Spring-2-透彻理解Spring 注解方式创建Bean--IOC
今日目标
学习使用XML配置第三方Bean
掌握纯注解开发定义Bean对象
掌握纯注解开发IOC模式
1. 第三方资源配置管理
说明:以管理DataSource连接池对象为例讲解第三方资源配置管理
1.1 XML管理Druid连接池(第三方Bean)对象【重点】
数据库准备
-- 创建数据库
create database if not exists spring_druid character set utf8;
use spring_druid;
-- 创建表
create table if not exists tbl_account(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
money double
);
-- 插入数据
insert into tbl_account values(null,'张三',1000);
insert into tbl_account values(null,'李四',1000);
-- 查询所有
select * from tbl_account;
1.2 代码实现XML管理Druid连接池对象(第三方Bean)
【第一步】创建12_1_xml_druid项目
【第二步】Pom.xml添加Druid连接池依赖
org.springframework
spring-context
5.3.15
mysql
mysql-connector-java
8.0.30
com.alibaba
druid
1.2.18
org.junit.jupiter
junit-jupiter
5.8.2
test
org.projectlombok
lombok
1.18.28
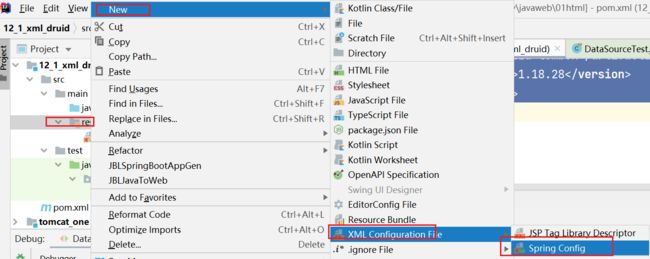
【第三步】配置DruidDataSource连接池Bean对象 思考:配置数据库连接参数时,注入驱动类名是用driverClassName还是driver? 在resources下创建Spring的核心配置文件:application.xml
【第四步】在测试类中从IOC容器中获取连接池对象并打印
package com.zbbmeta;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class DataSourceTest {
@Test
public void test() throws SQLException {
//目标:从IOC容器中获取德鲁伊连接池对象
//1.创建IOC容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
//2.获取连接池对象和数据库连接对象
DataSource dataSource = ac.getBean(DataSource.class);
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
//3.打印对象
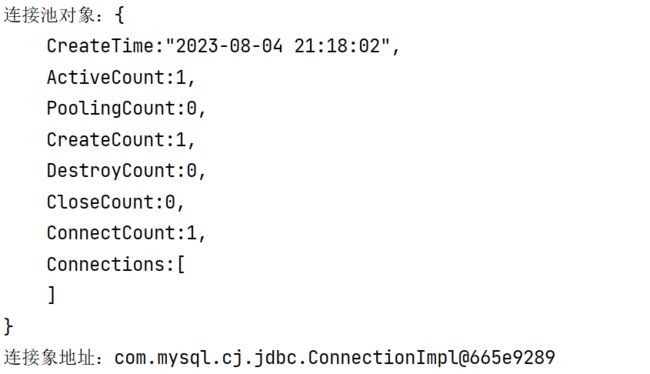
System.out.println("连接池对象:"+dataSource);
System.out.println("连接象地址:"+connection);
//4.关闭容器
ac.close();
}
}
-
控制台结果:
现在我们的数据库参数都是写死在xml文件中的,我们讲解druid,是希望大家可以通过这个第三方Bean创建,实现我们举一反三实现其他第三方Bean的创建
思考:根据上面描述我们向如果有一千个第三方Bean需要创建,那么我们把每一个Bean的参数都写死在xml里面?
肯定不是的,所以我们要学习如何将参数数据进行提取出来,每一个Bean的参数单独放一个文件,方便我们查找和修改
1.3 加载properties属性文件【重点】
目的:将数据库的连接参数抽取到一个单独的文件中,与Spring配置文件解耦。
1.3.1 properties基本用法
【第一步】在resources下编写jdbc.properties属性文件
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/spring_druid
username=root
jdbc.password=root
【第二步】在application.xml中开启开启context命名空间,加载jdbc.properties属性文件
【第三步】在配置连接池Bean的地方使用EL表达式获取jdbc.properties属性文件中的值
【第四步】配置完成之后,运行之前的获取Druid连接池代码
思考:会不会运行成功
不会
严重: create connection SQLException, url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/spring_druid, errorCode 1045, state 28000
java.sql.SQLException: Access denied for user 'zbb'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
为什么会出现这样的问题?
因为我们加载了系统的环变量
-
解决1:换一个名称,例如不叫username,叫jdbc.username。(了解)
【第五步】报错解决方式:在properties标签添加属性
application.xml完整配置
2.Spring容器
2.1 创建容器
-
方式一:类路径加载配置文件
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
-
方式二:文件路径加载配置文件
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("D:\\application.xml");
-
加载多个配置文件
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml", "bean2.xml");
2.2 Spring容器中获取bean对象
-
方式一:使用bean名称获取
弊端:需要自己强制类型转换
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource)ac.getBean("dataSource");
-
方式二:使用bean名称获取并指定类型
弊端:推荐使用
DataSource dataSource = ctx.getBean("dataSource", DataSource.class);
-
方式三:使用bean类型获取
弊端:如果IOC容器中同类型的Bean对象有多个,此处获取会报错
DataSource dataSource = ac.getBean(DataSource.class);
2.3 容器类层次结构
-
BeanFactory是IoC容器的顶层接口,初始化BeanFactory对象时,加载的bean延迟加载
-
ApplicationContext接口是Spring容器的核心接口,初始化时bean立即加载
-
ApplicationContext接口提供基础的bean操作相关方法,通过其他接口扩展其功能
- ApplicationContext接口常用初始化类
-
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(常用)
-
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
-
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
-
3. Spring注解开发
3.1 注解开发定义Bean对象【重点】
目的:xml配置Bean对象有些繁琐,使用注解简化Bean对象的定义
3.2代码实现注解开发
【第一步】创建12_2_annotation_ioc
【第二步】Pom.xml添加依赖
org.springframework
spring-context
5.2.10.RELEASE
junit
junit
4.13
test
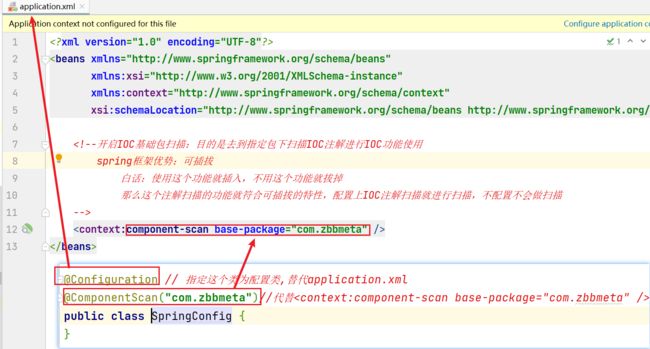
【第三步】在application.xml中开启Spring注解包扫描
【第四步】在类上使用@Component注解定义Bean。
public interface StudentDao {
/**
* 添加学生
*/
void save();
}
package com.zbbmeta.dao.impl;
import com.zbbmeta.dao.StudentDao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @Component
* 作用:相当于标签,用于创建IOC创建对象并加入IOC容器
* 使用方法2种格式:
* @Component 创建对象并且设置对象别名为类名小驼峰,
* 与 功能一样
* @Component("自定义别名") 创建对象并且设置别名加入IOC容器
*
* IOC创建对象注解还有衍生的3个
* @Controller 定义表现层的对象
* @Service 定义业务层的对象
* @Repository 定义数据访问层的对象
* 说明:这3个功能与@Component一样,只是为了增加可读性
* @Component适合在工具类的上面使用创建对象
*
*/
@Component
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao {
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("DAO: 添加学生信息到数据库...");
}
}
补充说明:如果@Component注解没有使用参数指定Bean的名称,那么类名首字母小写就是Bean在IOC容器中的默认名称。例如:StudentDaoImpl对象在IOC容器中的名称是studentDaoImpl。
【第五步】在测试类中获取Bean对象
package com.zbbmeta;
import com.zbbmeta.dao.StudentDao;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class StudentDaoAnnotationTest {
//目标:获取注解创建的Bean对象
@Test
public void testAnnotation(){
//1.根据配置文件application.xml创建IOC容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
//2.从IOC容器里面获取id="studentDao"对象
StudentDao studentDao = (StudentDao) ac.getBean("studentDaoImpl");
System.out.println(studentDao);
}
}
运行结果
com.zbbmeta.dao.impl.StudentDaoImpl@7d64e326
注意:每一个人获取的地址是不一样的
3.3 @Component三个衍生注解
说明:加粗的注解为常用注解
- Spring提供**
@Component**注解的三个衍生注解-
**
@Controller**:用于表现层bean定义 -
**
@Service**:用于业务层bean定义 -
@Repository:用于数据层bean定义
-
说明:这3个功能与@Component一样,只是为了增加可读性
@Component适合在工具类的上面使用创建对象
@Repository
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao {
}
我们上面代码虽然类中都使用注解,但是我们还是存在xml,说明现在spring开发还不是完全的注解开发,可以称为半注解开发
4 Spring纯注解开发模式IOC【重点】
问题导入
思考:配置类上使用什么注解进行Spring注解包扫描替代xml中的配置?
4.1 纯注解开发模式介绍
-
Spring3.0开启了纯注解开发模式,使用Java类替代配置文件,开启了Spring快速开发赛道
-
Java类代替Spring核心配置文件
-
@Configuration注解用于设定当前类为配置类
-
@ComponentScan注解用于设定扫描路径
注意:此注解只能添加一次,多个数据请用数组格式
@ComponentScan({com.zbbmeta.service","com.zbbmeta.dao"})
-
读取Spring注解配置类初始化容器对象
//加载配置类初始化容器
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
4.2 代码演示
【第零步】创建12_3_full_annotation_ioc项目并添加依赖
依赖和上一个项目相同
【第一步】定义配置类代替配置文件
@Configuration // 指定这个类为配置类,替代application.xml
@ComponentScan("com.zbbmeta")//代替【第二步】在测试类中加载配置类,获取Bean对象并使用
package com.zbbmeta;
import com.zbbmeta.config.SpringConfig;
import com.zbbmeta.service.StudentService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class StudentDaoAnnotationTest {
//目标:获取注解创建的Bean对象
@Test
public void testAnnotation(){
//1.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext加载Spring配置类初始化Spring容器
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
StudentService studentService = (StudentService) ctx.getBean("studentServiceImpl");
System.out.println(studentService);
//按类型获取bean
StudentService studentService2 = ctx.getBean(StudentService.class);
System.out.println(studentService2);
}
}
4.3 注解开发Bean作用范围和生命周期管理
问题导入
思考:在类上使用什么注解定义Bean的作用范围?
4.3.1 bean作用范围注解配置
-
使用@Scope定义bean作用范围
@Component
@Scope("singleton")
public class StudentUtils {
}
4.3.2 bean生命周期注解配置
-
使用@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy定义bean生命周期
package com.zbbmeta.utils;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
@Component
@Scope("singleton")
public class StudentUtil {
public StudentUtil() {
System.out.println("Student constructor ...");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("Student init ...");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("Student destory ...");
}
}
注意:@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解是jdk中提供的注解,从jdk9开始,jdk中的javax.annotation包被移除了,也就是说这两个注解就用不了了,可以额外导入一下依赖解决这个问题。
javax.annotation
javax.annotation-api
1.3.2
-
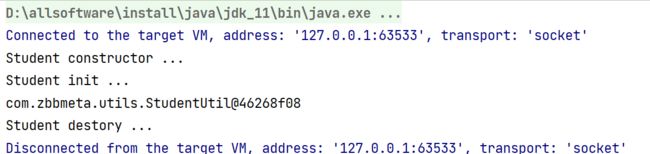
测试类
@Test
public void testStudentUtil(){
//1.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext加载Spring配置类初始化Spring容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
//按类型获取bean
StudentUtil studentUtil = ctx.getBean(StudentUtil.class);
System.out.println(studentUtil);
//关闭容器
ctx.close();
}
测试结果: