NOIP2012 疫情控制
也许更好的阅读体验
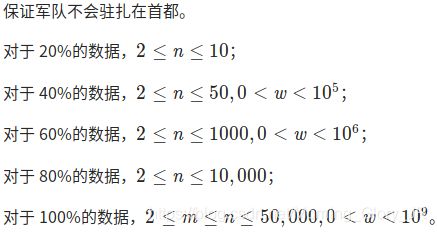
D e s c r i p t i o n \mathcal{Description} Description
原题链接

一句话题意
一个人可以堵住一个子树,不能一次堵住整棵树,求堵住每个通往叶子节点的路径,走的最远的那个人走的路程最少是多少,若不能堵住输出 − 1 -1 −1
S o l u t i o n \mathcal{Solution} Solution
看了下其他题解,都说很毒瘤
最开始我也认为很毒瘤
就是在决定一个点是否要跨过根这个地方比较麻烦
但是在码的途中,突然想到一个无脑的方法
于是写起来就很愉快了
最…最…,显然二分路程是多少
再继续想之前,先看一下我们 c h e c k check check函数要求在什么复杂度决定
n ≤ 50000 n\leq 50000 n≤50000,可以 n l o g 2 n nlog^2n nlog2n解决,也就是说 c h e c k check check的复杂度只要小于 n l o g n nlogn nlogn即可
一个人在二分到的路程内,尽量往上走是最优的
若一个人可以到达根节点,那么就要考虑其跨过这个根节点去堵其它子树
显然,若跨过根节点,那么走到根节点下面的那个节点就可以了
对于一个可以跨过根节点的人,他可能不要跨过根节点,也可能要跨过根节点
也可能一个子树里的人跨过根节点去堵其他子树,另外的一个子树的人跨过根节点来堵他的子树,这是因为原来这个子树的人比较靠近根节点,跨过根节点后走的较远,而他所在子树与根节点的路径又比较短
想想好像有点麻烦,想到这顿时觉得这题很毒瘤
但其实,我们不用想那么多
我们把所有能跨过根节点的人都走到根节点
将其还允许走的路程全部记下来
把所有需要人去堵的子树找出来,记下其与根节点的距离
显然,能走得最远的人去堵距离根节点最远的子树是最优的
也就是说要从大到小排序,这个过程我们用一个大根堆维护即可
对于一个到子树的距离,我们记下其子树的编号,对于每棵子树,我们记下其内可以跨过根节点的人中,还允许走的路程最少的路程是多少
再考虑一个人可能不要跨过根节点,我们在弹大根堆时,若发现这棵子树可以用比当前允许走的路程最大的人更小的人替代,那么那个人就不需要跨过根节点了
由于那个人仍然在大根堆内,我们把其记在一个队列里,表示有哪些路程被提前用了
这样就是最优的
仍有不懂请看代码,我觉得还是很无脑的,毕竟什么特殊的操作都没有,代码应该一下就看懂了
C o d e \mathcal{Code} Code
/*******************************
Author:Morning_Glory
LANG:C++
Created Time:2019年10月22日 星期二 20时50分59秒
*******************************/
#include 如有哪里讲得不是很明白或是有错误,欢迎指正