手写openFeign
目录
- 背景
- 步骤
-
- 应用级别:
-
- 1、建立被调用方
- 2、建立调用方
-
- 引入依赖
- 3、实现效果
- 原理级别:
-
- 调动方代码(注意impl在启动的时候里边是空的)
- 引入jar包的代码(写好以后推到nexus上,再拉到上述调用方服务中)
- 升华
背景
最近在手写各种组件,以便于更加了解组件的原理为我所用。现在写到openFeign,让我们一起来看一看是怎么用的吧。
了解基本概念看这里:OpenFeign官网相关知识
OpenFeign是一个用于构建基于Java的RESTful客户端的开源框架。它提供了一种简单的、声明性的方式来定义和使用HTTP请求,同时也有许多好处,包括:
简化HTTP请求:OpenFeign通过提供注解和接口的方式,使得定义HTTP请求变得非常简单明了。你只需要定义一个接口,然后在接口的方法上添加注解来描述请求参数、请求路径等信息,即可完成HTTP请求的构建。
减少样板代码:传统的HTTP请求通常涉及大量的样板代码,如创建HTTP连接、处理请求参数、处理响应等。OpenFeign自动处理这些细节,使得你的代码更加简洁,专注于业务逻辑。
内置负载均衡:OpenFeign与Spring Cloud等微服务框架集成时,可以使用Ribbon作为负载均衡器。这使得你可以在多个服务实例之间分发请求,提高系统的可伸缩性和容错性。
支持插件扩展:OpenFeign提供了许多扩展点,可以通过编写插件来增强或修改其默认行为,满足特定需求。
整合服务发现:OpenFeign可以与Eureka等服务发现组件集成,使得你可以通过服务名来访问其他微服务,而无需硬编码服务的具体地址。
与Spring Cloud集成:OpenFeign是Spring Cloud的一部分,因此与Spring Cloud的其他组件(如Eureka、Hystrix等)无缝集成,形成完整的微服务生态系统。
支持异步请求:OpenFeign可以通过@Async注解支持异步请求,使得你可以更高效地处理并发请求。
总的来说,OpenFeign简化了基于RESTful的HTTP请求的创建和使用过程,帮助你构建更加简洁、可维护、可扩展的微服务应用。同时,它的集成能力和插件扩展性使得它成为构建复杂分布式系统的有力工具。
步骤
应用级别:
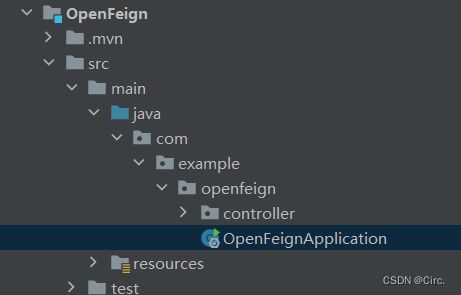
1、建立被调用方
package com.example.openfeign.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class FeignDemoController {
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test(){
return "hello openfegin";
}
}
server:
port: 8081
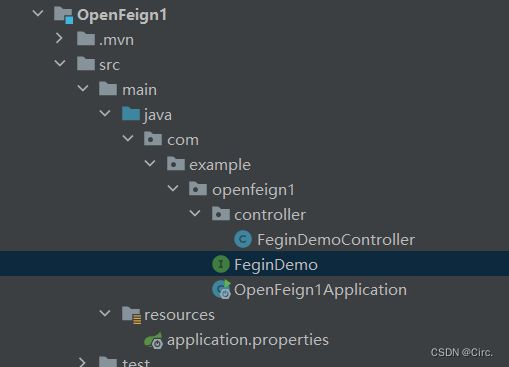
2、建立调用方
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
package com.example.openfeign1.controller;
import com.example.openfeign1.FeginDemo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/feginDemo")
public class FeginDemoController {
@Autowired
FeginDemo feginDemo;
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test(){
String test = feginDemo.test();
return test;
}
}
package com.example.openfeign1;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@FeignClient(name = "demo",url = "http://localhost:8081/demo")
public interface FeginDemo {
@GetMapping("test") //被调用接口的请求类型
String test();
}
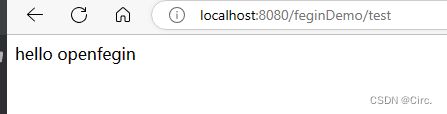
3、实现效果
原理级别:
调动方代码(注意impl在启动的时候里边是空的)
引入自定义jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>SDK</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-20230729.134847-9</version>
</dependency>
package com.example.sdk.positive.Annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // 指定注解保留时期,这里设置为运行时可见
public @interface MyAnnotationFeign {
// 定义属性
String name(); // 定义一个名为 "name" 的属性,没有默认值,使用时需要指定值
String url(); // 定义一个名为 "url" 的属性,没有默认值,使用时需要指定值
}
package com.example.sdk.positive.controller;
import com.example.sdk.positive.Interface.RemoteService;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/feginDemo")
public class FeginDemoController {
static RemoteService remoteService;
// public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// FeignClientProxy feignClientProxy = new FeignClientProxy();
// feignClientProxy.proxy();
// String test = remoteService.test();
return test;
// }
@GetMapping("/test1")
public String test1() throws Exception {
String test = remoteService.test();
return test;
}
import com.example.sdk.positive.Annotation.MyAnnotationFeign;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@MyAnnotationFeign(name = "demo",url = "http://localhost:8080")
public interface RemoteService {
@GetMapping("/test")
String test() throws NoSuchMethodException;
}
@SpringBootApplication
public class OpenFeignByHandApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OpenFeignByHandApplication.class, args);
}
}
package com.example.positive.Impl;
import com.example.positive.Annotation.MyAnnotationFeign;
import com.example.positive.Interface.${ClassName};
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ${ClassName}Impl implements ${ClassName} {
public ${ClassName}Impl() {
}
@Override
public String ${MethodName}() throws NoSuchMethodException {
Class<${ClassName}> clazz =${ClassName}.class;
Annotation[] annotations = clazz.getAnnotations();
String url = null;
String methodUrl = null;
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
if (annotation instanceof MyAnnotationFeign) {
MyAnnotationFeign myClassAnnotation = (MyAnnotationFeign) annotation;
url = myClassAnnotation.url();
}
}
Method method = RemoteService.class.getMethod("${MethodName}");
GetMapping getMappingAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(GetMapping.class);
if (getMappingAnnotation != null) {
methodUrl = getMappingAnnotation.value()[0];
} else {
System.out.println("GetMapping annotation not found.");
}
String baseUrl = url+methodUrl;
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String result = restTemplate.getForObject(baseUrl, String.class);
System.out.println(result);
return result;
}
}
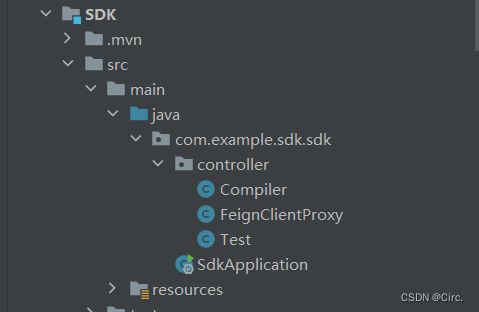
引入jar包的代码(写好以后推到nexus上,再拉到上述调用方服务中)
package com.example.sdk.sdk.controller;
import javax.tools.JavaCompiler;
import javax.tools.ToolProvider;
public class Compiler extends ClassLoader {
public void compiler(String compilerPath,String javaPath){
JavaCompiler javac = ToolProvider.getSystemJavaCompiler();
int status = javac.run(null, null, null, "-d",
compilerPath,javaPath);
if(status!=0){
System.out.println("没有编译成功!");
}
}
}
package com.example.sdk.sdk.controller;
//import com.example.proxy1.Compiler;
import org.apache.velocity.Template;
import org.apache.velocity.VelocityContext;
import org.apache.velocity.app.VelocityEngine;
import org.apache.velocity.runtime.RuntimeConstants;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.StringWriter;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class FeignClientProxy {
public void proxy() throws Exception {
//遍历包下的接口,获取接口的名称还有方法名
String packageName = "com.example.positive.Interface";
List<Class<?>> interfaces = getInterfacesInPackage(packageName);
String interfaceName;
String methodName = null;
for (Class<?> interfaceClass : interfaces) {
interfaceName = interfaceClass.getSimpleName();
System.out.println("Interface Name: " + interfaceName);
Method[] methods = interfaceClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
methodName = method.getName();
System.out.println(" Method Name: " + methodName);
}
String path = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\OpenFeignByHand\\src\\main\\resources";
VelocityEngine velocityEngine = new VelocityEngine();
// 配置资源加载器为FileResourceLoader
velocityEngine.setProperty(RuntimeConstants.RESOURCE_LOADER, "file");
velocityEngine.setProperty(RuntimeConstants.FILE_RESOURCE_LOADER_PATH, path);
velocityEngine.init();
Template template = velocityEngine.getTemplate("ImplTemplate.vm");
// 创建Velocity上下文
VelocityContext context = new VelocityContext();
// 设置变量值
context.put("MethodName", methodName);
context.put("ClassName", interfaceName);
// 将模板解析为字符串
StringWriter stringWriter = new StringWriter();
template.merge(context, stringWriter);
String javaPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\OpenFeignByHand\\src\\main\\java\\com\\example\\positive\\Impl\\";
//替换后输出的文件位置
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(javaPath + interfaceName + "Impl.java");
printWriter.write(stringWriter.toString().toCharArray());
printWriter.flush();
printWriter.close();
String path1 = javaPath + interfaceName + "Impl.java";
Compiler compiler = new Compiler();
compiler.compiler(System.getProperty("user.dir")+"\\target\\classes",path1);
Class<?> implClass = Class.forName("com.example.positive.Impl."+interfaceName+"Impl");
//将controller中的属性值注入进去,扫描到当前接口,将实现类注入进去,怎么办?
//
// Class feginDemoControllerClass = FeginDemoController.class;
String packageName1 = "com.example.positive.controller";
List<Class<?>> interfaces1 = getInterfacesInPackage(packageName1);
Class<?> feginDemoControllerClass = interfaces1.get(0);
String result = firstLetterToLower(interfaceName);
Field nameField = feginDemoControllerClass.getDeclaredField(result);
nameField.setAccessible(true);
Object instance = implClass.newInstance();
nameField.set(feginDemoControllerClass, instance);
}
}
public static String firstLetterToLower(String input) {
if (input == null || input.isEmpty()) {
return input;
}
return input.substring(0, 1).toLowerCase() + input.substring(1);
}
private static List<Class<?>> getInterfacesInPackage(String packageName) {
List<Class<?>> interfaces = new ArrayList<>();
try {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
String path = packageName.replace('.', '/');
java.net.URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
if (resource != null) {
java.io.File folder = new java.io.File(resource.getFile());
if (folder.exists() && folder.isDirectory()) {
for (java.io.File file : folder.listFiles()) {
String fileName = file.getName();
if (fileName.endsWith(".class")) {
String className = packageName + '.' + fileName.substring(0, fileName.length() - 6);
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
// if (clazz.isInterface()) {
interfaces.add(clazz);
// }
}
}
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return interfaces;
}
}
package com.example.sdk.sdk.controller;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Test implements ApplicationRunner {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
FeignClientProxy feignClientProxy = new FeignClientProxy();
feignClientProxy.proxy();
}
}
被调用方和应用级别的被调用方一样。
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class NegativeApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(NegativeApplication.class, args);
}
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test() {
return "Hello from Provider!";
}
}
最后展示效果是和上边一样的。
原理很简单,先生成实现类,实现类里边有方法根据接口上边的url地址进行拼接,使用restTemplate 调用(controller中调用的时候使用实现类对象触发这个方法),就是这么简单。
升华
组件没有这么难,连接底层原理都很简单。