- java中vector和list_java中vector和list的区别
Creamy络
java中vector和list的区别发布时间:2020-06-1917:07:11来源:亿速云阅读:106作者:元一vector的概念Vector类是在java中可以实现自动增长的对象数组,vector在C++标准模板库中的部分内容,它是一个多功能的,能够操作多种数据结构和算法的模板类和函数库。vector的使用连续存储结构:vector是可以实现动态增长的对象数组,支持对数组高效率的访问和在数
- C语言,记录一次局部变量被意外修改的问题
三日沐水
嵌入式全套学习教程c语言
背景:单片机开发过程中,我在函数体内(begin_face_record)定义了一个局部变量data_length,在使用的时候,该局部变量一直别改变,每次调用其他函数,例如c库里面的函数memcpy,不知什么情况data_length值就会被改变。1、源码分析voidmain(void){init_gpio();init_face();face_power_up();begin_face_rec
- 【C++】Vector和List的区别
信手斩龙
C++
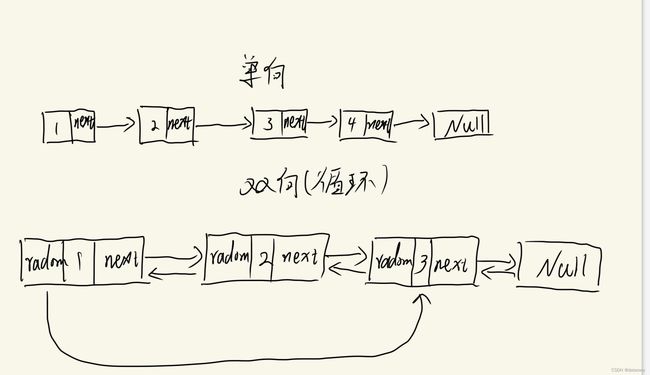
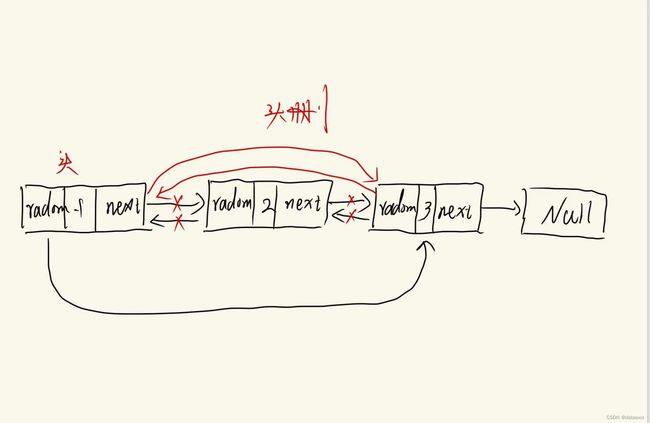
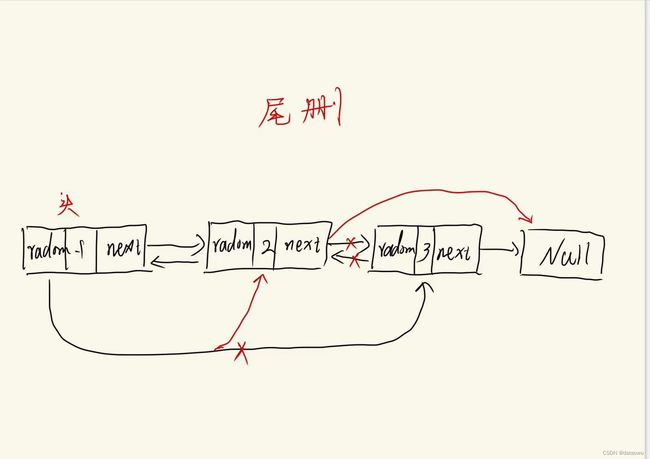
在学习stl的时候,总是有同学分不清楚Vector和List的使用,在这里我总结一下它们的区别和使用方法。一、底层结构 vector的底层结构是动态顺序表,在内存中是一段连续的空间。 list的底层结构是带头节点的双向循环链表,在内存中不是一段连续的空间。二、支持随机访问 vector支持随机访问,可以利用下标精准定位到一个元素上,访问某个元素的时间复杂度是O(1)。 list不支持随机访问,要
- 【C++】priority_queue的使用及模拟实现(含仿函数介绍)
梓䈑
C++学习c++开发语言
文章目录前言一、priority_queue的介绍二、priority_queue的使用三、仿函数四、priority_queue的模拟实现前言一、priority_queue的介绍(优先级队列是默认使用vector作为其底层存储数据的容器适配器,在vector上又使用了堆算法将vector中元素构造成堆的结构,因此priority_queue就是堆)二、priority_queue的使用及模拟实
- 大二下开始学数据结构与算法--06,判断两个节点是否相交,删除链表倒数第K个节点
爱我的你不说话
链表数据结构
自习所完成的任务完成函数判断单项链表是否相交的代码编写和测试。完成函数删除倒数第K个节点的代码编写和测试。感悟其实这篇是昨天晚上写的,但是昨天下午在实验室呆了一下,然后写完这些代码后感觉脑袋昏沉,晚上十点就回宿舍了,想着看会儿书,但是,没看成,还是玩手机了。感觉坚持做一件事,还挺难的,老是为自己找逃避的借口,比如说周三晚上跟舍友出去吃,就放下了写代码的每日任务。我在想,是不是应该改变一下观念,以进
- 【致100位技术同路人:代码无边界,GIS×编程的双向奔赴!】
喆星时瑜
留言感谢你们的关注
今天在地理信息科学的坐标系里标记了一个闪亮锚点——我的CSDN粉丝破百啦!✨破百节点亮起的不只是GISer,还有无数程序员伙伴的坐标!感谢你们的关注,是你们的每一次的让这些文章有了生命力,每一次的都化作我深夜调试的动力。作为穿梭在GIS与通用编程之间的开发者,我始终相信:空间算法是经纬度的代码诗,而工程思维是让地理智能落地的坐标系。未来会继续用PostGIS的严谨写空间索引,用React/Vue的
- oceanbase与mysql性能对比_金融业分布式数据库:TDSQL、HotDB、OceanBase等原理、POC性能对比及选择是......
高中物理宋老师
本帖最后由Amygo于2020-3-1501:33编辑1、分布式的实现,是通过中间件实现分布式,还是源码级别引入分布式算法实现的?解答:(1)分布式数据库是至少由计算节点、存储节点、管理平台、备份还原程序四个部分组成,从数据库系统理论知识上说分成:全局自治和场地自治,也粗略认为:全局可理解为计算节点、场地可理解为存储节点(2)这个问题的标题“中间件实现分布式还是源码级别引入分布式算法”这个说法存在
- 深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索详细解析和区别
潇杨爱吃粉
深度优先宽度优先算法数据结构
一、深度优先搜索(DFS)1.核心思想像探险家走迷宫,遇到岔路就选一条路走到头,无路可走时返回上一个岔路口换另一条路。2.实现方式数据结构:栈(Stack,先进后出)或递归(隐式栈)遍历顺序:纵向深入,优先访问最深层的节点3.图解示例假设有以下树结构:A/\BC/\/DEFDFS遍历顺序(从根节点A出发):A→B→D→E→C→F4.代码实现(Python)defdfs(graph,start):s
- DeepSeek 模型未来怎么走?技术创新、行业落地全解析!
网罗开发
AI大模型人工智能人工智能职场和发展
网罗开发(小红书、快手、视频号同名) 大家好,我是展菲,目前在上市企业从事人工智能项目研发管理工作,平时热衷于分享各种编程领域的软硬技能知识以及前沿技术,包括iOS、前端、HarmonyOS、Java、Python等方向。在移动端开发、鸿蒙开发、物联网、嵌入式、云原生、开源等领域有深厚造诣。图书作者:《ESP32-C3物联网工程开发实战》图书作者:《SwiftUI入门,进阶与实战》超级个体:CO
- 深度优先搜索(DFS)完全解析:从原理到 Java 实战
my_realmy
Java基础知识深度优先java算法
深度优先搜索(DFS)完全解析:从原理到Java实战@TOC作为一名程序员,你是否遇到过需要在复杂的图结构中寻找路径、检测环,或者进行树遍历的问题?深度优先搜索(Depth-FirstSearch,DFS)作为一种经典的图遍历算法,能够轻松应对这些场景。在CSDN社区中,技术文章的受欢迎程度往往取决于内容的实用性、代码的可读性以及图文结合的讲解方式。因此,本文将为你带来一篇深入浅出、图文并茂、代码
- 2025年渗透测试面试题总结-某四字大厂实习面试复盘 一面 二面 三面(题目+回答)
独行soc
2025年渗透测试面试指南面试职场和发展安全web安全红蓝攻防python
网络安全领域各种资源,学习文档,以及工具分享、前沿信息分享、POC、EXP分享。不定期分享各种好玩的项目及好用的工具,欢迎关注。目录一面1.数组和链表各自的优势和原因2.操作系统层面解析和进程3.线程和进程通信方式及数据安全问题4.线程和多进程的选用场景及原因5.SQL注入绕WAF方式6.FUZZ绕WAF的payload长度通常是多少7.不查资料直接写IPv4正则regex8.Fastjson反序
- 贪心算法(10)(java)跳跃游戏
奋进的小暄
贪心算法java游戏
题目:给定一个长度为n的0索引整数数组nums。初始位置为nums[0]。每个元素nums[i]表示从索引i向前跳转的最大长度。换句话说,如果你在nums[i]处,你可以跳转到任意nums[i+j]处:1.0=n-1)//判断是否以经跳到最后一个位置{returnret;}for(inti=left;i<=right;i++)//更新下一层最右端点{maxPos=Math.max(maxPos,n
- SvelteKit 最新中文文档教程(6)—— 状态管理
冴羽yayujs
Svelte中文文档前端javascript前端框架vue.jsreactsveltesveltekit
前言Svelte,一个语法简洁、入门容易,面向未来的前端框架。从Svelte诞生之初,就备受开发者的喜爱,根据统计,从2019年到2024年,连续6年一直是开发者最感兴趣的前端框架No.1:Svelte以其独特的编译时优化机制著称,具有轻量级、高性能、易上手等特性,非常适合构建轻量级Web项目。为了帮助大家学习Svelte,我同时搭建了Svelte最新的中文文档站点。如果需要进阶学习,也可以入手我
- Java编程:从入门到实践
AR新视野
JavaScanner类分隔符增量开发字符串操作
背景简介本文将深入探讨Java编程中的标准类使用,特别是Scanner类的实用性和灵活性。通过实例和代码分析,我们将展示如何更有效地使用Scanner类进行用户输入处理,以及如何通过设置分隔符来接收用户输入的完整数据。此外,文章还将介绍增量开发技术在软件开发中的应用,并通过一个简单的Java程序实例,讨论如何设计和实现程序,以及如何在开发过程中考虑到用户体验。使用Scanner类获取用户输入Jav
- PySimpleGUI模块用法的示例(从入门到进阶)
赵阿萌
java前端服务器linuxjavascript
入门版下面是几个全面展示PySimpleGUI模块用法的示例,并附有详细的代码注释,帮助你更好地掌握该模块的使用。示例1:简单的输入输出界面这是一个基础的GUI示例,展示了如何使用文本输入框、按钮和文本输出框。登录后复制importPySimpleGUIassg#定义布局layout=[[sg.Text("请输入您的名字:")],#标签组件[sg.InputText(key="-NAME-")],
- 视频管理平台:应急安全生产的坚实护盾
智联视频超融合平台
音视频安全人工智能视频编解码网络协议
在应急安全生产中,视频管理平台作为现代科技的重要组成部分,发挥着不可替代的作用。它不仅能够实时监测生产环境,还能在事故发生时提供关键信息,帮助企业快速响应、降低损失。以下是视频管理平台在应急安全生产中的具体作用:一、实时监控与风险预警1、全方位监控:通过部署高清摄像头,覆盖生产车间、仓库、设备区等关键区域,实现无死角监控,确保安全隐患无处遁形。2、智能分析:结合AI算法,自动识别异常行为(如人员违
- Python 网络爬虫:从入门到实践
一ge科研小菜菜
编程语言Pythonpython
个人主页:一ge科研小菜鸡-CSDN博客期待您的关注网络爬虫是一种自动化的程序,用于从互联网上抓取数据。Python以其强大的库和简单的语法,是开发网络爬虫的绝佳选择。本文将详细介绍Python网络爬虫的基本原理、开发工具、常用框架以及实践案例。一、网络爬虫的基本原理网络爬虫的工作流程通常包括以下步骤:发送请求:向目标网站发送HTTP请求,获取网页内容。解析内容:提取需要的数据,可以是HTML标签
- 算法-枚 举
Java版蜡笔小新
算法算法
信息在计算机之间的演示计算机的电路由逻辑门电路组成。一个逻辑门电路可以看成一个开关,每个开关的状态是“开"(高电位)或“关”(低电位),即对应于或0二进制数的一位,取值只能是0或1,称为一个“比特”(bit),简写:b八个二进制位称为一个“字节”(byte),简写:B1024(2的10次方)字节称为1KB,1024KB称作1MB(1兆),1024MB称作1GB,1024GB0和1足以表示和传播各种
- 合并两个有序链表
陆仁贾笨贾
链表数据结构
题目:将两个升序链表合并为一个新的升序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。示例1:输入:l1=[1,2,4],l2=[1,3,4]输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]思路:虚拟头结点:使用一个虚拟头结点(dummy)来简化链表操作。虚拟头结点的next指针指向合并后的链表的头结点。通过一个指针p来追踪新链表的最后一个节点。遍历链表:使用两个指针p1和p2分别遍历链表l1和l2。
- C语言循环案例
Litao_woaidetin
算法
#include#include#includeintmain(intargc,char*argv[]){//初始化随机数种子(以时间为种子)srand((unsigned)time(NULL));//游戏主循环控制,默认是可以重复玩的intgame_running=1;//游戏的头printf("======================================\n");printf(
- 模拟退火算法:原理、应用与优化策略
尹清雅
算法
摘要模拟退火算法是一种基于物理退火过程的随机搜索算法,在解决复杂优化问题上表现出独特优势。本文详细阐述模拟退火算法的原理,深入分析其核心要素,通过案例展示在函数优化、旅行商问题中的应用,并探讨算法的优化策略与拓展方向,为解决复杂优化问题提供全面的理论与实践指导,助力该算法在多领域的高效应用与创新发展。一、引言在现代科学与工程领域,复杂优化问题无处不在,如资源分配、路径规划、机器学习模型参数调优等。
- 不会用AI大模型的程序员,5年后必将被淘汰?真相远比你想的更残酷!
小城哇哇
人工智能语言模型AI大模型DeepSeekOpenAIagi程序员
前言在技术飞速发展的今天,AI大模型已经成为程序员技能库中的“标配”。如果你还认为AI只是“锦上添花”的工具,那么5年后,你可能真的会被时代无情淘汰。这不是危言耸听,而是技术变革的必然趋势。AI大模型:程序员的“效率革命”AI大模型如DeepSeek等工具,正在彻底改变程序员的开发模式。它们不仅能自动生成代码、优化算法,还能快速解决复杂的技术问题。过去需要几天甚至几周才能完成的任务,现在可能只需要
- 如何通过Python实现自动化任务:从入门到实践
小弟有话说1.0
python自动化开发语言
在当今快节奏的数字化时代,自动化技术正逐渐成为提高工作效率的利器。无论是处理重复性任务,还是管理复杂的工作流程,自动化都能为我们节省大量时间和精力。本文将以Python为例,带你从零开始学习如何实现自动化任务,并通过一个实际案例展示其强大功能。一、为什么选择Python实现自动化?Python作为一种简单易学、功能强大的编程语言,已经成为自动化领域的首选工具。以下是Python在自动化中的几大优势
- Swift高效解法!一文搞懂 LeetCode 236「二叉树的最近公共祖先」,助你快速拿下面试!
网罗开发
Swiftswiftleetcode面试
摘要最近公共祖先(LCA,LowestCommonAncestor)在二叉树、二叉搜索树(BST)等数据结构中有广泛应用,比如权限管理、网络路由、基因分析等。今天我们用Swift来解LeetCode236:「二叉树的最近公共祖先」,不仅会给出代码,还会分析它的时间复杂度、空间复杂度,并结合实际场景聊聊它的应用。问题描述给定一个二叉树,找到两个节点的最近公共祖先(LCA)。LCA的定义:“对于两个节
- 区跨链密码学
NO如果
密码学
1.哈希算法(Hash)❓1.1什么是哈希算法?区块链中为什么需要哈希?哈希算法是一种不可逆的、确定性的、固定长度的散列函数,用于将输入数据映射成固定长度的字符串。在区块链中的作用:数据完整性:确保区块内容未被篡改(MerkleTree)。唯一标识:区块哈希值用于唯一标识区块。密码学安全性:哈希值难以逆推,保证安全性。常见哈希算法:SHA-256(比特币):固定256位输出,抗碰撞强。Keccak
- C++和Java相比,哪个更适合初学者学习?
c++java
C++和Java都是非常流行的编程语言,但它们在设计理念、应用场景和学习难度上存在显著差异。对于初学者来说,选择哪种语言更适合,取决于学习目标、兴趣和未来的职业规划。以下是对C++和Java的详细对比,帮助初学者做出选择:一、学习难度C++复杂性高:C++继承了C语言的复杂性,支持多种编程范式(如面向对象、泛型编程等),语法复杂,学习曲线陡峭。内存管理:C++需要手动管理内存,容易出现内存泄漏和悬
- 凌晨三点的代码和引擎轰鸣声
前端后端程序员
凌晨三点,我盯着屏幕上第37次报错的算法,随手抓起桌角已经冷透的咖啡猛灌一口。显示器蓝光里,同事阿杰突然弹出一条消息:"哥们儿,苏州有个车展能撸代码,去不去?"我对着这句话愣了三秒。车展?在我的认知里,那应该是西装革履的销售围着超模拍宣传片的场合,和我们这种格子衫生物有什么关系?直到阿杰甩来一张海报——黑底荧光绿字刺破视网膜:"CISHOWGTSHOW,程序员特别通道,票免费送。"01被编译器耽误
- 深入探索C++:从基础到高级
c++
深入探索C++:从基础到高级一、C++简介C++是一种通用的、静态类型的、大小写敏感的、自由格式的编程语言,支持过程化编程、面向对象编程和泛型编程。它最初由BjarneStroustrup在1980年代设计,目的是在C语言的基础上增加面向对象的功能。C++广泛应用于系统/应用程序软件、游戏开发、高性能服务器和客户端应用等领域。二、C++的核心特性(一)数据类型C++提供了丰富的数据类型,包括基本数
- 借Kinect 扫描 软件 reconstructMe skanect ksan3d
learn deep learning
三维重建
[基础技术]3D扫描教程http://bbs.kechuang.org/read/59979楼主#更多发布于:2013-08-2314:48入门级的3D扫描ReconstructMe硬件kinectXBox360不兼容kinectforwindows或者XtionProLive(XtionProLive开发版包装,有Microphone和RGBsensor)有电动转盘更好,win732位或者64位
- 10.2 如何解决从复杂 PDF 文件中提取数据的问题?
墨染辉
大语言模型pdf
10.2如何解决从复杂PDF文件中提取数据的问题?解决方案:嵌入式表格检索解释:嵌入式表格检索是一种专门针对从复杂PDF文件中的表格提取数据的技术。它结合了表格识别、解析和语义理解,使得从复杂结构的表格中检索信息成为可能。具体步骤:表格检测和识别:目标:在PDF页面中准确地定位和识别表格区域。方法:使用计算机视觉和深度学习技术,如卷积神经网络(CNN)或其他先进的图像处理算法。效果:能够检测出页面
- java工厂模式
3213213333332132
java抽象工厂
工厂模式有
1、工厂方法
2、抽象工厂方法。
下面我的实现是抽象工厂方法,
给所有具体的产品类定一个通用的接口。
package 工厂模式;
/**
* 航天飞行接口
*
* @Description
* @author FuJianyong
* 2015-7-14下午02:42:05
*/
public interface SpaceF
- nginx频率限制+python测试
ronin47
nginx 频率 python
部分内容参考:http://www.abc3210.com/2013/web_04/82.shtml
首先说一下遇到这个问题是因为网站被攻击,阿里云报警,想到要限制一下访问频率,而不是限制ip(限制ip的方案稍后给出)。nginx连接资源被吃空返回状态码是502,添加本方案限制后返回599,与正常状态码区别开。步骤如下:
- java线程和线程池的使用
dyy_gusi
ThreadPoolthreadRunnabletimer
java线程和线程池
一、创建多线程的方式
java多线程很常见,如何使用多线程,如何创建线程,java中有两种方式,第一种是让自己的类实现Runnable接口,第二种是让自己的类继承Thread类。其实Thread类自己也是实现了Runnable接口。具体使用实例如下:
1、通过实现Runnable接口方式 1 2
- Linux
171815164
linux
ubuntu kernel
http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v4.1.2-unstable/
安卓sdk代理
mirrors.neusoft.edu.cn 80
输入法和jdk
sudo apt-get install fcitx
su
- Tomcat JDBC Connection Pool
g21121
Connection
Tomcat7 抛弃了以往的DBCP 采用了新的Tomcat Jdbc Pool 作为数据库连接组件,事实上DBCP已经被Hibernate 所抛弃,因为他存在很多问题,诸如:更新缓慢,bug较多,编译问题,代码复杂等等。
Tomcat Jdbc P
- 敲代码的一点想法
永夜-极光
java随笔感想
入门学习java编程已经半年了,一路敲代码下来,现在也才1w+行代码量,也就菜鸟水准吧,但是在整个学习过程中,我一直在想,为什么很多培训老师,网上的文章都是要我们背一些代码?比如学习Arraylist的时候,教师就让我们先参考源代码写一遍,然
- jvm指令集
程序员是怎么炼成的
jvm 指令集
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/hudashi/article/details/7062675#comments
将值推送至栈顶时 const ldc push load指令
const系列
该系列命令主要负责把简单的数值类型送到栈顶。(从常量池或者局部变量push到栈顶时均使用)
0x02 &nbs
- Oracle字符集的查看查询和Oracle字符集的设置修改
aijuans
oracle
本文主要讨论以下几个部分:如何查看查询oracle字符集、 修改设置字符集以及常见的oracle utf8字符集和oracle exp 字符集问题。
一、什么是Oracle字符集
Oracle字符集是一个字节数据的解释的符号集合,有大小之分,有相互的包容关系。ORACLE 支持国家语言的体系结构允许你使用本地化语言来存储,处理,检索数据。它使数据库工具,错误消息,排序次序,日期,时间,货
- png在Ie6下透明度处理方法
antonyup_2006
css浏览器FirebugIE
由于之前到深圳现场支撑上线,当时为了解决个控件下载,我机器上的IE8老报个错,不得以把ie8卸载掉,换个Ie6,问题解决了,今天出差回来,用ie6登入另一个正在开发的系统,遇到了Png图片的问题,当然升级到ie8(ie8自带的开发人员工具调试前端页面JS之类的还是比较方便的,和FireBug一样,呵呵),这个问题就解决了,但稍微做了下这个问题的处理。
我们知道PNG是图像文件存储格式,查询资
- 表查询常用命令高级查询方法(二)
百合不是茶
oracle分页查询分组查询联合查询
----------------------------------------------------分组查询 group by having --平均工资和最高工资 select avg(sal)平均工资,max(sal) from emp ; --每个部门的平均工资和最高工资
- uploadify3.1版本参数使用详解
bijian1013
JavaScriptuploadify3.1
使用:
绑定的界面元素<input id='gallery'type='file'/>$("#gallery").uploadify({设置参数,参数如下});
设置的属性:
id: jQuery(this).attr('id'),//绑定的input的ID
langFile: 'http://ww
- 精通Oracle10编程SQL(17)使用ORACLE系统包
bijian1013
oracle数据库plsql
/*
*使用ORACLE系统包
*/
--1.DBMS_OUTPUT
--ENABLE:用于激活过程PUT,PUT_LINE,NEW_LINE,GET_LINE和GET_LINES的调用
--语法:DBMS_OUTPUT.enable(buffer_size in integer default 20000);
--DISABLE:用于禁止对过程PUT,PUT_LINE,NEW
- 【JVM一】JVM垃圾回收日志
bit1129
垃圾回收
将JVM垃圾回收的日志记录下来,对于分析垃圾回收的运行状态,进而调整内存分配(年轻代,老年代,永久代的内存分配)等是很有意义的。JVM与垃圾回收日志相关的参数包括:
-XX:+PrintGC
-XX:+PrintGCDetails
-XX:+PrintGCTimeStamps
-XX:+PrintGCDateStamps
-Xloggc
-XX:+PrintGC
通
- Toast使用
白糖_
toast
Android中的Toast是一种简易的消息提示框,toast提示框不能被用户点击,toast会根据用户设置的显示时间后自动消失。
创建Toast
两个方法创建Toast
makeText(Context context, int resId, int duration)
参数:context是toast显示在
- angular.identity
boyitech
AngularJSAngularJS API
angular.identiy 描述: 返回它第一参数的函数. 此函数多用于函数是编程. 使用方法: angular.identity(value); 参数详解: Param Type Details value
*
to be returned. 返回值: 传入的value 实例代码:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
- java-两整数相除,求循环节
bylijinnan
java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class CircleDigitsInDivision {
/**
* 题目:求循环节,若整除则返回NULL,否则返回char*指向循环节。先写思路。函数原型:char*get_circle_digits(unsigned k,unsigned j)
- Java 日期 周 年
Chen.H
javaC++cC#
/**
* java日期操作(月末、周末等的日期操作)
*
* @author
*
*/
public class DateUtil {
/** */
/**
* 取得某天相加(减)後的那一天
*
* @param date
* @param num
*
- [高考与专业]欢迎广大高中毕业生加入自动控制与计算机应用专业
comsci
计算机
不知道现在的高校还设置这个宽口径专业没有,自动控制与计算机应用专业,我就是这个专业毕业的,这个专业的课程非常多,既要学习自动控制方面的课程,也要学习计算机专业的课程,对数学也要求比较高.....如果有这个专业,欢迎大家报考...毕业出来之后,就业的途径非常广.....
以后
- 分层查询(Hierarchical Queries)
daizj
oracle递归查询层次查询
Hierarchical Queries
If a table contains hierarchical data, then you can select rows in a hierarchical order using the hierarchical query clause:
hierarchical_query_clause::=
start with condi
- 数据迁移
daysinsun
数据迁移
最近公司在重构一个医疗系统,原来的系统是两个.Net系统,现需要重构到java中。数据库分别为SQL Server和Mysql,现需要将数据库统一为Hana数据库,发现了几个问题,但最后通过努力都解决了。
1、原本通过Hana的数据迁移工具把数据是可以迁移过去的,在MySQl里面的字段为TEXT类型的到Hana里面就存储不了了,最后不得不更改为clob。
2、在数据插入的时候有些字段特别长
- C语言学习二进制的表示示例
dcj3sjt126com
cbasic
进制的表示示例
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i = 0x32C;
printf("i = %d\n", i);
/*
printf的用法
%d表示以十进制输出
%x或%X表示以十六进制的输出
%o表示以八进制输出
*/
return 0;
}
- NsTimer 和 UITableViewCell 之间的控制
dcj3sjt126com
ios
情况是这样的:
一个UITableView, 每个Cell的内容是我自定义的 viewA viewA上面有很多的动画, 我需要添加NSTimer来做动画, 由于TableView的复用机制, 我添加的动画会不断开启, 没有停止, 动画会执行越来越多.
解决办法:
在配置cell的时候开始动画, 然后在cell结束显示的时候停止动画
查找cell结束显示的代理
- MySql中case when then 的使用
fanxiaolong
casewhenthenend
select "主键", "项目编号", "项目名称","项目创建时间", "项目状态","部门名称","创建人"
union
(select
pp.id as "主键",
pp.project_number as &
- Ehcache(01)——简介、基本操作
234390216
cacheehcache简介CacheManagercrud
Ehcache简介
目录
1 CacheManager
1.1 构造方法构建
1.2 静态方法构建
2 Cache
2.1&
- 最容易懂的javascript闭包学习入门
jackyrong
JavaScript
http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2009/08/learning_javascript_closures.html
闭包(closure)是Javascript语言的一个难点,也是它的特色,很多高级应用都要依靠闭包实现。
下面就是我的学习笔记,对于Javascript初学者应该是很有用的。
一、变量的作用域
要理解闭包,首先必须理解Javascript特殊
- 提升网站转化率的四步优化方案
php教程分享
数据结构PHP数据挖掘Google活动
网站开发完成后,我们在进行网站优化最关键的问题就是如何提高整体的转化率,这也是营销策略里最最重要的方面之一,并且也是网站综合运营实例的结果。文中分享了四大优化策略:调查、研究、优化、评估,这四大策略可以很好地帮助用户设计出高效的优化方案。
PHP开发的网站优化一个网站最关键和棘手的是,如何提高整体的转化率,这是任何营销策略里最重要的方面之一,而提升网站转化率是网站综合运营实力的结果。今天,我就分
- web开发里什么是HTML5的WebSocket?
naruto1990
Webhtml5浏览器socket
当前火起来的HTML5语言里面,很多学者们都还没有完全了解这语言的效果情况,我最喜欢的Web开发技术就是正迅速变得流行的 WebSocket API。WebSocket 提供了一个受欢迎的技术,以替代我们过去几年一直在用的Ajax技术。这个新的API提供了一个方法,从客户端使用简单的语法有效地推动消息到服务器。让我们看一看6个HTML5教程介绍里 的 WebSocket API:它可用于客户端、服
- Socket初步编程——简单实现群聊
Everyday都不同
socket网络编程初步认识
初次接触到socket网络编程,也参考了网络上众前辈的文章。尝试自己也写了一下,记录下过程吧:
服务端:(接收客户端消息并把它们打印出来)
public class SocketServer {
private List<Socket> socketList = new ArrayList<Socket>();
public s
- 面试:Hashtable与HashMap的区别(结合线程)
toknowme
昨天去了某钱公司面试,面试过程中被问道
Hashtable与HashMap的区别?当时就是回答了一点,Hashtable是线程安全的,HashMap是线程不安全的,说白了,就是Hashtable是的同步的,HashMap不是同步的,需要额外的处理一下。
今天就动手写了一个例子,直接看代码吧
package com.learn.lesson001;
import java
- MVC设计模式的总结
xp9802
设计模式mvc框架IOC
随着Web应用的商业逻辑包含逐渐复杂的公式分析计算、决策支持等,使客户机越
来越不堪重负,因此将系统的商业分离出来。单独形成一部分,这样三层结构产生了。
其中‘层’是逻辑上的划分。
三层体系结构是将整个系统划分为如图2.1所示的结构[3]
(1)表现层(Presentation layer):包含表示代码、用户交互GUI、数据验证。
该层用于向客户端用户提供GUI交互,它允许用户