch-box Classification):遮掩Patch分类任务,给定图文对,并遮掩掉图片中包含具体对象的patch,训练模型预测被遮掩的对象种类。
- PBC (Patch-box classification):Patch分类任务。给定图文对,预测图片中的哪些patch与文本描述相关。
VLE在14M的英文图文对数据上进行了25000步的预训练,batch大小为2048。下图展示了VLE的模型结构和部分预训练任务(MLM、ITM和MPC)。
3.下游任务适配
3.1视觉问答 (VQA)
- 我们遵循标准做法,使用VQA的训练集(training set)和验证集(validation set)训练模型,在test-dev集上进行验证。我们采用模型的融合层的pooler的输出进行分类任务的训练。
3.2 视觉常识推理 (VCR)
- 我们将VCR格式化为一个类似于RACE的选择题任务,并对于每张图像中的对象,将覆盖该对象的patch的表示的平均池化值添加到融合模块之前的图像特征序列中。我们还为图像和文本中的对象添加额外的token_type_ids,以注入不同模态之间的对齐信息,提升模型的对齐性能。
3.3 模型下载
本次发布了VLE-base和VLE-large两个版本的预训练模型,模型权重为PyTorch格式,可以选择手动从 transformers模型库下载权重和配置文件,或者在代码中使用 from_pretrained(model_name) 以自动加载模型。详细方法参加模型使用。
3.4 预训练权重
| 模型 | 文本编码器 | 图像编码器 | 参数量* | MODEL_NAME | 链接 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VLE-base | DeBERTa-v3-base | CLIP-ViT-base-patch16 | 378M | hfl/vle-base | link |
| VLE-large | DeBERTa-v3-large | CLIP-ViT-large-patch14 | 930M | hfl/vle-large | link |
* : 仅计算encoder和emebddings的参数。特定任务的预测层的参数量未计入。
3.5 精调权重
| 模型 | 文本编码器 | 图像编码器 | MODEL_NAME | 链接 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VLE-base-for-VQA | DeBERTa-v3-base | CLIP-ViT-base-patch16 | hfl/vle-base-for-vqa | link |
| VLE-large-for-VQA | DeBERTa-v3-large | CLIP-ViT-large-patch14 | hfl/vle-large-for-vqa | link |
| VLE-base-for-VCR-q2a | DeBERTa-v3-base | CLIP-ViT-base-patch16 | hfl/vle-base-for-vcr-q2a | link |
| VLE-large-for-VCR-q2a | DeBERTa-v3-large | CLIP-ViT-large-patch14 | hfl/vle-large-for-vcr-q2a | link |
| VLE-base-for-VCR-qa2r | DeBERTa-v3-base | CLIP-ViT-base-patch16 | hfl/vle-base-for-vcr-qa2r | link |
| VLE-large-for-VCR-qa2r | DeBERTa-v3-large | CLIP-ViT-large-patch14 | hfl/vle-large-for-vcr-qa2r | link |
3.6 模型对比
在下表中,我们比较了VLE、METER以及其他多模态模型的参数量、预训练数据和下游任务效果。其中VQA展示的的是test-dev集上的效果;VCR展示的是dev集上的效果。
| 模型 | VQA | VCR (QA2R) | VCR (Q2A) | 参数量 | 预训练数据量* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoCa | 82.3 | - | - | 2.1 B | 未知 |
| BeiT-3 | 84.2 | - | - | 1.9 B | 21M(I-T) + 14M(I) + 160G(T) |
| OFA | 82.0 | - | - | 930M | 20M(I-T) + 39M(I) + 140G(T) |
| BLIP | 78.3 | - | - | 385M | ~130M(I-T) |
| METER-base | 77.7 (76.8†‡) | 79.8§ | 77.6§ | 345M | 9M(I-T) |
| METER-Huge | 80.3 | - | - | 878M | 20M(I-T) |
| VLE-base | 77.6‡ | 83.7§ | 79.9§ | 378M | 15M(I-T) |
| VLE-large | 79.3‡ | 87.5§ | 84.3§ | 930M | 15M(I-T) |
† : 复现效果
‡ : 精调参数: lr=7e-6, batch_size={256, 512}, num_epochs=10
§ : 精调参数: lr=1e-5, batch_size=128, num_epochs=5
* : I-T: 图文对. I: 图像. T: 文本.
观察上表可以发现:
- VLE的预训练更高效:与大小相近的模型相比,VLE使用了更少的预训练数据,并在视觉问答上取得了相当甚至更好的效果。
- VLE有更强的推理能力: 特别地,在对推理能力要求更高的视觉常识推理(VCR)任务上,VLE显著地超过了具有相似结构的METER。
4.结合大模型的视觉问答
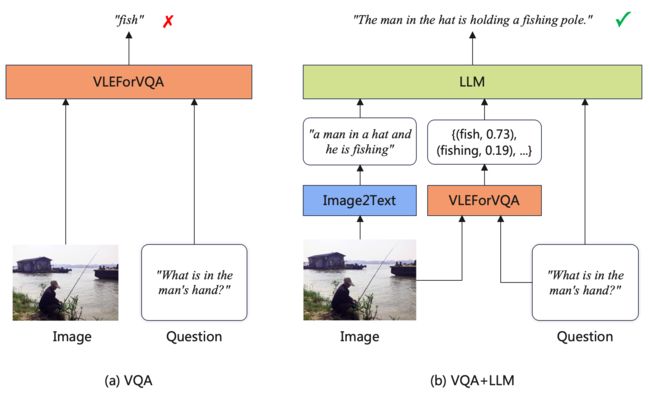
最近,随着指令微调、RLHF等技术的发展,LLM在多种文本任务中取得了巨大的成功。尽管LLM是单模态模型,但它们的能力也可用于辅助多模态理解任务。具体而言,我们提出一种VQA + LLM方案,将多模态模型与LLM集成到视觉问答任务中,从而帮助VQA模型生成更准确和流畅的答案。下图展示了系统流程。
(a) VQA: 这是使用判别模型执行VQA任务的标准方式。输入问题和图像到多模态模型中,训练模型预测正确的答案标签。
(b) VQA + LLM: 首先利用captioning模型生成图片的描述;将图片描述、问题以及VQA模型的详细预测结果拼接,组合成合适的prompt的形式送入LLM,最后要求LLM模型回复最合理的答案。
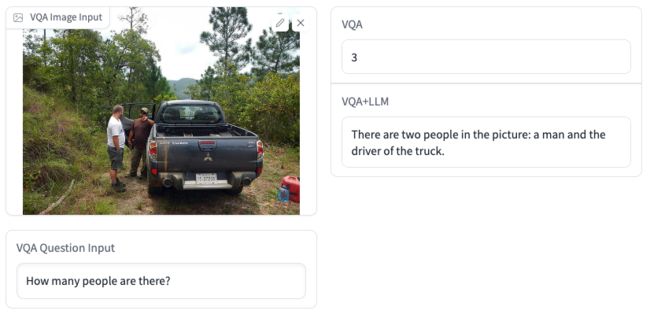
VQA+LLM生成的答案更准确,也有更高的可读性。下面是一些例子:
Demo地址(仅供学术研究):https://huggingface.co/spaces/hfl/VQA_VLE_LLM
4.1 模型使用
环境要求
- PIL
- Transformers >= 4.25
- PyTorch Lightning (仅用于运行精调脚本)
模型相关代码位于models/VLE目录下的*py文件中。因此,要使用VLE模型,仅需把models目录复制到你的项目代码目录即可。
要运行以下演示代码,请使用git clone命令下载本仓库至本地,并进入仓库的根目录。
4.2 加载VLEModel
from models.VLE import VLEModel, VLEProcessor
from PIL import Image
import torch
model_name="hfl/vle-large"
images = [Image.open('pics/dogs.png')]
text = ["There are dogs on the grass."]
model = VLEModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
vle_processor = VLEProcessor.from_pretrained(model_name)
multimodal_inputs = vle_processor(text=text,images=images, return_tensors='pt',padding=True)
#forward
vle_output = model(**multimodal_inputs)
5.推理
5.1 视觉问答 (VQA)
from models.VLE import VLEForVQA, VLEProcessor, VLEForVQAPipeline
from PIL import Image
model_name="hfl/vle-base-for-vqa"
text= "What is the color of the floor?"
image = Image.open("pics/door.png")
model = VLEForVQA.from_pretrained(model_name)
vle_processor = VLEProcessor.from_pretrained(model_name)
vqa_pipeline = VLEForVQAPipeline(model=model, device='cpu', vle_processor=vle_processor)
vqa_answers = vqa_pipeline(image=image, question=text, top_k=5)
print(f"Question: {text}. Answers: {vqa_answers}")
5.2 图文匹配(ITM)
from models.VLE import VLEForITM, VLEProcessor, VLEForITMPipeline
from PIL import Image
model_dir = 'hfl/vle-base'
itm_text = ["a photo of a cat.", "a photo of dogs."]
itm_images = Image.open("pics/dogs.png")
print("Init ITM model")
model = VLEForITM.from_pretrained(model_dir)
vle_processor = VLEProcessor.from_pretrained(model_dir)
print("init ITM pipeline")
itm_pipeline = VLEForITMPipeline(model=model, device='cpu', vle_processor=vle_processor)
itm_pred = itm_pipeline([{"image": itm_images, "text": itm_text[0]},
{"image": itm_images, "text": itm_text[1]}])
for t, pred in zip(itm_text,itm_pred):
print(t,pred)
5.3 Patch分类(PBC)
from models.VLE import VLEForPBC, VLEProcessor, VLEForPBCPipeline
from PIL import Image
model_dir = 'hfl/vle-base'
pbc_text = "pink tongues"
pbc_image = Image.open("pics/dogs.png")
print("Init PBC model")
model = VLEForPBC.from_pretrained(model_dir)
vle_processor = VLEProcessor.from_pretrained(model_dir)
print("init PBC pipeline")
pbc_pipeline = VLEForPBCPipeline(model=model, device='cpu', vle_processor=vle_processor)
pbc_pred = pbc_pipeline(image=pbc_image,text=pbc_text)
print(pbc_text)
pbc_pred['image'].save('pics/pink_tongues.png')