分布式 - 消息队列Kafka:Kafka生产者发送消息的分区策略
文章目录
-
-
- 1. PartitionInfo 分区源码
- 2. Partitioner 分区器接口源码
- 3. 自定义分区策略
- 4. 轮询策略 RoundRobinPartitioner
- 5. 黏性分区策略 UniformStickyPartitioner
- 6. hash分区策略
- 7. 默认分区策略 DefaultPartitioner
-
分区的作用就是提供负载均衡的能力,或者说对数据进行分区的主要原因,就是为了实现系统的高伸缩性。不同的分区能够被放置到不同节点的机器上,而数据的读写操作也都是针对分区这个粒度而进行的,这样每个节点的机器都能独立地执行各自分区的读写请求处理。并且,我们还可以通过添加新的节点机器来增加整体系统的吞吐量。
除了提供负载均衡这种最核心的功能之外,利用分区也可以实现其他一些业务级别的需求,比如实现业务级别的消息顺序的问题。
生产者发送的消息实体 ProducerRecord 的构造方法:
我们发送消息时可以指定分区号,如果不指定那就需要分区器,这个很重要,一条消息该发往哪一个分区,关系到顺序消息问题。下面我们说说 Kafka 生产者的分区策略。所谓分区策略是决定生产者将消息发送到哪个分区的算法。Kafka 为我们提供了默认的分区策略,同时它也支持你自定义分区策略。
1. PartitionInfo 分区源码
/**
* This is used to describe per-partition state in the MetadataResponse.
*/
public class PartitionInfo {
// 表示该分区所属的主题名称。
private final String topic;
// 表示该分区的编号。
private final int partition;
// 表示该分区的领导者节点。
private final Node leader;
// 表示该分区的所有副本节点。
private final Node[] replicas;
// 表示该分区的所有同步副本节点。
private final Node[] inSyncReplicas;
// 表示该分区的所有离线副本节点。
private final Node[] offlineReplicas;
public PartitionInfo(String topic, int partition, Node leader, Node[] replicas, Node[] inSyncReplicas) {
this(topic, partition, leader, replicas, inSyncReplicas, new Node[0]);
}
public PartitionInfo(String topic,
int partition,
Node leader,
Node[] replicas,
Node[] inSyncReplicas,
Node[] offlineReplicas) {
this.topic = topic;
this.partition = partition;
this.leader = leader;
this.replicas = replicas;
this.inSyncReplicas = inSyncReplicas;
this.offlineReplicas = offlineReplicas;
}
// ....
}
2. Partitioner 分区器接口源码
Kafka的Partitioner接口是用来决定消息被分配到哪个分区的。它定义了一个方法partition,该方法接收三个参数:topic、key和value,返回一个int类型的分区号,表示消息应该被分配到哪个分区。
public interface Partitioner extends Configurable {
/**
* Compute the partition for the given record.
*
* @param topic The topic name
* @param key The key to partition on (or null if no key)
* @param keyBytes The serialized key to partition on( or null if no key)
* @param value The value to partition on or null
* @param valueBytes The serialized value to partition on or null
* @param cluster The current cluster metadata
*/
int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster);
/**
* This is called when partitioner is closed.
*/
default void close() {}
}
Partitioner接口的实现类可以根据不同的业务需求来实现不同的分区策略,例如根据消息的键、值、时间戳等信息来决定分区。
这里的topic、key、keyBytes、value和valueBytes都属于消息数据,cluster则是集群信息。Kafka 给你这么多信息,就是希望让你能够充分地利用这些信息对消息进行分区,计算出它要被发送到哪个分区中。
3. 自定义分区策略
只要你自己的实现类定义好了 partition 方法,同时设置partitioner.class 参数为你自己实现类的 Full Qualified Name,那么生产者程序就会按照你的代码逻辑对消息进行分区。
① 实现自定义分区策略 DefinePartitioner:
public class MyPartitioner implements Partitioner {
private final AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {
// 获取该 topic 可用的所有分区信息
List<PartitionInfo> partitionInfos = cluster.availablePartitionsForTopic(topic);
int size = partitionInfos.size();
if(keyBytes==null){
// 如果 keyBytes 为 null,表示该消息没有 key,此时采用 round-robin 的方式将消息均匀地分配到不同的分区中。
// 每次调用 getAndIncrement() 方法获取计数器的当前值并自增,然后对可用分区数取模,得到该消息应该被分配到的分区编号。
return counter.getAndIncrement() % size;
}else{
// 如果 keyBytes 不为 null,表示该消息有 key,此时采用 murmur2 哈希算法将 key 转换为一个整数值,并对可用分区数取模,得到该消息应该被分配到的分区编号。
return Utils.toPositive(Utils.murmur2(keyBytes) % size);
}
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
@Override
public void configure(Map<String, ?> map) {
}
}
② 显式地配置生产者端的参数 partitioner.class:
public class CustomProducer01 {
private static final String brokerList = "10.65.132.2:9093";
private static final String topic = "test";
public static Properties initConfig(){
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,brokerList);
properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName());
properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName());
// 使用自定义分区器
properties.put(ProducerConfig.PARTITIONER_CLASS_CONFIG, MyPartitioner.class.getName());
return properties;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// kafka生产者属性配置
Properties properties = initConfig();
// kafka生产者发送消息,默认是异步发送方式
KafkaProducer<String, String> kafkaProducer = new KafkaProducer<String, String>(properties);
ProducerRecord<String, String> producerRecord = new ProducerRecord<>(topic, "你好,kafka,使用自定义分区器");
kafkaProducer.send(producerRecord, new Callback() {
@Override
public void onCompletion(RecordMetadata recordMetadata, Exception e) {
if(e==null){
System.out.println("recordMetadata发送的分区为:"+recordMetadata.partition());
}
}
});
// 关闭资源
kafkaProducer.close();
}
}
4. 轮询策略 RoundRobinPartitioner
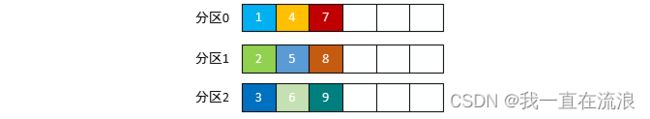
也称 Round-robin 策略,即顺序分配。比如一个主题下有 3 个分区,那么第一条消息被发送到分区 0,第二条被发送到分区 1,第三条被发送到分区 2,以此类推。当生产第 4 条消息时又会重新开始,即将其分配到分区 0,就像下面这张图展示的那样。
这就是所谓的轮询策略,轮询策略是 Kafka Java 生产者 API 默认提供的分区策略。如果你未指定partitioner.class参数,那么你的生产者程序会按照轮询的方式在主题的所有分区间均匀地“码放”消息。
轮询策略有非常优秀的负载均衡表现,它总是能保证消息最大限度地被平均分配到所有分区上,故默认情况下它是最合理的分区策略,也是我们最常用的分区策略之一。
轮询策略实现类为 RoundRobinPartitioner,实现源码:
/**
* The "Round-Robin" partitioner
*
* This partitioning strategy can be used when user wants
* to distribute the writes to all partitions equally. This
* is the behaviour regardless of record key hash.
*
*/
public class RoundRobinPartitioner implements Partitioner {
private final ConcurrentMap<String, AtomicInteger> topicCounterMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public void configure(Map<String, ?> configs) {}
/**
* Compute the partition for the given record.
*
* @param topic The topic name
* @param key The key to partition on (or null if no key)
* @param keyBytes serialized key to partition on (or null if no key)
* @param value The value to partition on or null
* @param valueBytes serialized value to partition on or null
* @param cluster The current cluster metadata
*/
@Override
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {
// 获取该 topic 所有的分区
List<PartitionInfo> partitions = cluster.partitionsForTopic(topic);
int numPartitions = partitions.size();
int nextValue = nextValue(topic);
// 获取该 topic 所有可用的分区
List<PartitionInfo> availablePartitions = cluster.availablePartitionsForTopic(topic);
if (!availablePartitions.isEmpty()) {
// 取模,这样获取的就是一个轮询的方式,从可用的分区列表中获取分区
// Utils.toPositive(nextValue) 的作用是将传入的参数 nextValue 转换为正数。
// 如果 nextValue 是负数,则返回 0,否则返回 nextValue 的值。
int part = Utils.toPositive(nextValue) % availablePartitions.size();
return availablePartitions.get(part).partition();
} else {
// no partitions are available, give a non-available partition
// 取模,这样获取的就是一个轮询的方式,从分区列表中获取分区
return Utils.toPositive(nextValue) % numPartitions;
}
}
// 在ConcurrentMap中插入一个键值对,如果该键不存在,则使用提供的函数计算值并将其插入到Map中。
// 如果该键已经存在,则返回与该键关联的值。
private int nextValue(String topic) {
// 在ConcurrentMap中插入一个键值对,如果该键不存在,则使用AtomicInteger的默认值0初始化值
// 如果该键已经存在,则返回与该键关联的AtomicInteger对象。
AtomicInteger counter = topicCounterMap.computeIfAbsent(topic, k -> {
return new AtomicInteger(0);
});
// 使用返回的AtomicInteger对象对值进行原子操作,增加值
return counter.getAndIncrement();
}
public void close() {}
}
Kafka的RoundRobinPartitioner是一种分区策略,它将消息依次分配到可用的分区中。具体来说,它会维护一个计数器,每次将消息分配到下一个分区,直到计数器达到分区总数,然后重新从第一个分区开始分配。这种策略可以确保消息在所有分区中均匀分布,但可能会导致某些分区负载过重,因为它无法考虑分区的实际负载情况。
5. 黏性分区策略 UniformStickyPartitioner
黏性分区策略会随机选择一个分区,并尽可能一直使用该分区,待该分区的batch已满或者已完成,Kafka再随机选一个分区进行使用(和上一次的分区不同)。 Sticky Partitioning Strategy 会随机地选择一个分区并会尽可能地坚持使用该分区——即所谓的粘住这个分区。
kafka 在发送消息的时候 , 采用批处理方案 , 当达到一批后进行分送 , 但是如果一批数据中有不同分区的数据 , 就无法放置到一个批处理中, 而老版本(2.4版本之前)的轮询策略方案 , 就会导致一批数据被分到多个小的批次中 , 从而影响效率 , 故在新版本中 , 采用这种粘性的划分策略。
UniformStickyPartitioner 实现源码:
/**
* The partitioning strategy:
*
* - If a partition is specified in the record, use it
*
- Otherwise choose the sticky partition that changes when the batch is full.
*
* NOTE: In constrast to the DefaultPartitioner, the record key is NOT used as part of the partitioning strategy in this
* partitioner. Records with the same key are not guaranteed to be sent to the same partition.
*
* See KIP-480 for details about sticky partitioning.
*/
public class UniformStickyPartitioner implements Partitioner {
private final StickyPartitionCache stickyPartitionCache = new StickyPartitionCache();
public void configure(Map<String, ?> configs) {}
/**
* Compute the partition for the given record.
*
* @param topic The topic name
* @param key The key to partition on (or null if no key)
* @param keyBytes serialized key to partition on (or null if no key)
* @param value The value to partition on or null
* @param valueBytes serialized value to partition on or null
* @param cluster The current cluster metadata
*/
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {
return stickyPartitionCache.partition(topic, cluster);
}
public void close() {}
/**
* If a batch completed for the current sticky partition, change the sticky partition.
* Alternately, if no sticky partition has been determined, set one.
*/
public void onNewBatch(String topic, Cluster cluster, int prevPartition) {
stickyPartitionCache.nextPartition(topic, cluster, prevPartition);
}
}
分析 StickyPartitionCache 源码:
/**
* An internal class that implements a cache used for sticky partitioning behavior. The cache tracks the current sticky
* partition for any given topic. This class should not be used externally.
*/
public class StickyPartitionCache {
// ConcurrentMap类型的indexCache成员变量,用于存储主题和其对应的粘性分区。
private final ConcurrentMap<String, Integer> indexCache;
public StickyPartitionCache() {
this.indexCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
}
// 获取给定主题的当前粘性分区。如果该主题的粘性分区尚未设置,则返回下一个分区。
public int partition(String topic, Cluster cluster) {
Integer part = indexCache.get(topic);
if (part == null) {
return nextPartition(topic, cluster, -1);
}
return part;
}
// 获取给定主题的下一个粘性分区。
public int nextPartition(String topic, Cluster cluster, int prevPartition) {
List<PartitionInfo> partitions = cluster.partitionsForTopic(topic);
// 获取给定主题的粘性分区
Integer oldPart = indexCache.get(topic);
Integer newPart = oldPart;
// 如果该主题的粘性分区尚未设置,则计算粘性分区
if (oldPart == null || oldPart == prevPartition) {
// 1. 计算分区号
// 如果没有可用分区,则从所有分区列表中随机选择一个可用分区
List<PartitionInfo> availablePartitions = cluster.availablePartitionsForTopic(topic);
if (availablePartitions.size() < 1) {
Integer random = Utils.toPositive(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt());
newPart = random % partitions.size();
// 如果只有一个可用分区,则选择该分区
} else if (availablePartitions.size() == 1) {
newPart = availablePartitions.get(0).partition();
// 从可用分区列表中随机选择一个分区
} else {
while (newPart == null || newPart.equals(oldPart)) {
int random = Utils.toPositive(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt());
newPart = availablePartitions.get(random % availablePartitions.size()).partition();
}
}
// 2. 填充 indexCache
if (oldPart == null) {
indexCache.putIfAbsent(topic, newPart);
} else {
indexCache.replace(topic, prevPartition, newPart);
}
return indexCache.get(topic);
}
return indexCache.get(topic);
}
}
6. hash分区策略
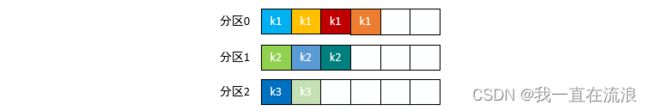
Kafka 允许为每条消息定义消息键,简称为 Key。这个 Key 的作用非常大,它可以是一个有着明确业务含义的字符串,比如客户代码、部门编号或是业务 ID 等;也可以用来表征消息元数据。特别是在 Kafka 不支持时间戳的年代,在一些场景中,工程师们都是直接将消息创建时间封装进 Key 里面的。一旦消息被定义了 Key,那么你就可以保证同一个 Key 的所有消息都进入到相同的分区里面,由于每个分区下的消息处理都是有顺序的,故这个策略被称为按消息键保序策略,如下图所示。
7. 默认分区策略 DefaultPartitioner
Kafka 默认使用的分区器为 DefaultPartitioner,这是一个默认的分区策略实现类,其分区策略如下:
- 如果记录中指定了分区,则使用该分区,不会调用分区器接口实现类。
- 如果记录中没有指定分区但有key,则使用hash分区策略。
- 如果记录中既没有指定分区也没有key,则 kafka 2.4版本前使用轮询策略,2.4版本后使用粘性分区策略。
/**
The default partitioning strategy:
If a partition is specified in the record, use it
If no partition is specified but a key is present choose a partition based on a hash of the key
If no partition or key is present choose the sticky partition that changes when the batch is full.
*/
public class DefaultPartitioner implements Partitioner {
private final StickyPartitionCache stickyPartitionCache = new StickyPartitionCache();
public void configure(Map<String, ?> configs) {}
/**
* Compute the partition for the given record.
*
* @param topic The topic name
* @param key The key to partition on (or null if no key)
* @param keyBytes serialized key to partition on (or null if no key)
* @param value The value to partition on or null
* @param valueBytes serialized value to partition on or null
* @param cluster The current cluster metadata
*/
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {
return partition(topic, key, keyBytes, value, valueBytes, cluster, cluster.partitionsForTopic(topic).size());
}
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster,int numPartitions) {
// 如果没有指定key,则使用粘性分区策略
if (keyBytes == null) {
return stickyPartitionCache.partition(topic, cluster);
}
// hash the keyBytes to choose a partition
// Utils.murmur2(keyBytes) 是一个使用 MurmurHash2 算法计算给定字节数组的哈希值的方法。
// 如果制定了key,则使用key的hash值对分区数取模得到分区。
return Utils.toPositive(Utils.murmur2(keyBytes)) % numPartitions;
}
public void close() {}
/**
* If a batch completed for the current sticky partition, change the sticky partition.
* Alternately, if no sticky partition has been determined, set one.
*/
public void onNewBatch(String topic, Cluster cluster, int prevPartition) {
stickyPartitionCache.nextPartition(topic, cluster, prevPartition);
}
}
基于 kafka 3.0 版本:
① 如果记录中指定了分区,则使用该分区,此时不会进入任何分区器:
public class KafkaProducer<K, V> implements Producer<K, V> {
// ...
@Override
public Future<RecordMetadata> send(ProducerRecord<K, V> record, Callback callback) {
ProducerRecord<K, V> interceptedRecord = this.interceptors.onSend(record);
return doSend(interceptedRecord, callback);
}
private Future<RecordMetadata> doSend(ProducerRecord<K, V> record, Callback callback) {
TopicPartition tp = null;
try {
// ...
int partition = partition(record, serializedKey, serializedValue, cluster);
// ...
}
}
/**
* computes partition for given record.
* if the record has partition returns the value otherwise calls configured partitioner class to compute the partition.
*/
private int partition(ProducerRecord<K, V> record, byte[] serializedKey, byte[] serializedValue, Cluster cluster) {
// 如果记录中指定了分区,则使用该分区,不会继续调用partitioner.partition()方法
Integer partition = record.partition();
return partition != null ?
partition :
partitioner.partition(record.topic(), record.key(), serializedKey, record.value(), serializedValue, cluster);
}
}
② 如果记录中没有指定分区但有key,则会使用hash分区策略计算分区:
public class DefaultPartitioner implements Partitioner {
private final StickyPartitionCache stickyPartitionCache = new StickyPartitionCache();
public void configure(Map<String, ?> configs) {}
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {
return partition(topic, key, keyBytes, value, valueBytes, cluster, cluster.partitionsForTopic(topic).size());
}
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster,int numPartitions) {
if (keyBytes == null) {
return stickyPartitionCache.partition(topic, cluster);
}
// hash the keyBytes to choose a partition
// 使用key的hash值对分区数取模得到分区
return Utils.toPositive(Utils.murmur2(keyBytes)) % numPartitions;
}
public void close() {}
public void onNewBatch(String topic, Cluster cluster, int prevPartition) {
stickyPartitionCache.nextPartition(topic, cluster, prevPartition);
}
}
③ 如果记录中既没有指定分区也没有key,则会使用粘性分区策略计算分区: