数字IC笔面基础,三大核心代码架构之计数器(计数器设计要素及Verilog示例)
计数器设计要素及Verilog示例
- 写在前面的话
- 计数器设计要素
- 计数器设计示例
-
- 加法计数器
- 减法计数器
- 带使能标志计数器
- 格雷码计数器
- 环形计数器
- Johnson计数器
- Ripple计数器(低功耗计数器的一种)
- BCD计数器
- 总结
写在前面的话
计数器设计是数字IC设计的核心,也是最常用的代码片段,通过记录时钟周期个数,可以控制电路的时序。通过计数器可以实现测量、计数、状态控制以及分频等功能,计数器由触发器和逻辑门共同构成。在《手把手教你学FPGA设计——基于大道至简的至简设计法》书中,将模块划分为三大架构,分别是FIFO架构、状态机架构以及计数器架构。从我个人理解,计数器和状态机分别对应了数字电路中的时序以及计算流程,而FIFO架构则是对应两个计算模块之间的连接关系以及对应的数据流。
下图摘自《手把手教你学FPGA设计——基于大道至简的至简设计法》,三大架构:
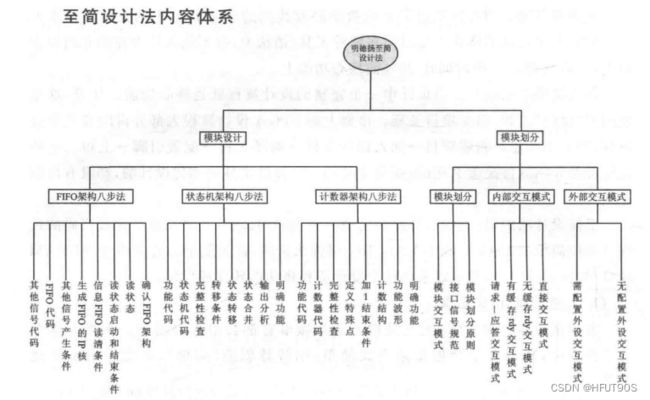
注意:
我们可能不会具体设计某一种计数器,但是在每个设计中都能找到计数器的影子。关键的是理解不同计数器的特点,并在项目中使用他们,同时计数器也是笔面中常考的一个关键知识点。
计数器设计要素
要素1: 初始值是多少?
这里要考虑的是复位信号和其他标志信号,一般复位信号计数器清零,其他标志信号看具体情况。
要素2: 结束值是多少?
结束值同样重要,默认在计数满的时候自动清零,而在某些情况,为避免清零后重新计数,也可以强制要求计数值保持在量程外,避开判断的组合模块。
要素3: 往哪个方向计数?
和初始值、结束值对应的则是往哪个方向计数,是采用加法计数还是减法计数?在同一个设计里面,计数的方向要保持统一。
要素4: 计数步长是多少?
除了计数方向,还要考虑的是每次计数步长,默认步长就为1。
要素5: 计数条件是什么?
默认的计数条件就是时钟跳变沿,除此之外还有使能信号、标志信号以及计数条件是否有优先级?
合理使用上述要素,可以简化计数器的使用,例如,在需要多个量程的计数模块,而各个计数模块又不会同时工作时,可以统一采用一个大量程的计数器,通过合理的设置要素,减少资源的消耗。
计数器设计示例
加法计数器
一个指令周期或外部脉冲时将计数器内容加1。
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Copyright (c) 2014-2022 All rights reserved
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Author : HFUT904 [email protected]
// File : up_counter.v
// Create : 2022-11-02 13:53:52
// Revise : 2022-11-02 13:53:52
// Editor : HFUT Integrated Circuit Design & Research Center
// Verdion: v1.0
// Description: 8bit 加法计数器
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
module up_counter (
input clk , // Clock
input rst_n , // Asynchronous low level reset
output reg [7:0] cnt // Count value
);
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
cnt <= 8'd0;
end
else begin
cnt <= cnt +8'd1 ;
end
end
endmodule
减法计数器
一个指令周期或外部脉冲时将计数器内容减1。
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Copyright (c) 2014-2022 All rights reserved
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Author : HFUT904 [email protected]
// File : down_counter.v
// Create : 2022-11-02 14:00:39
// Revise : 2022-11-02 14:00:39
// Editor : HFUT Integrated Circuit Design & Research Center
// Verdion: v1.0
// Description: 8bit 减法计数器
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
module down_counter (
input clk , // Clock
input rst_n , // Asynchronous reset active low
output reg [7:0] cnt // Count value
);
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
cnt <= 8'hff;
end
else begin
cnt <= cnt - 8'd1;
end
end
endmodule
带使能标志计数器
使能信号有效时计数。
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Copyright (c) 2014-2022 All rights reserved
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Author : HFUT904 [email protected]
// File : ena_counter.v
// Create : 2022-11-02 14:23:48
// Revise : 2022-11-02 14:23:48
// Editor : HFUT Integrated Circuit Design & Research Center
// Verdion: v1.0
// Description: 8bit 计数器 带使能信号
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
module ena_counter (
input clk , // Clock
input rst_n , // Asynchronous reset active low
input ena , // Enable signal active high
output reg [7:0 ] cnt //Count value
);
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin : proc_
if(~rst_n) begin
cnt <= 8'd0;
end
else if (ena == 1'b1) begin //使能信号有效 计数
cnt <= cnt +8'd1 ;
end
else begin
cnt <= cnt ; // cnt <= 8'd0 ; //保持上次计数值或清零
end
end
endmodule
格雷码计数器
格雷码计数器是为了在异步时钟域之间传递计数结果而用到的计数器。
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Copyright (c) 2014-2022 All rights reserved
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Author : CHAO LI [email protected]
// File : gray_counter.v
// Create : 2022-11-02 14:59:32
// Revise : 2022-11-02 14:59:32
// Editor : HFUT Integrated Circuit Design & Research Center
// Verdion: v1.0
// Description: 8bit 格雷码计数器
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module gray_counter(
input clk , //Clock
input rst_n , //Asynchronous reset active low
output reg [7:0] gray_out //Gray code output
);
reg[8:0] count;
reg rev;
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n)
count <= 8'b0;
else
count <= count + 8'b1;
end
always@(*) begin
if(!rst_n)
gray_out = 8'b0;
else
gray_out = count[8:1] ^ (count[8:1] >> 1);
end
endmodule
环形计数器
最简单的移位寄存器,对应N位环型计数器有N个状态。
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Copyright (c) 2014-2022 All rights reserved
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Author : HFUT904 [email protected]
// File : ring_conuter.v
// Create : 2022-11-02 15:15:21
// Revise : 2022-11-02 15:15:21
// Editor : HFUT Integrated Circuit Design & Research Center
// Verdion: v1.0
// Description: 8bit 环形计数器
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
module ring_conuter (
input clk , // Clock
input rst_n , // Asynchronous reset active low
input ena , // Enable
output reg [7:0] cnt // ring count value
);
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
cnt <= 8'b0000_0001;
end
else if(ena == 1'b1) begin
cnt <= {cnt[0],cnt[7:1]};
end
else begin
cnt <= cnt ;
end
end
endmodule
Johnson计数器
约翰逊(Johnson)计数器又称扭环计数器,是一种用n位触发器来表示2n个状态的计数器。约翰逊(Johnson)计数器相邻两组数只有一位不同,避免竞争冒险。
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Copyright (c) 2014-2022 All rights reserved
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Author : HFUT904 [email protected]
// File : johnson_counter.v
// Create : 2022-11-02 15:23:15
// Revise : 2022-11-02 15:23:15
// Editor : HFUT Integrated Circuit Design & Research Center
// Verdion: v1.0
// Description: 8bit 扭环形计数器
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
module johnson_counter (
input clk , // Clock
input ena , // Enable
input rst_n , // Asynchronous reset active low
output reg [7:0] cnt // johnson count value
);
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
cnt <= 8'd0;
end
else if(ena == 1'b1 ) begin
cnt <= {~cnt[0],cnt[7:1]};
end
else begin
cnt <= cnt ;
end
end
endmodule
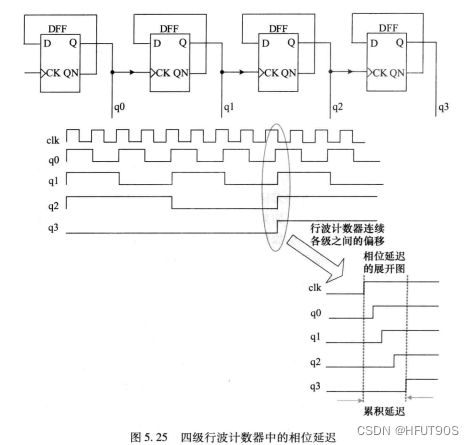
Ripple计数器(低功耗计数器的一种)
行波计数器一般指异步计数器,使用触发器输出作为下一级触发器的时钟输入端。
缺点:
(1)信号产生偏移(延迟);
(2)STA和综合麻烦,验证工作量大。
优点:
降低电路的功耗,属于低功耗计数器的一种。
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Copyright (c) 2014-2022 All rights reserved
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Author : HFUT904 [email protected]
// File : ripple_counter.v
// Create : 2022-11-02 15:39:04
// Revise : 2022-11-02 15:39:04
// Editor : HFUT Integrated Circuit Design & Research Center
// Verdion: v1.0
// Description: 4bit 行波计数器 低功耗计数器
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
//顶层模块
module ripple_counter (
input clk , // Clock
input reset , // Asynchronous reset active high
output [3:0] cnt // ripple count value
);
T_FF tff0(cnt[0], clk , reset);
T_FF tff1(cnt[1], cnt[0] , reset);
T_FF tff2(cnt[2], cnt[1] , reset);
T_FF tff3(cnt[3], cnt[2] , reset);
endmodule
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
//TFF模块
module T_FF(
output t_out ,
input clk ,
input reset
);
wire d_in;
D_FF dff0(t_out, d_in, clk, reset);//按照接口顺序来写
not n1(d_in, t_out);
endmodule
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
//DFF模块
//D触发器
module D_FF(
output reg d_out ,
input d_in ,
input clk ,
input reset
);
always @ (posedge reset or negedge clk) begin
if (reset) //高电平复位
d_out <= 1'b0;
else
d_out <= d_in;
end
endmodule
BCD计数器
用4位二进制数,来表示一位十进制数(0~9)。十进制计数,计满进位。
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Copyright (c) 2014-2022 All rights reserved
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Author : HFUT904 [email protected]
// File : bcd_counter.v
// Create : 2022-11-02 15:53:31
// Revise : 2022-11-02 15:53:31
// Editor : HFUT Integrated Circuit Design & Research Center
// Verdion: v1.0
// Description: 4bit BCD计数器
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
module bcd_counter (
input clk , // Clock
input rst_n , // Asynchronous reset active low
input cin , // Carry input
output reg cout , // Carry output
output reg [3:0] cnt //bcd count value
);
//count
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
cnt <= 4'd0;
end
else if (cin == 1'b1)begin
if (cnt == 4'd9 )
cnt <= 4'd0 ;
else
cnt <= cnt +4'd1 ;
end
else begin
cnt <= cnt ;
end
end
//carry out
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin //体会一下 时序逻辑和组合逻辑的区别
if(~rst_n) begin
cout <= 1'b0 ;
end
else if(cin == 1'b1 && cnt == 4'd9 ) begin
cout <= 1'b1 ;
end
else begin
cout <= 1'b0 ;
end
end
endmodule
总结
所有涉及时序的电路,均离不开计数器,数字电路以时钟周期为基准,通过计数器可以确定当前状态。作为最基础的模块,这里仅仅是列举了一些常用的计数器示例,感兴趣的同学可以继续寻找相关的知识点。同时,在设计电路时,也要多关注代码中的计数器的变种,熟练掌握计数器的设计,可以继续练习PWM、UART、VGA等常用的模块,仔细体会计数器的重要性。