《剑指offer》(4)二叉树篇
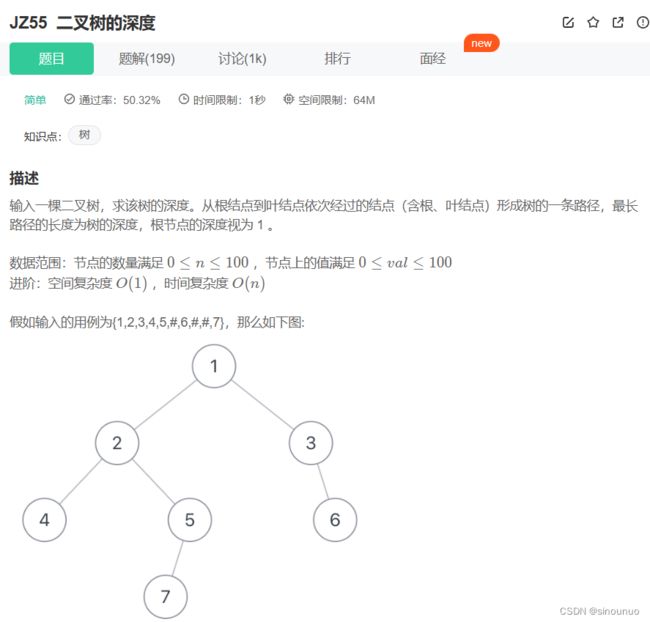
二叉树深度有两种递归思路:
(1)递归返回当前的深度,当root是空时,返回0
(2)将当前深度和节点一起传入递归,设置全局变量,每经过一个节点就更新全局变量的值。
方法一:
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self,val):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution:
def TreeDepth(self , pRoot: TreeNode) -> int:
if pRoot is None:
return 0
l = self.TreeDepth(pRoot.left)
r = self.TreeDepth(pRoot.right)
return max(l,r)+1
方法二:
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self,val):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution:
def TreeDepth(self , pRoot: TreeNode) -> int:
ans = 0
def f(node,cnt):
if node is None:
return
cnt += 1
nonlocal ans
ans = max(ans,cnt)
f(node.left,cnt)
f(node.right,cnt)
f(pRoot,0)
return ans
class Solution:
def Mirror(self , pRoot: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
if pRoot is None:
return pRoot #空就返回空
#交换左右子树
pRoot.left,pRoot.right = pRoot.right,pRoot.left
#递归左右子树
self.Mirror(pRoot.left)
self.Mirror(pRoot.right)
#返回根节点
return pRoot
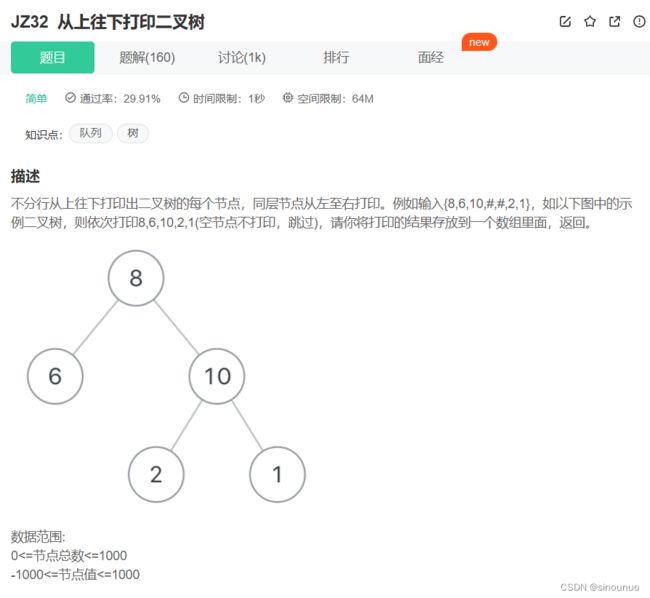
class Solution:
def PrintFromTopToBottom(self , root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
#层序遍历
import collections
ans = []
if root is None:
return []
#把root写入队列里
q = collections.deque([root])
#当队列中存在元素时
while q:
for _ in range(len(q)):
node = q.popleft() #出队
ans.append(node.val) #加入到答案中
if node.left: #遍历左子树
q.append(node.left)
if node.right: #遍历右子树
q.append(node.right)
return ans
class Solution:
def IsBalanced_Solution(self , pRoot: TreeNode) -> bool:
#递归左子树和右子树的深度,如果深度差超过1,就返回-1,遇到-1就直接退出
def f(node):
if node is None:
return 0
l = f(node.left)
if l == -1:
return -1
r = f(node.right)
if r == -1 or abs(l-r) > 1:
return -1
return max(l,r)+1
return f(pRoot) != -1
class Solution:
#判断两颗二叉树是否相等(镜像)
def isSame(self,l,r):
if l is None or r is None:
return l == r
return l.val == r.val and self.isSame(l.left,r.right) and self.isSame(l.right,r.left)
def isSymmetrical(self , pRoot: TreeNode) -> bool:
if pRoot is None:
return True
return self.isSame(pRoot.left,pRoot.right)
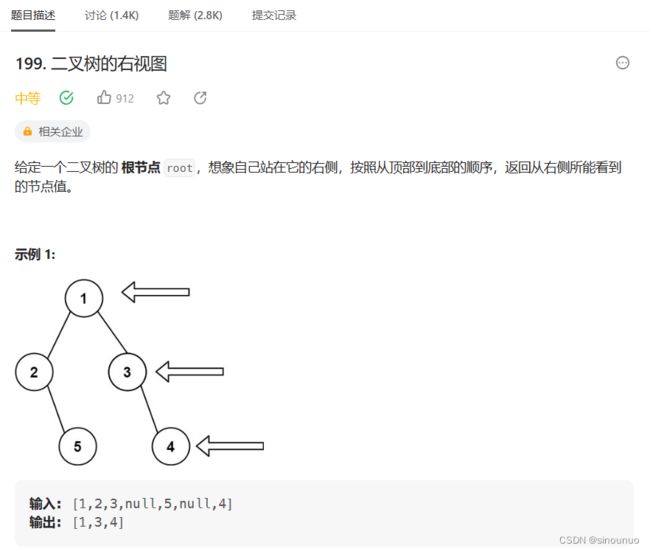
class Solution:
def rightSideView(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
#设置全局变量记录答案,把当前深度和答案长度对比,如果相等,就可以记入答案
#先遍历右子树,再遍历左子树
ans = []
def f(node,cnt):
if node is None:
return
if len(ans) == cnt:
ans.append(node.val)
f(node.right,cnt+1)
f(node.left,cnt+1)
f(root,0)
return ans
方法一:前序遍历
class Solution:
def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode],left = -inf,right = inf) -> bool:
if root is None:
return True
x = root.val #取值
return left < x < right and self.isValidBST(root.left,left,x) and self.isValidBST (root.right, x, right) #判断该值的范围and该节点左右子树是不是二叉搜索树
方法二:中序遍历(得到一个严格递增的数组)
class Solution:
pre = -inf
def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
#如果是空直接返回True
if root is None:
return True
#遍历左子树,如果左子树是False,就返回False
if not self.isValidBST(root.left):
return False
#记录下当前节点值
x = root.val
#让节点值和前一个值比对,如果小于等于前一个值,就False
if x <= self.pre:
return False
#更新前一个节点值
self.pre = x
#递归右子树
return self.isValidBST(root.right)
方法三:后序遍历
class Solution:
def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
def f(root):
#如果是空返回inf,-inf(True)
if root is None:
return inf,-inf
#取左右子树的最小值,最大值
l_min,l_max = f(root.left)
r_min,r_max = f(root.right)
#取当前节点值
x = root.val
#当前节点如果小于左边的最大值,或者大于右边的最小值,返回-inf,inf(Fasle)
if x <= l_max or x >= r_min:
return -inf,inf
#返回左边的最小值,右边的最大值
return min(l_min,x),max(r_max,x)
return f(root)[1] != inf #如果最后收回来是inf,那就False
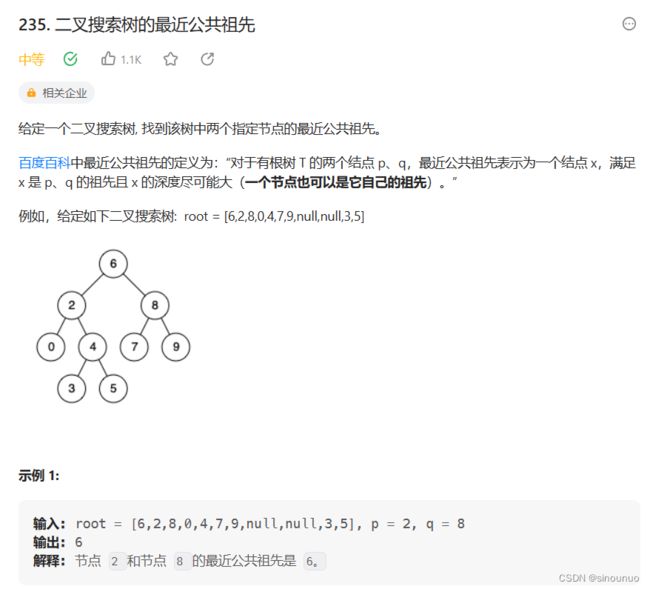
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
#如果当前节点是空,或者就是p,q就返回当前节点
if root is None or root is p or root is q:
return root
#递归左右子树
left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q)
right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q)
#如果左右子树都有,就返回当前节点
if left and right:
return root
#如果在左子树,就返回左子树
if left:
return left
#如果在右子树,或者左右都没有,就返回right(可能是空)
return right
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
#取当前节点的值
x = root.val
#如果q,p的值都大于x,那就在都在右子树中,递归右子树
if q.val > x and p.val > x:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q)
#如果都小于x,就递归左子树
if q.val < x and p.val < x:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q)
#其他情况:q,p是当前节点,或者p,q各自在左右子树中,返回当前节点
return root
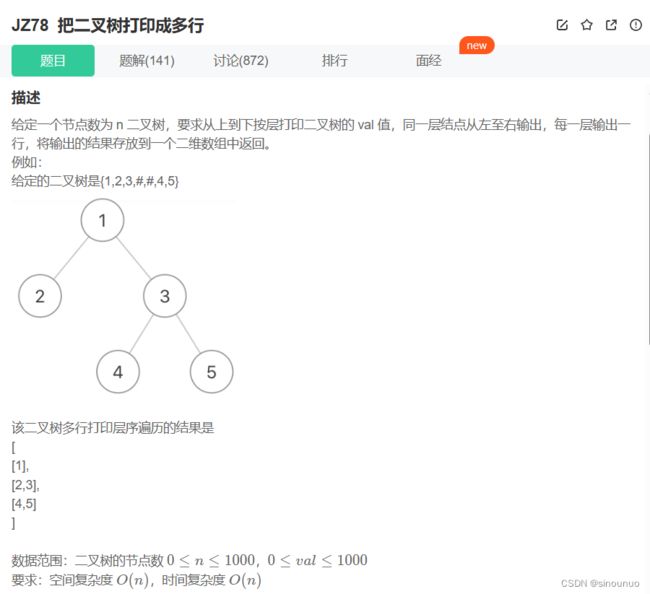
#层序遍历二叉树,偶数层反转
class Solution:
def Print(self , pRoot: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
# 层序遍历的时候,把偶数层反转
ans = []
if pRoot is None:
return []
import collections
q = deque([pRoot])
is_odd = True
while q:
res = []
for _ in range(len(q)):
x = q.popleft()
res.append(x.val)
if x.left: q.append(x.left)
if x.right: q.append(x.right)
if is_odd:
ans.append(res)
is_odd = False
else:
ans.append(res[::-1])
is_odd = True
return ans
#层序遍历
class Solution:
def Print(self , pRoot: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
#层序遍历
if pRoot is None:
return []
import collections
q = collections.deque([pRoot])
ans = []
while q:
res = []
for _ in range(len(q)):
x = q.popleft()
res.append(x.val)
if x.left: q.append(x.left)
if x.right: q.append(x.right)
ans.append(res)
return ans
#二叉搜索树的中序遍历是一个严格递增序列,中序遍历二叉树后,选择第k-1个值输出
class Solution:
def KthNode(self , proot: TreeNode, k: int) -> int:
# 二叉搜索树的中序遍历是严格递增序列
res = []
if proot is None or k == 0: #注意特殊情况
return -1
def f(node): #中序遍历
if node is None:
return
f(node.left)
nonlocal res
res.append(node.val)
f(node.right)
f(proot)
if len(res) < k: #特殊情况
return -1
else:
return res[k-1]
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
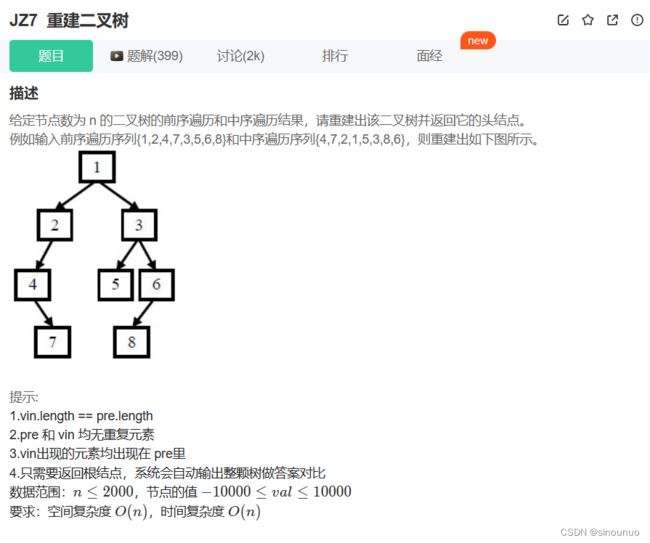
class Solution:
def reConstructBinaryTree(self , preOrder: List[int], vinOrder: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
#从前序遍历中找到当前的根节点,然后划分中序遍历中的左右子树。将左子树的前序和中序递归得到左子树,右子树的前序和中序递归,得到右子树。
#判断错误情况
if len(preOrder) == 0:
return None
#构建根节点
root = TreeNode(preOrder[0])
#找到根节点在中序中的下标
index = vinOrder.index(preOrder[0])
#左子树的前序和中序
l_pre = preOrder[1:index+1]
l_vin = vinOrder[:index]
root.left = self.reConstructBinaryTree(l_pre,l_vin)
#右子树的前序和中序
r_pre = preOrder[index+1:]
r_vin = vinOrder[index+1:]
root.right = self.reConstructBinaryTree(r_pre,r_vin)
return root
class Solution:
def isSubStructure(self, pRoot1: TreeNode, pRoot2: TreeNode) -> bool:
if pRoot2 is None or pRoot1 is None: #异常判断
return False
#设置全局变量记录当前比对结果
status = False
#遍历树A和B的根节点比较
def dfs(a):
if a is None: return
nonlocal status
if a.val == pRoot2.val : status = check(a,pRoot2) #遇到相等的节点就check一下
if a.left: dfs(a.left)
if a.right: dfs(a.right)
def check(a,b):
if b is None: #如果比对之后,B是空,那说明之前比对的都符合子树
return True
if a is None: #如果比对之后A是空,但是B不是空,那就说明不符合
return False
if a.val != b.val: #A和B的数据不一样,说明不符合
return False
return check(a.left,b.left) and check(a.right,b.right)
dfs(pRoot1)
return status
class Solution:
def VerifySquenceOfBST(self , sequence: List[int]) -> bool:
#先判断是否为空
if len(sequence) == 0:
return False
#递归树的左右子树,判断其是不是二叉搜索树
def check(sequence):
#如果只有一个节点了,那就返回True
if len(sequence) <= 1:
return True
#确定根节点
root = sequence[-1]
#确定左右子树的分界,因为值各不相等,如果遍历到了大于等于树的值,则遍历到了根或者右子树
ind = 0
while ind < len(sequence):
if sequence[ind] >= root:
break
ind += 1
#查询左右子树中是否有不符合条件的
a = [j for j in sequence[:ind] if j > root]
b = [j for j in sequence[ind:-1] if j < root]
if a or b:
return False
#递归判断左右子树
return check(sequence[:ind]) and check(sequence[ind:-1])
#返回判断的结果
return check(sequence)
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self , root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> bool:
# 如果遍历到了空,就返回fasle
if root is None:
return False
#当遍历到叶子节点的时候,当前节点的值等于sum,就返回True
if not root.left and not root.right and sum == root.val:
return True
#遍历左右子树,并且把sum-root.val当做下一次的sum传入
return self.hasPathSum(root.left,sum-root.val) or self.hasPathSum(root.right,sum-root.val)
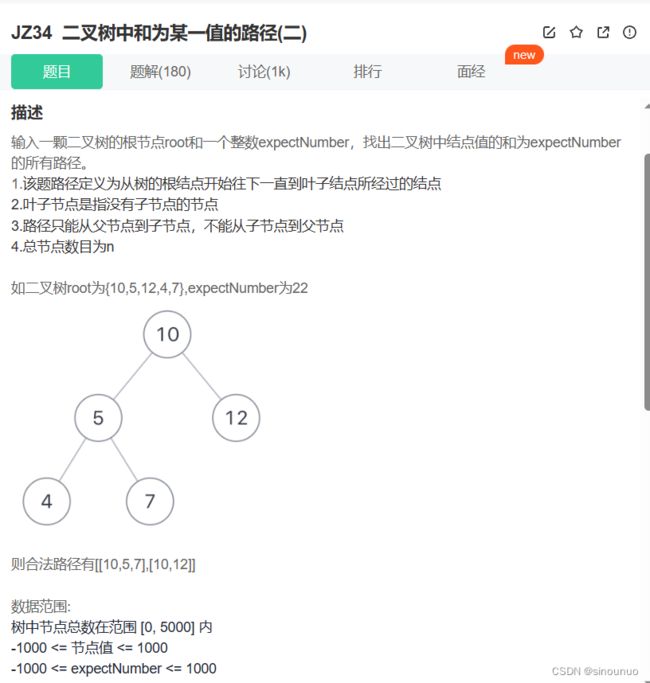
class Solution:
def FindPath(self , root: TreeNode, target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
#判断异常情况
if root is None:
return []
#全局变量存储答案
ans = []
def dfs(node,path): #将路径传入
if node is None:
return
#路径保存当前节点的值
path.append(node.val)
#遇到叶子节点而且路径内的值与目标相等
if not node.left and not node.right and sum(path) == target:
nonlocal ans
ans.append(path.copy()) #路径存入答案(用copy存,否则之后会改变)
#递归左右子树
dfs(node.left,path)
dfs(node.right,path)
#遍历完该路径后,恢复现场
path.pop()
dfs(root,[])
return ans
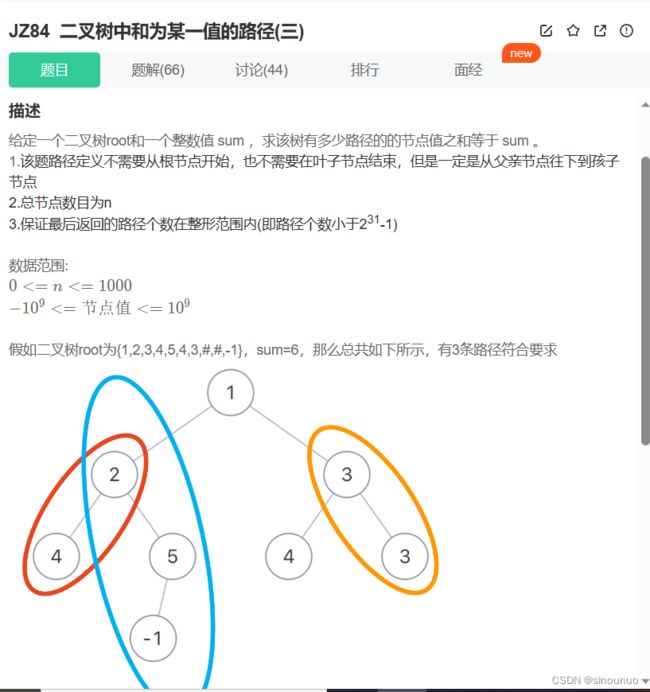
class Solution:
def FindPath(self , root: TreeNode, s: int) -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
ans = 0
#第一层递归,遍历每个节点
def func(root):
if root is None:
return
dfs(root,s,[])
func(root.left)
func(root.right)
#第二层循环,检查以node为根节点的树中有没有路径
def dfs(node,target,path):
if node is None:
return
path.append(node.val)
if sum(path) == target: #不需要走到叶子节点,相等就直接添加答案
nonlocal ans
ans += 1
dfs(node.left,target,path)
dfs(node.right,target,path)
path.pop()
func(root)
return ans
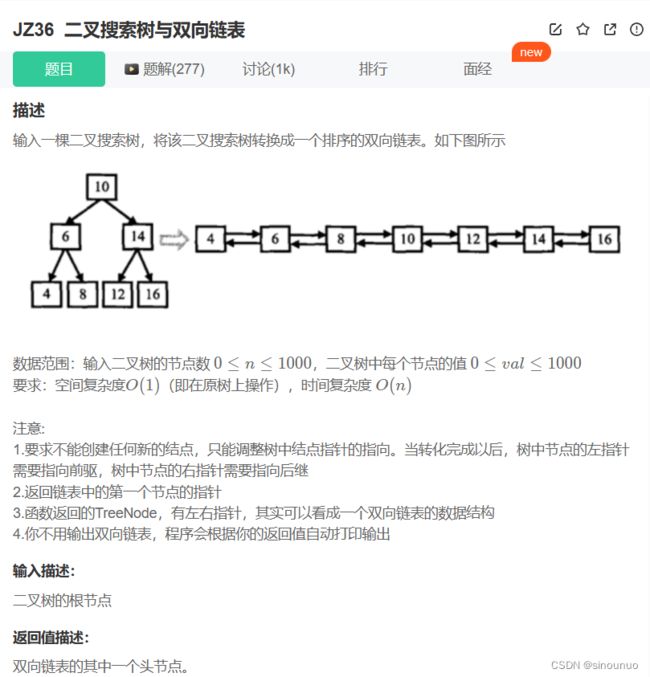
class Solution:
head = None #记录头结点
pre = None #记录当前节点的前一个节点
def Convert(self , pRootOfTree ):
#二叉搜索树中序遍历是一个有序表,当遍历到叶子时,改变左右指针
if pRootOfTree is None:
return None
#先搜索左边
self.Convert(pRootOfTree.left)
#如果前置是空,初始化pre和head
if not self.pre:
self.head = pRootOfTree
self.pre = pRootOfTree
else:
#左指针是指向小节点,有指针指向大节点
self.pre.right = pRootOfTree #前一个节点的值一定小于当前节点,用右指针指
pRootOfTree.left = self.pre #将当前节点的左指针指向pre
self.pre = pRootOfTree #更新pre的值
self.Convert(pRootOfTree.right)
return self.head
class Solution:
def GetNext(self, pNode):
#分成情况讨论:是否有右孩子?自己是左or右or根?如果自己是右,判断在左子树还是在右子树
#情况一:有右孩子,取右孩子最左边的左孩子
if pNode.right:
p = pNode.right
while p.left:
p = p.left
return p
else:
#情况二:没有右孩子,且自己是左孩子,取父亲节点
if pNode.next and pNode.next.left == pNode:
return pNode.next
if not pNode.next: #没有右孩子,还没有父亲节点,那根节点就是最后一个
return None
#情况三:没有右孩子,且自己是右孩子
else:
pre = None
#寻找根节点
while pNode.next:
pre = pNode
pNode = pNode.next
#在左子树中,返回根节点
if pNode.left == pre:
return pNode
else: #在右子树中,返回空
return None
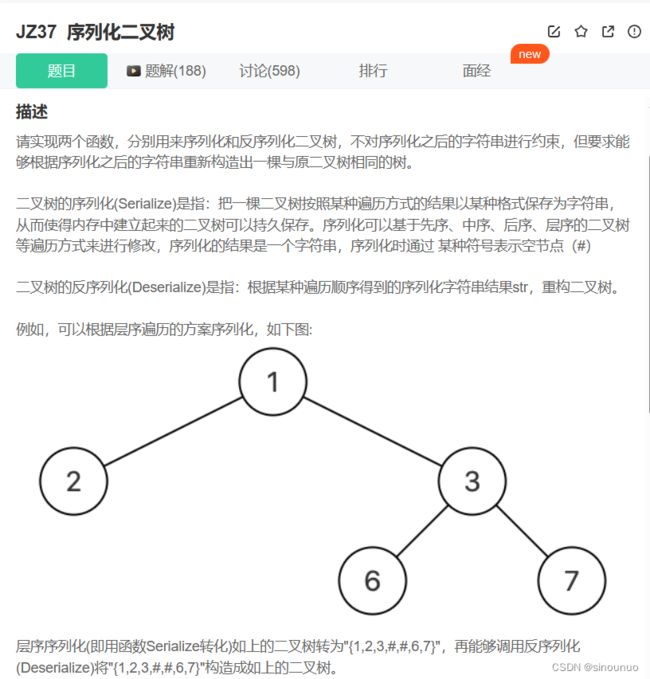
import collections
class Solution:
def Serialize(self, root):
#层序遍历序列化二叉树
ans = []
if root is None:
return ''
q = collections.deque([root])
while q:
for _ in range(len(q)):
x = q.popleft()
if x: #如果x不是空
#将该元素写入,加空格为了分割数字
ans.append(str(x.val)+' ')
if x.left : q.append(x.left)
else: q.append(None) #没有左子树就把空放进去
if x.right : q.append(x.right)
else: q.append(None)
else: #如果是空
ans.append('#'+' ') #将‘#’填入
return ''.join(ans)
def Deserialize(self, s):
#反序列化的时候,依旧按照入队出队,把根节点入队,然后取s中的两个数,如果不是'#'创建左子树并入队,i每次增加2
if len(s) == 0:
return None
#消除前后空格后按照空格分割成list
s = s.strip().split(' ')
root = TreeNode(int(s[0]))
q = collections.deque([root])
i = 1
while i < len(s)-1:
node = q.popleft()
a,b = s[i],s[i+1]
if a != '#':
node.left = TreeNode(int(s[i]))
q.append(node.left)
if b != '#':
node.right = TreeNode(int(s[i+1]))
q.append(node.right)
i +=2
return root