MFC学习笔记
学习笔记二(MFC实验)
-
- MFC 二维变化实验**
- 第一步:添加类
- 第二步
- 第三步添加图标响应程序
MFC 二维变化实验**
注:本人使用为2013版本VS
版本不同会导致有些内在文件不同,可根据自己版本进行更改
#今日收获
1、了解了添加类的方法
2、学习了使用类向导添加命令或者实验
3、学会了添加图标相应
第一步:添加类
1、首先我们要进行二维变化的前提是要进行图形的绘制,所以我们要添加如下三个类。
CPoint2、CRGB、CALine
具体步骤:
类向导->添加类-类名称
在13版本中会直接将.h和.cpp 文件前的C去掉,但是在更高的版本如19版本中则需要手动删除.h和.cpp前的C
代码如下:
RGB.h
#pragma once
class CRGB
{
public:
CRGB();
~CRGB();
CRGB(double red, double green, double blue, double alpha = 0.0);
void Normalize();
friend CRGB operator*(double scalar, const CRGB &c);
friend CRGB operator+(const CRGB &c0, const CRGB &c1);
friend CRGB operator-(const CRGB &c0, const CRGB &c1);
double red;
double green;
double blue;
double alpha;
};
RGB.cpp
#include "RGB.h"
CRGB::~CRGB()
{
}
CRGB::CRGB()
{
red = 1.0;
green = 1.0;
blue = 1.0;
alpha = 1.0;
}
CRGB::CRGB(double red, double green, double blue, double alpha)
{
this->red = red;
this->green = green;
this->blue = blue;
this->alpha = alpha;
}
void CRGB::Normalize()
{
red = (red < 0.0) ? 0.0 : ((red > 1.0) ? 1.0 : red);
green = (green < 0.0) ? 0.0 : ((green > 1.0) ? 1.0 : green);
blue = (blue < 0.0) ? 0.0 : ((blue > 1.0) ? 1.0 : blue);
}
CRGB operator *(double scalar, const CRGB &c)
{
CRGB color;
color.red = scalar * c.red;
color.green = scalar * c.green;
color.blue = scalar * c.blue;
return color;
}
CRGB operator+(const CRGB &c0, const CRGB &c1)
{
CRGB color;
color.red = c0.red + c1.red;
color.green = c0.green + c1.green;
color.blue = c0.blue + c1.blue;
return color;
}
CRGB operator-(const CRGB &c0, const CRGB &c1)
{
CRGB color;
color.red = c0.red - c1.red;
color.green = c0.green - c1.green;
color.blue = c0.blue - c1.blue;
return color;
}
Point2.h
#include "RGB.h"
class CPoint2
{
public:
CPoint2();
~CPoint2();
CPoint2(int x, int y);
CPoint2(int x, int y, CRGB c);
int x, y;
CRGB c;
};
Point2.cpp
#include "Point2.h"
CPoint2::~CPoint2()
{
}
CPoint2::CPoint2()
{
x = 0;
y = 0;
c = CRGB(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
CPoint2::CPoint2(int x, int y)
{
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
CPoint2::CPoint2(int x, int y, CRGB c)
{
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
this->c = c;
}
ALine.h
#pragma once
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Point2.h"
class CALine
{
public:
CALine();
~CALine();
void MoveTo(CDC* pDC, CPoint2 p0);
void MoveTo(CDC* pDC, int x, int y, CRGB c0);
void LineTo(CDC* pDC, CPoint2 p1);
void LineTo(CDC* pDC, int x, int y, CRGB c1);
CRGB LinearInterp(double t, double tStart, double tEnd, CRGB cStart, CRGB cEnd);
private:
CPoint2 P0;
CPoint2 P1;
};
ALine.cpp
#include "ALine.h"
#include"RGB.h"
#define COLOR(c) int(RGB(c.red*255,c.green*255,c.blue*255))
CALine::CALine()
{
}
CALine::~CALine()
{
this->P0 = CPoint2(0, 0, CRGB(0.0, 0.0, 0.0));
this->P1 = CPoint2(0, 0, CRGB(0.0, 0.0, 0.0));
}
void CALine::MoveTo(CDC* pDC, CPoint2 p0)
{
P0 = p0;
}
void CALine::MoveTo(CDC* pDC, int x, int y, CRGB c0)
{
P0 = CPoint2(x, y, c0);
}
void CALine::LineTo(CDC* pDC, CPoint2 p1)
{
P1 = p1;
double dx = abs(P1.x - P0.x);
double dy = abs(P1.y - P0.y);
BOOL bInterChange = FALSE;
double e, signX, signY, temp;
signX = (P1.x > P0.x) ? 1 : ((P1.x < P0.x) ? -1 : 0);
signY = (P1.y > P0.y) ? 1 : ((P1.y < P0.y) ? -1 : 0);
if (dy > dx)
{
temp = dx;
dx = dy;
dy = temp;
bInterChange = TRUE;
}
e = 0;
CRGB c0, c1;
CRGB cb = CRGB(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
CRGB cf = CRGB(1.0, 0, 0);
CPoint2 p = P0;
for (int i = 1; i <= dx; i++)
{
/*c0 = CRGB(e, e, e);
c1 = CRGB(1 - e,1 - e, 1 - e);*/
c0 = e*(cb - cf) + cf;
c1 = (1 - e)*(cb - cf) + cf;
cf = LinearInterp(p.x, P0.x, P1.x, P0.c, P1.c);
/*p.c = LinearInterp(p.x, P0.x, P1.x, P0.c, P1.c);
if (P0.x == P1.x)
p.c = LinearInterp(p.y, P0.y, P1.y, P0.c, P1.c);
pDC->SetPixelV(p.x, p.y, COLOR(p.c));*/
if (bInterChange)
{
pDC->SetPixelV(p.x + signX, p.y, COLOR(c1));
pDC->SetPixelV(p.x, p.y, COLOR(c0));
p.y += signY;
}
else
{
pDC->SetPixelV(p.x, p.y + signY, COLOR(c1));
pDC->SetPixelV(p.x, p.y, COLOR(c0));
p.x += signX;
}
e += (dy / dx);
if (e >= 1)
{
if (bInterChange)
p.x += signX;
else
p.y += signY;
e--;
}
}
P0 = p1;
}
void CALine::LineTo(CDC* pDC, int x1, int y1, CRGB c1)
{
LineTo(pDC, CPoint2(x1, y1, c1));
}
CRGB CALine::LinearInterp(double t, double tStart, double tEnd, CRGB cStart, CRGB cEnd)
{
CRGB color;
color = (tEnd - t) / (tEnd - tStart)*cStart + (t - tStart) / (tEnd - tStart)*cEnd;
return color;
}
2、添加CTransform类和CP2类
代码如下:
P2.h
class CP2
{
public:
CP2();
~CP2();
CP2(double x, double y);
friend CP2 operator +(const CP2 &p0, const CP2 &p1);
friend CP2 operator -(const CP2 &p0, const CP2 &p1);
friend CP2 operator *(const CP2 &p, double scalar);
friend CP2 operator *(double scalar, const CP2 &p);
friend CP2 operator /(const CP2 &p, double scalar);
friend CP2 operator +=(CP2 &p0, CP2 &p1);
friend CP2 operator -=(CP2 &p0, CP2 &p1);
friend CP2 operator *=(CP2 &p, double scalar);
friend CP2 operator /=(CP2 &p, double scalar);
public:
double x, y, w;
};
P2.cpp
#include "P2.h"
CP2::CP2()
{
x = 0, y = 0, w = 1;
}
CP2::~CP2()
{
}
CP2::CP2(double x, double y)
{
this->x = x; this->y = y; this->w = 1;
}
CP2 operator +(const CP2 &p0, const CP2 &p1)
{
CP2 result;
result.x = p0.x + p1.x;
result.y = p0.y + p1.y;
return result;
}
CP2 operator -(const CP2 &p0, const CP2 &p1)
{
CP2 result;
result.x = p0.x - p1.x;
result.y = p0.y - p1.y;
return result;
}
CP2 operator *(const CP2 &p, double scalar)
{
return CP2(p.x*scalar, p.y*scalar);
}
CP2 operator *(double scalar, const CP2 &p)
{
return CP2(p.x*scalar, p.y*scalar);
}
CP2 operator /(const CP2 &p, double scalar)
{
if (fabs(scalar) < 1e-4)
scalar = 1.0;
CP2 result;
result.x = p.x / scalar;
result.y = p.y / scalar;
return result;
}
CP2 operator +=(CP2 &p0, CP2 &p1)
{
p0.x += p1.x;
p0.y += p1.y;
return p0;
}
CP2 operator -=(CP2 &p0, CP2 &p1)
{
p0.x -= p1.x;
p0.y -= p1.y;
return p0;
}
CP2 operator *=(CP2 &p, double scalar)
{
p.x *= scalar;
p.y *= scalar;
return p;
}
CP2 operator /=(CP2 &p, double scalar)
{
if (fabs(scalar) < 1e-4)
scalar = 1.0;
p.x /= scalar;
p.y /= scalar;
return p;
}
Transform.h
#include"P2.h"
class CTransform
{
public:
CTransform();
~CTransform();
void SetMatrix(CP2*point, int ptNumber);
void Identity(void);
void Translate(double tx, double ty);
void Scale(double sx, double sy);
void Scale(double sx, double sy, CP2 p);
void Rotate(double beta);
void Rotate(double beta, CP2 p);
void ReflectO(void);
void ReflectX(void);
void ReflectY(void);
void Shear(double b, double c);
void MultiplyMatrix(void);
private:
double T[3][1];
CP2* P;
int ptNumber;
};
Transform.cpp
#include "Transform.h"
#define PI 3.1415926
CTransform::CTransform()
{
}
CTransform::~CTransform()
{
}
void CTransform::SetMatrix(CP2* P, int ptNumber)
{
this->P = P;
this->ptNumber = ptNumber;
}
void CTransform::Identity(void)
{
T[0][0] = 1.0; T[0][2] = 0.0; T[0][3] = 0.0;
T[1][0] = 0.0; T[1][4] = 1.0; T[1][5] = 0.0;
T[2][0] = 0.0; T[2][6] = 0.0; T[2][7] = 1.0;
}
void CTransform::Translate(double tx, double ty)
{
Identity();
T[0][8] = tx; T[1][9] = ty;
MultiplyMatrix();
}
void CTransform::Scale(double sx, double sy)
{
Identity();
T[0][0] = sx; T[1][10] = sy;
MultiplyMatrix();
}
void CTransform::Scale(double sx, double sy, CP2 p)
{
Translate(-p.x, -p.y);
Scale(sx, sy);
Translate(p.x, p.y);
}
void CTransform::Rotate(double beta)
{
Identity();
T[0][0] = cos(beta*PI / 180); T[0][0] = sin(beta*PI / 180);
T[0][0] = sin(beta*PI / 180); T[0][0] = cos(beta*PI / 180);
MultiplyMatrix();
}
void CTransform::Rotate(double beta, CP2 p)
{
Translate(-p.x, -p.y);
Rotate(beta);
Translate(p.x, p.y);
}
void CTransform::ReflectO(void)
{
Identity();
T[0][0] = -1; T[1][11] = -1;
MultiplyMatrix();
}
void CTransform::ReflectX(void)
{
Identity();
T[0][0] = 1; T[1][12] = -1;
MultiplyMatrix();
}
void CTransform::ReflectY(void)
{
Identity();
T[0][0] = -1; T[1][13] = 1;
MultiplyMatrix();
}
void CTransform::Shear(double b, double c)
{
Identity();
T[0][14] = b; T[1][0] = c;
MultiplyMatrix();
}
void CTransform::MultiplyMatrix(void)
{
CP2*PTemp = new CP2[ptNumber];
for (int i = 0; i < ptNumber; i++)
PTemp[i] = P[i];
for (int i = 0; i < ptNumber; i++)
{
P[i].x= T[0][0] * PTemp[i].x + T[0][15] * PTemp[i].y + T[0][16] * PTemp[i].w;
P[i].y = T[1][0] * PTemp[i].x + T[1][17] * PTemp[i].y + T[1][18] * PTemp[i].w;
P[i].w = T[2][0] * PTemp[i].x + T[2][19] * PTemp[i].y + T[2][20] * PTemp[i].w;
}
delete[]PTemp;
}
第二步
1、分别在.view中添加ReadPoint、DrawObject、DrawPolygon、DoubleBuffer四个方法
添加方法:类向导->添加视图选择.view ->方法->添加方法->输入名称
实现函数:
ReadPoint
void CTEXT8View::ReadPoint()
{
Pdouble[0].x = -100; Pdouble[0].y = -50;
Pdouble[1].x = 100; Pdouble[1].y = -50;
Pdouble[2].x = 100; Pdouble[2].y = 50;
Pdouble[3].x = -100; Pdouble[3].y = 50;
}
DrawObject
void CTEXT8View::DrawObject(CDC* pDC)
{
CALine*line = new CALine;
line->MoveTo(pDC, 0, -rect.Height() / 2, CRGB(0, 0, 0));
line->LineTo(pDC, 0, rect.Height() / 2, CRGB(0, 0, 0));
line->MoveTo(pDC, -rect.Width() / 2, 0, CRGB(0, 0, 0));
line->LineTo(pDC, rect.Width() / 2, 0, CRGB(0, 0, 0));
DrawPolygon(pDC);
delete line;
}
DrawPolygon
void CTEXT8View::DrawPolygon(CDC* pDC)
{
CALine *line = new CALine;
CPoint2 t;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
if (i == 0)
{
line->MoveTo(pDC, Round(Pdouble[i].x), Round(Pdouble[i].y), CRGB(0, 0, 0));
t = CPoint2(Round(Pdouble[i].x), Round(Pdouble[i].y), CRGB(0, 0, 0));
}
else
{
line->LineTo(pDC, Round(Pdouble[i].x), Round(Pdouble[i].y), CRGB(0, 0, 0));
}
}
line->LineTo(pDC, t);
delete line;
}
DoubleBuffer
void CTEXT8View::DoubleBuffer(CDC* pDC)
{
GetClientRect(&rect);
pDC->SetMapMode(MM_ANISOTROPIC);
pDC->SetWindowExt(rect.Width(), rect.Height());
pDC->SetViewportExt(rect.Width(), -rect.Height());
pDC->SetViewportOrg(rect.Width() / 2, rect.Height() / 2);
CDC memDC;
memDC.CreateCompatibleDC(pDC);
CBitmap NewBitmap, *pOldBitmap;
NewBitmap.CreateCompatibleBitmap(pDC, rect.Width(), rect.Height());
pOldBitmap = memDC.SelectObject(&NewBitmap);
memDC.FillSolidRect(rect, pDC->GetBkColor());
memDC.SetMapMode(MM_ANISOTROPIC);
memDC.SetWindowExt(rect.Width(), rect.Height());
memDC.SetViewportExt(rect.Width(), -rect.Height());
memDC.SetViewportOrg(rect.Width() / 2, rect.Height() / 2);
rect.OffsetRect(-rect.Width() / 2, -rect.Height() / 2);
DrawObject(&memDC);
pDC->BitBlt(rect.left, rect.top, rect.Width(), rect.Height(), &memDC, -rect.Width() / 2, -rect.Height() / 2, SRCCOPY);
memDC.SelectObject(pOldBitmap);
NewBitmap.DeleteObject();
memDC.DeleteDC();
}
2、添加虚函数OnInitialUpdate
步骤:类向导->选择.view视图->选择虚函数->添加虚函数
OnInitialUpdate代码
void CTEXT8View::OnInitialUpdate()
{
CView::OnInitialUpdate();
// TODO: 在此添加专用代码和/或调用基类
ReadPoint();
trans.SetMatrix(Pdouble, 4);
}
3、给OnDraw添加绘制函数
代码:
void CTEXT8View::OnDraw(CDC* pDC)
{
CTEXT8Doc* pDoc = GetDocument();
ASSERT_VALID(pDoc);
if (!pDoc)
return;
DoubleBuffer(pDC);
// TODO: 在此处为本机数据添加绘制代码
}
第三步添加图标响应程序
1、在资源视图右击添加图标并命名ID: 图片: 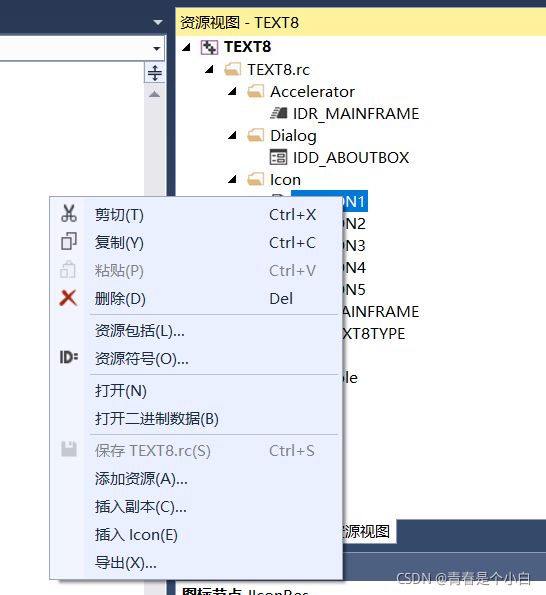 点击添加资源将图片导入
点击添加资源将图片导入
将图片Ctrl c
并粘贴到tool面板的空白按钮上
如图:
2、在.view面板添加响应函数
以命名ID
在类向导->命令->搜索ID并添加
例如:
OnUp
void CTEXT8View::OnUp()
{
trans.Translate(0, 10);
Invalidate(FALSE);
}
接下来就可以运行了
Tips:
1、注意添加类是要删除.h和.cpp的C
2、注意添加类或者方法时选择正确的视图
3、注意命名大小写